인코넬 파우더 3D 프린터의 verview
목차
인코넬 분말 3D 프린터 는 오스테나이트 니켈-크롬 기반 슈퍼 합금인 인코넬과 함께 작동하도록 설계된 특수 적층 제조 시스템입니다. 이 합금은 뛰어난 강도, 내산화성, 극한의 온도를 견디는 능력으로 잘 알려져 있어 항공우주, 자동차, 에너지 산업의 응용 분야에 이상적입니다.
인코넬 3D 프린팅을 사용하면 기존 제조 방법으로는 달성하기 어렵거나 불가능한 복잡한 형상과 복잡한 디자인을 만들 수 있습니다. 이 프린터는 얇은 층의 인코넬 분말을 서로 융합하여 뛰어난 치수 정확도와 재료 낭비를 최소화하면서 매우 복잡하고 내구성이 뛰어난 부품을 생산할 수 있습니다.
인코넬 파우더 3D 프린터 가이드
인코넬 파우더 3D 프린터는 일반적으로 파우더 베드 융합(PBF) 또는 방향성 에너지 증착(DED) 기술을 사용하는 산업용 기계입니다. 선택적 레이저 용융(SLM) 및 전자빔 용융(EBM)과 같은 PBF 공정은 컴퓨터 지원 설계(CAD) 모델에 따라 인코넬 분말의 얇은 층을 선택적으로 용융하고 융합하는 과정을 포함합니다. 반면 DED 공정은 레이저 또는 전자빔과 같은 집속 에너지원을 사용하여 인코넬 분말을 기판에 직접 증착하고 융합하는 방식입니다.
인코넬 파우더 3D 프린터 유형
| 프린터 유형 | 기술 | 장점 | 제한 사항 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 선택적 레이저 용융(SLM) | 파우더 베드 퓨전(PBF) | 고정밀, 우수한 표면 마감, 복잡한 형상에 적합 | 제한된 빌드 볼륨, 상대적으로 느린 빌드 속도 |
| 전자빔 용융(EBM) | 파우더 베드 퓨전(PBF) | 빠른 제작 속도, 고온 응용 분야, 응력 완화 부품에 이상적 | 진공 환경, 거친 표면 마감이 필요함 |
| 직접 에너지 증착(DED) | 직접 에너지 증착 | 대량 제작, 다중 재료 기능, 수리 및 코팅 애플리케이션에 적합 | PBF에 비해 낮은 해상도 및 표면 마감 |

인코넬 3D 프린팅 프로세스
인코넬 3D 프린팅 프로세스에는 일반적으로 다음 단계가 포함됩니다:
- CAD 모델링: CAD(컴퓨터 지원 설계) 소프트웨어를 사용하여 원하는 구성 요소의 3D 모델을 생성합니다.
- 파일 준비: 그런 다음 CAD 모델을 호환 가능한 파일 형식(예: STL, AMF)으로 변환하고 프린터가 해석할 수 있도록 얇은 레이어로 슬라이스합니다.
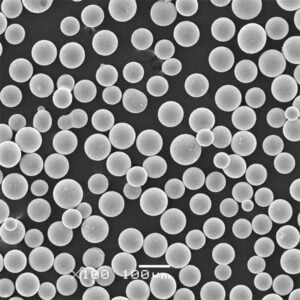
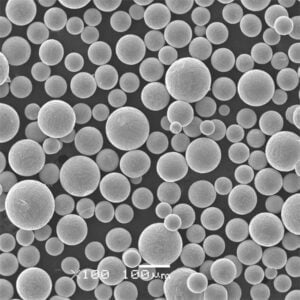
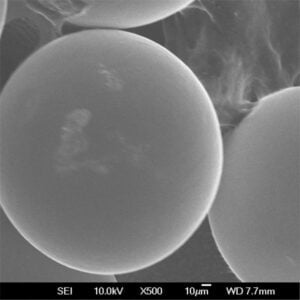
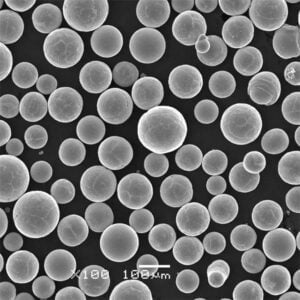
- 분말 준비: 인코넬 파우더는 신중하게 준비되어 프린터의 파우더 전달 시스템에 적재됩니다.
- 빌드 설정: 빌드 플랫폼이 준비되고 프린터가 특정 인코넬 합금 및 빌드 파라미터에 맞게 보정됩니다.
- 레이어별 제작: 프린터는 디지털 모델에 따라 인코넬 파우더 층을 선택적으로 녹이고 융합하여 원하는 부품을 만듭니다.
- 포스트 프로세싱: 빌드가 완료되면 애플리케이션 요구 사항에 따라 열처리, 표면 마감 또는 기계 가공과 같은 다양한 후처리 단계를 거칠 수 있습니다.
인코넬 파우더 3D 프린터 기능
| 기능 | 세부 정보 |
|---|---|
| 볼륨 구축 | 데스크톱 크기의 빌드 챔버부터 대규모 산업용 시스템까지 다양합니다. |
| 재료 | 인코넬 625, 718 등 다양한 인코넬 합금으로 마킹 가능 |
| 정밀도 | 일반적인 레이어 두께는 20~100미크론으로 뛰어난 치수 정확도를 제공합니다. |
| 기능 해상도 | 복잡한 형상과 내부 피처를 밀리미터 이하 수준까지 제작할 수 있습니다. |
| 표면 마감 | 공정 및 후처리에 따라 준공 시 표면 마감은 거친 것부터 거울에 가까운 것까지 다양할 수 있습니다. |
| 사용자 지정 | 일부 시스템은 커스터마이징 가능한 빌드 파라미터, 머티리얼 및 포스트 프로세싱 옵션을 제공합니다. |
인코넬 분말 3D 프린터 공급업체 및 가격대
| 공급업체 | 프린터 모델 | 가격 범위(USD) |
|---|---|---|
| EOS | EOS M 290(EBM) | $800,000 – $1,200,000 |
| SLM 솔루션 | SLM 500(SLM) | $600,000 – $900,000 |
| 컨셉 레이저 | 컨셉 레이저 M2(SLM) | $500,000 – $800,000 |
| 옵토멕 | 렌즈 850-R(DED) | $400,000 – $700,000 |
| 3D Systems | DMP 플렉스 350(DED) | $300,000 – $600,000 |
참고: 가격은 구성, 액세서리 및 지역별 가격에 따라 달라질 수 있습니다.
인코넬 분말 3D 프린터의 설치, 작동 및 유지보수
| 측면 | 세부 정보 |
|---|---|
| 설치 | 일반적으로 적절한 전원, 환기 및 안전 시스템을 갖춘 전용 시설이 필요합니다. |
| 운영자 교육 | 이러한 복잡한 시스템을 안전하고 효과적으로 운영하려면 광범위한 교육이 필요합니다. |
| 자재 취급 | 일관된 인쇄 품질을 보장하려면 인코넬 분말을 올바르게 취급하고 보관하는 것이 중요합니다. |
| 유지 관리 | 청소, 캘리브레이션, 부품 교체를 포함한 정기적인 유지보수는 필수입니다. |
| 안전 고려 사항 | 적절한 개인 보호 장비(PPE) 및 안전 프로토콜을 준수해야 합니다. |
인코넬 파우더 3D 프린터 공급업체 선택하기
인코넬 파우더 3D 프린터 공급업체를 선택할 때는 다음 요소를 고려해야 합니다:
| 팩터 | 고려 사항 |
|---|---|
| 애플리케이션 요구 사항 | 제작 볼륨, 재료, 정밀도 및 피처 해상도 측면에서 프린터의 기능을 평가합니다. |
| 생산량 | 생산 요구 사항을 충족하는 프린터의 처리량과 확장성을 평가합니다. |
| 서비스 및 지원 | 공급업체의 기술 지원, 교육 및 유지 관리 서비스를 고려하세요. |
| 인증 | 공급업체가 관련 업계 인증 및 표준을 충족하는지 확인합니다. |
| 총 소유 비용 | 초기 투자, 운영 비용, 소모품, 유지보수 비용을 고려하세요. |
인코넬 분말 3D 프린팅의 장단점
| 장점 | 단점 |
|---|---|
| 복잡한 지오메트리 생성 기능 | 높은 초기 투자 및 운영 비용 |
| 우수한 소재 특성(강도, 내열성) | 일부 시스템에서 제한된 빌드 볼륨 |
| 감산 제조에 비해 재료 낭비 최소화 | 잔류 스트레스 및 결함 가능성 |
| 사용자 지정 및 디자인 유연성 | 엄격한 자재 취급 및 안전 요건 |
| 경량화 및 성능 최적화 가능성 | 특정 애플리케이션의 경우 후처리가 필요할 수 있습니다. |
인코넬 분말 3D 프린터의 장점과 한계
| 장점 | 제한 사항 |
|---|---|
| 복잡한 내부 피처와 복잡한 지오메트리 생성 기능 | 일반적으로 기존 제조 방식에 비해 빌드 볼륨이 더 작습니다. |
| 뛰어난 기계적 특성 및 고온 성능 | 엄격한 자재 취급 및 안전 프로토콜이 필요합니다. |
| 설계 유연성 및 사용자 지정 가능성 | 인쇄된 부품의 잔류 응력 및 결함 발생 가능성 |
| 감산 제조에 비해 재료 낭비 최소화 | 높은 초기 투자 및 운영 비용 |
| 경량화 및 성능 최적화 가능성 | 제한된 재료 선택(인코넬 합금으로 제한됨) |
참고: 장점과 제한 사항은 특정 프린터 모델, 애플리케이션 및 사용자 요구 사항에 따라 달라질 수 있습니다.
자주 묻는 질문
| 질문 | 답변 |
|---|---|
| 인코넬 파우더 3D 프린터를 주로 사용하는 산업 분야는 무엇인가요? | 항공우주, 자동차, 에너지 및 기타 뛰어난 강도와 내열성을 갖춘 고성능 부품이 필요한 분야. |
| 인코넬 3D 프린팅은 기존 제조 방식과 어떻게 다릅니까? | 인코넬 3D 프린팅을 사용하면 주조나 기계 가공과 같은 기존 방법으로는 달성하기 어렵거나 불가능한 복잡한 형상과 내부 피처를 만들 수 있습니다. 하지만 일반적으로 제작 부피가 작고, 공정에 더 엄격한 자재 취급 및 안전 프로토콜이 필요합니다. |
| 인코넬 3D 프린터로 달성할 수 있는 일반적인 레이어 두께와 피처 해상도는 어느 정도인가요? | 레이어 두께는 일반적으로 20~100미크론이며 피처 해상도는 밀리미터 미만 수준까지 가능하므로 복잡한 형상과 내부 피처를 제작할 수 있습니다. |
| 인코넬 3D 프린터는 인코넬 합금 이외의 다른 소재와도 작동할 수 있나요? | 대부분의 인코넬 3D 프린터는 인코넬 합금용으로 특별히 설계되었지만 일부 시스템은 다른 니켈 기반 초합금 또는 고온 재료와의 호환성이 제한될 수 있습니다. |
| 3D 프린팅된 인코넬 부품의 표면 마감은 기존 제조 부품과 비교했을 때 어떤 차이가 있을까요? | 출고 시 표면 마감은 특정 인쇄 공정과 사용된 매개변수에 따라 거친 표면에서 거울에 가까운 표면까지 다양할 수 있습니다. 원하는 표면 품질을 얻기 위해 가공 또는 표면 마감과 같은 후처리 단계가 필요할 수 있습니다. |
| 인코넬 3D 프린터의 일반적인 유지보수 요건은 무엇인가요? | 일관된 인쇄 품질과 시스템 성능을 보장하려면 청소, 보정 및 부품 교체를 포함한 정기적인 유지 관리가 필수적입니다. 인코넬 분말을 올바르게 취급하고 보관하는 것도 중요합니다. |
| 올바른 Inconel 3D 프린터 공급업체를 선택하려면 어떻게 해야 하나요? | 공급업체를 선택할 때는 애플리케이션 요구 사항, 생산량, 서비스 및 지원, 인증, 총 소유 비용과 같은 요소를 고려하세요. 또한 제작량, 재료, 정밀도, 피처 해상도 측면에서 프린터의 기능을 평가합니다. |
공유
중국 칭다오에 본사를 둔 선도적인 적층 제조 솔루션 제공업체인 MET3DP Technology Co. 당사는 산업용 3D 프린팅 장비와 고성능 금속 분말을 전문으로 합니다.
관련 기사
Met3DP 소개
최근 업데이트
제품

3D 프린팅 및 적층 제조용 금속 분말
문의 정보
- 칭다오시, 산둥성, 중국
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- +86 19116340731