니켈 초합금 : 유형, 가격, 공급 업체
목차
제트 엔진의 뜨거운 열이나 가스 터빈의 강한 압력을 견딜 수 있을 정도로 강한 소재를 상상해 보세요. 이 같은 소재가 비교할 수 없는 정밀도로 복잡한 부품으로 성형된다고 상상해 보세요. 이것은 공상 과학 소설이 아니라 니켈 초합금의 현실입니다. 3D 프린팅.
니켈 초합금은 고온에서 뛰어난 특성으로 유명한 금속 재료의 한 종류입니다. 강도, 내산화성, 크리프 저항성이 독특하게 결합되어 있어 항공우주, 에너지 생산 및 기타 고성능 산업의 까다로운 응용 분야에 가장 적합한 소재입니다. 하지만 3D 프린팅 기술은 이러한 놀라운 소재의 진정한 잠재력을 발휘하여 전례 없는 디자인 자유도를 갖춘 복잡하고 가벼운 부품을 제작할 수 있게 해줍니다.

3D 프린팅을 위한 니켈 초합금의 힘 공개
니켈 초합금은 똑같이 만들어지지 않습니다. 각 배합은 특정 원소의 조합을 자랑하며, 그 결과 고유한 특성을 갖게 됩니다. 3D 프린팅에서 니켈 합금의 기능을 이해하기 위해 세부 사항을 자세히 살펴보겠습니다:
3D 프린팅용 니켈 초합금의 구성 및 특성
| 요소 | 기능 | 속성에 미치는 영향 |
|---|---|---|
| 니켈(Ni) | 기본 금속 | 강도와 연성을 위한 토대 제공 |
| 크롬(Cr) | 주요 강화 요소 | 내산화성 및 고온 강도 향상 |
| 코발트 (Co) | 견고한 솔루션 강화 | 고온 성능 및 크리프 저항성 향상 |
| 알루미늄(Al) | 라이트닝 에이전트 | 근력을 유지하면서 체중 감량 |
| 티타늄(Ti) | 곡물 정제기 | 향상된 기계적 특성을 위한 미세 구조 제어 |
| 탄탈륨(Ta) | 카바이드 포머 | 고온 강도 및 내산화성 향상 |
| 텅스텐(W) | 카바이드 포머 | 고온에서 소재를 강화합니다. |
3D 프린팅에서 니켈 초합금의 응용 분야
| 산업 | 애플리케이션 | 3D 프린팅의 이점 |
|---|---|---|
| 항공우주 | 터빈 블레이드, 연소기 라이너, 열교환기 | 엔진 효율성과 성능 향상을 위한 가볍고 복잡한 설계 |
| 에너지 생산 | 가스터빈 부품, 방열판 | 무게 감소 및 설계 유연성을 통한 효율적인 전력 생산 |
| 화학 처리 | 원자로, 열교환기 | 열악한 환경을 위한 부식 방지, 맞춤형 설계 구성 요소 |
| 의료 기기 | 임플란트, 수술 기구 | 복잡한 형상의 개인 맞춤형 의료 솔루션을 위한 생체 적합성 옵션 |
3D 프린팅용 니켈 초합금의 사양, 크기, 등급 및 표준
니켈 초합금 분말은 다양한 용도의 특성으로 인해 다양한 사양으로 제공됩니다. 다음은 고려해야 할 주요 요소에 대한 분석입니다:
- 입자 크기 분포: 유동성, 인쇄 가능성 및 최종 구성 요소 속성에 영향을 줍니다. 일반적인 범위는 15-45미크론 및 45-90미크론입니다.
- 파우더 유동성: 인쇄 과정에서 파우더가 고르게 퍼지는 능력에 영향을 미칩니다. 유동성이 우수하여 일관된 레이어 형성을 보장합니다.
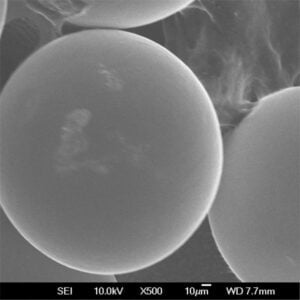
- 구형 및 형태: 분말 모양은 인쇄 시 포장 밀도와 레이저 흡수에 영향을 미칩니다. 최적의 결과를 얻으려면 구형 모양이 선호됩니다.
- 화학 성분: 인쇄된 구성 요소의 최종 속성을 결정합니다. ASTM 국제(ASTM) 또는 항공우주 재료 사양(AMS)과 같은 특정 표준은 허용 가능한 구성을 정의합니다.
3D 프린팅용 인기 니켈 초합금 분말
- AM260S: 적층 제조를 위해 특별히 개발된 AM260S 파우더는 탁월한 인쇄성과 고온 성능을 제공합니다. IN718에 비해 AM260S는 고온에서 우수한 크리프 저항성과 강도를 자랑하므로 까다로운 항공우주 분야에 적합한 강력한 경쟁자입니다.
- MarM247 LC: 이 고급 합금 분말은 극한의 온도에서 탁월한 크리프 저항성과 산화 저항성으로 잘 알려져 있습니다. MarM247 LC는 이러한 측면에서 Rene 41을 능가하여 차세대 터빈 블레이드 및 제트 엔진의 핫 섹션 부품에 이상적입니다.
- 니켈 합금 헤인즈 282: 고온 강도와 우수한 용접성의 독특한 조합을 제공하는 Haynes 282 분말은 성능과 제작 용이성을 모두 필요로 하는 응용 분야에 적합한 선택입니다. 이 소재는 열교환기, 배기 시스템 및 기타 고온 부품에 사용됩니다.
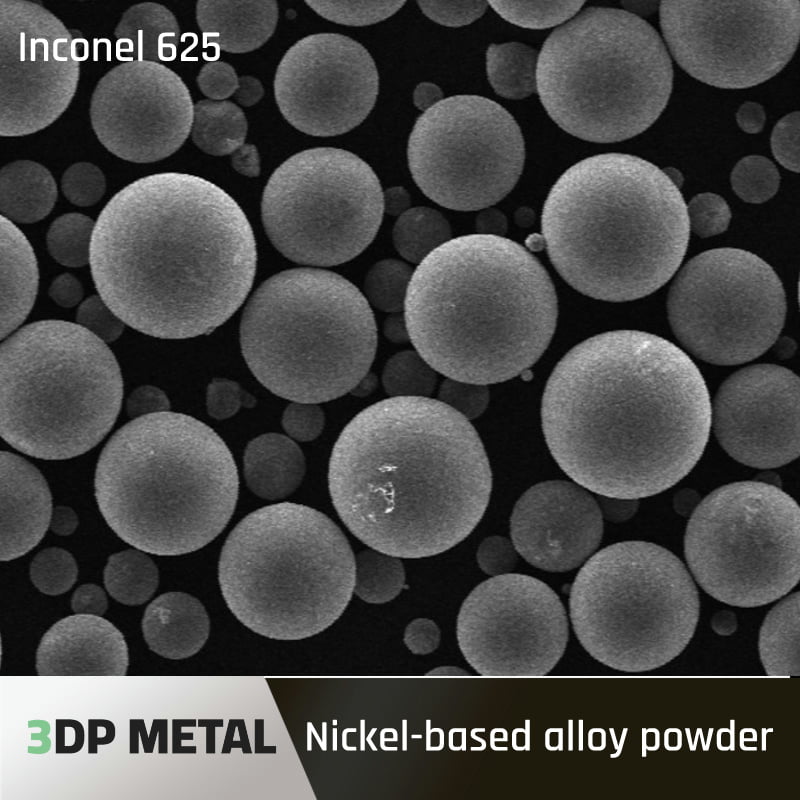
- Met3DP 니켈 초합금 분말: 3D 프린팅용 금속 분말의 선도적인 제조업체인 Met3DP는 다양한 용도에 최적화된 다양한 고품질 니켈 초합금 분말을 제공합니다. 이 포트폴리오에는 IN718 및 인코넬 625와 같은 기존 옵션과 함께 특정 성능 요구 사항에 맞춘 보다 혁신적인 합금이 포함됩니다.
3D 프린팅용 니켈 초합금 분말의 가격 및 공급업체
니켈 초합금 분말의 가격은 특정 합금, 입자 크기, 공급업체에 따라 달라집니다. 일반적으로 이러한 분말은 복잡한 제조 공정으로 인해 기존 금속 분말에 비해 더 비쌉니다. 가격 책정 환경을 간략히 살펴보세요:
- 가격 범위: IN718 및 인코넬 625와 같이 일반적으로 사용되는 합금의 경우 킬로그램당 $100-300의 가격대를 예상할 수 있습니다. MarM247 LC와 같은 고급 옵션은 특수한 특성으로 인해 더 높은 가격대에 도달할 수 있습니다.
- 공급업체: 여러 유명 회사에서 3D 프린팅용 고품질 니켈 초합금 분말을 공급합니다. 대표적인 업체로는 EOS GmbH, Elementum 3D, SLM Solutions, 그리고 앞서 언급했듯이 Met3DP가 있습니다.
3D 프린팅용 니켈 초합금의 장단점
장점:
- 탁월한 고온 성능: 니켈 초합금은 다른 소재가 실패할 수 있는 온도에서도 강도와 무결성을 유지하므로 까다로운 애플리케이션에 이상적입니다.
- 디자인의 자유와 경량화: 3D 프린팅은 무게를 줄이면서 복잡한 형상을 구현할 수 있는 가능성을 열어주어 항공우주 및 기타 무게가 중요한 산업에서 효율성을 향상시킵니다.
- 낭비 감소 및 그물 모양에 가까운 제조: 기존의 감산 제조 기술에 비해 3D 프린팅은 재료 낭비를 최소화하고 그물 모양에 가까운 생산이 가능하므로 가공 요구 사항을 줄일 수 있습니다.
- 향상된 부품 기능: 3D 프린팅으로 복잡한 내부 기능을 만들 수 있어 니켈 초합금으로 만든 부품의 기능과 성능이 향상됩니다.
단점:
- 더 높은 재료비: 니켈 초합금 분말은 일반적으로 적층 제조에 사용되는 다른 금속 분말보다 더 비쌉니다.
- 제한된 자료 가용성: 사용 가능한 니켈 초합금 분말의 범위가 확대되고 있지만, 특정 용도에 필요한 모든 특정 합금 조성을 포함하지는 않을 수 있습니다.
- 프로세스 최적화가 필요합니다: 니켈 초합금을 성공적으로 3D 프린팅하려면 우수한 인쇄성을 보장하고 최종 부품에서 원하는 재료 특성을 얻기 위해 세심한 파라미터 최적화가 필요합니다.
- 후처리 고려 사항: 일부 니켈 초합금 부품은 최종 특성을 최적화하기 위해 열처리 또는 열간 등방성 프레스(HIP)와 같은 추가 후처리 단계가 필요할 수 있습니다.
3D 프린팅용 니켈 초합금에 대한 FAQ
Q: 3D 프린팅에 니켈 초합금을 사용하면 어떤 이점이 있나요?
A: 니켈 초합금은 탁월한 고온 성능, 경량화를 위한 자유로운 설계, 그물 모양에 가까운 제조로 폐기물 감소, 복잡한 내부 기능을 통한 부품 기능 향상 가능성을 제공합니다.
Q: 3D 프린팅 니켈 초합금과 관련된 도전 과제에는 어떤 것이 있나요?
A: 주요 과제는 높은 재료 비용, 표준 옵션에 비해 제한된 재료 가용성, 성공적인 인쇄를 위한 공정 최적화의 필요성, 잠재적인 후처리 요구 사항 등입니다.
Q: 3D 프린팅으로 인쇄된 니켈 초합금의 일반적인 응용 분야에는 어떤 것이 있나요?
A: 터빈 블레이드, 연소기 라이너, 열교환기(항공우주), 가스터빈 부품, 열 차폐(에너지 생산), 원자로, 열교환기(화학 처리), 임플란트, 수술 기구(의료기기) 등이 일반적인 응용 분야입니다.
Q: 3D 프린팅용 니켈 초합금 분말은 어디에서 구입할 수 있나요?
A: EOS GmbH, Elementum 3D, SLM Solutions, Met3DP 등 여러 유명 공급업체에서 니켈 초합금 분말을 제공합니다. Met3DP는 특히 레이저 및 전자빔 파우더 베드 융합에 최적화된 다양한 고품질 금속 분말을 제조합니다. 이 회사의 포트폴리오에는 TiNi, TiTa, TiAl, TiNbZr, CoCrMo, 스테인리스강, 초합금 등과 같은 혁신적인 합금이 포함되어 있어 다양한 3D 프린팅 요구 사항을 충족하는 원스톱 숍이 됩니다.
3D 프린팅에서 니켈 초합금의 미래
3D 프린팅에서 니켈 초합금의 미래는 가능성으로 가득 차 있습니다. 연구와 개발 노력이 계속됨에 따라 기대해 볼 수 있습니다:
- 새로운 합금 개발: 재료 과학자들은 3D 프린팅에 최적화된 새로운 니켈 초합금 배합을 끊임없이 혁신하고 있습니다. 이러한 합금은 성능의 한계를 뛰어넘어 더욱 뛰어난 강도, 내산화성, 고온 성능을 제공합니다.
- 3D 프린팅 기술의 발전: 더 높은 레이저 출력과 더 엄격한 공정 제어와 같은 3D 프린팅 기술의 개선으로 니켈 초합금으로 훨씬 더 복잡한 고성능 부품을 만들 수 있게 되었습니다.
- 비용 절감 및 가용성 확대: 기술이 성숙하고 생산량이 증가함에 따라 니켈 초합금 분말의 가격은 하락할 것으로 예상됩니다. 이를 통해 더 다양한 애플리케이션에 더 쉽게 접근할 수 있게 될 것입니다.
- 중요 애플리케이션에 대한 자격: 니켈 초합금 3D 프린팅 부품을 중요한 항공우주 및 에너지 애플리케이션에 사용하기 위한 엄격한 자격 인증 절차가 진행 중입니다. 이를 통해 이러한 까다로운 산업 분야에서 이 기술이 널리 채택될 수 있는 길이 열릴 것입니다.
결론적으로, 니켈 초합금은 3D 프린팅의 미래에서 혁신적인 역할을 할 준비가 되어 있습니다. 고온 성능, 설계의 자유, 경량화 가능성이라는 독특한 조합으로 인해 매우 까다로운 다양한 응용 분야에 이상적입니다. 기술 발전이 계속됨에 따라 니켈 초합금은 의심할 여지 없이 3D 프린팅의 한계를 뛰어넘는 초석 소재가 될 것입니다.
공유
중국 칭다오에 본사를 둔 선도적인 적층 제조 솔루션 제공업체인 MET3DP Technology Co. 당사는 산업용 3D 프린팅 장비와 고성능 금속 분말을 전문으로 합니다.
관련 기사
Met3DP 소개
최근 업데이트
제품

3D 프린팅 및 적층 제조용 금속 분말
문의 정보
- 칭다오시, 산둥성, 중국
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- +86 19116340731