진공 유도 용융
목차
개요 진공 유도 용융
진공 유도 용해(VIM)는 금속 산업에서 정교하고 필수적인 공정으로, 주로 고품질 금속 합금을 생산하는 데 사용됩니다. 이 방법은 진공 상태에서 금속을 용융함으로써 가스 및 불순물로 인한 오염 위험을 최소화하여 우수한 재료 특성을 얻을 수 있습니다. 항공우주, 의료 기기, 고성능 엔지니어링 부품 등 고순도 및 특정 합금 구성이 중요한 산업에서 널리 사용되고 있습니다.
진공 유도 용융의 이해
진공 유도 용해는 전자기 유도를 활용하여 진공 밀폐 환경에서 금속을 가열하고 용해하는 방식으로 작동합니다. 진공 조건은 최종 제품에 결함을 일으킬 수 있는 산소, 질소, 수소의 존재를 감소시킵니다. 이 공정을 통해 생산된 금속은 우수한 기계적 특성, 고순도 및 제어된 조성을 갖습니다.
주요 구성 요소 및 프로세스
- 인덕션 퍼니스: 교류 전류를 사용하여 금속에 열을 유도하는 전자기장을 생성하는 VIM 공정의 핵심입니다.
- 진공 챔버: 유도로를 둘러싸서 진공 또는 불활성 분위기에서 용해가 이루어지도록 합니다.
- 전원 공급 장치: 유도가열에 필요한 전력을 공급합니다.
- 냉각 시스템: 적절한 온도를 유지하고 과열을 방지합니다.
진공 유도 용융의 이점
- 고순도: 오염 물질을 제거하여 매우 순수한 금속을 생성합니다.
- 정밀한 제어: 합금 구성을 정밀하게 제어할 수 있습니다.
- 우수한 기계적 특성: 소재의 강도, 연성 및 전반적인 성능을 향상시킵니다.
- 다용도성: 다양한 금속 및 합금에 적합합니다.
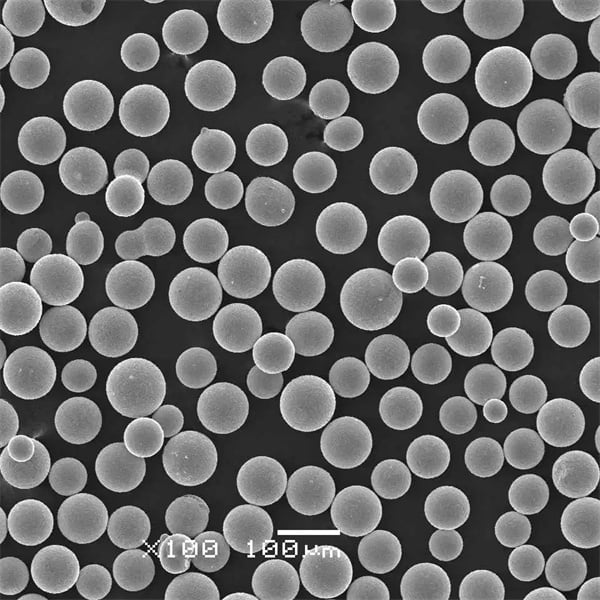
금속 분말을 사용하여 생산되는 금속 분말의 종류 진공 유도 용융
일반적인 금속 분말과 그 용도
| 금속분말 | 구성 | 속성 | 애플리케이션 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 니켈 합금 625 | Ni, Cr, Mo, Nb | 고강도, 내식성 | 항공우주, 해양, 화학 공정 |
| 티타늄 합금 Ti-6Al-4V | Ti, Al, V | 높은 중량 대비 강도, 생체 적합성 | 의료용 임플란트, 항공우주 |
| 코발트-크롬 합금 | Co, Cr, Mo | 내마모성, 생체 적합성 | 치과 및 정형외과 임플란트 |
| 인코넬 718 | Ni, Cr, Fe, Nb, Mo | 높은 내열성, 강도 | 가스터빈, 원자로 |
| 스테인리스 스틸 316L | Fe, Cr, Ni, Mo | 부식 방지, 우수한 용접성 | 의료 기기, 식품 가공 |
| 알루미늄 합금 7075 | 알, 아연, 마그네슘, 구리 | 고강도, 경량 | 항공우주, 스포츠용품 |
| 공구강 H13 | Fe, Cr, Mo, V | 높은 인성, 내마모성 | 다이캐스팅, 압출 도구 |
| 구리 합금 C18200 | Cu, Cr | 높은 전도성, 내식성 | 전기 부품, 용접 전극 |
| 마그네슘 합금 AZ91D | Mg, Al, Zn | 가볍고 우수한 캐스팅성 | 자동차, 전자 |
| 탄탈륨 | 퓨어 타 | 높은 융점, 내식성 | 화학 처리, 전자 제품 |
진공 유도 용융의 응용 분야
진공 유도 용융은 다양한 산업 분야에서 높은 무결성과 특정 재료 특성이 필요한 부품을 생산하는 데 활용됩니다. 다음은 몇 가지 주요 응용 분야입니다:
| 산업 | 생산된 구성 요소 |
|---|---|
| 항공우주 | 터빈 블레이드, 엔진 부품 |
| 의료 | 임플란트, 수술 기구 |
| 자동차 | 고성능 엔진 부품 |
| 전자 제품 | 전도성 재료, 반도체 부품 |
| 에너지 | 터빈 부품, 원자로 부품 |
사양, 크기, 등급 및 표준
진공 유도 용융을 통해 생산되는 금속 분말 및 부품을 취급할 때는 품질과 성능을 보장하기 위해 특정 표준 및 사양을 준수하는 것이 중요합니다. 다음은 일반적인 사양에 대한 개요입니다:
| 재질 | 사양 | 크기 | 성적 | 표준 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 니켈 합금 625 | ASTM B446, AMS 5666 | 다양한 크기 | UNS N06625 | ISO 9001, AS9100 |
| 티타늄 합금 Ti-6Al-4V | ASTM F136, AMS 4911 | 다양한 크기 | 5학년 | ISO 5832-3, ASTM F136 |
| 스테인리스 스틸 316L | ASTM A240, A276 | 다양한 크기 | UNS S31603 | ISO 9001, ASTM A276 |
| 인코넬 718 | ASTM B637, AMS 5663 | 다양한 크기 | UNS N07718 | ISO 9001, AS9100 |
| 공구강 H13 | ASTM A681, AISI H13 | 다양한 크기 | H13 등급 | ISO 9001, ASTM A681 |
의 장단점 비교 진공 유도 용융
| 장점 | 단점 |
|---|---|
| 고순도: 불순물과 결함이 적은 금속을 생산합니다. | 비용: 높은 초기 설정 및 운영 비용. |
| 제어된 분위기: 가스 및 기타 요소로 인한 오염을 최소화합니다. | 복잡성: 숙련된 운영자와 정밀한 제어 시스템이 필요합니다. |
| 다용도성: 다양한 금속 및 합금에 사용 가능. | 규모: 다른 방식에 비해 배치 크기가 제한적입니다. |
| 향상된 속성: 금속의 기계적 특성과 성능을 향상시킵니다. | 유지 관리: 진공 시스템과 인덕션 퍼니스의 정기적인 유지보수가 필요합니다. |
주요 공급업체 및 가격 세부 정보
진공 유도 용융을 통해 생산되는 금속 분말 및 부품을 소싱할 때는 공급업체의 평판, 품질 표준 및 가격을 고려하는 것이 필수적입니다. 다음은 몇 가지 주목할 만한 공급업체를 요약한 것입니다:
| 공급업체 | 위치 | 제품 | 가격(대략) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ATI 금속 | 미국 | 니켈 합금, 티타늄 합금 | $50 - $200/kg |
| 카펜터 기술 | 미국 | 특수 합금, 스테인리스 스틸 | $40 - $180/kg |
| 샌드빅 재료 기술 | 스웨덴 | 스테인리스 스틸, 고성능 합금 | $30 - $150/kg |
| VSMPO-AVISMA | 러시아 | 티타늄 합금 | $60 - $220/kg |
| H.C. 스탁 솔루션 | 독일 | 내화성 금속, 고급 합금 | $70 - $250/kg |
진공 유도 용융의 장점과 한계
장점
- 순도 및 품질: VIM의 가장 중요한 이점 중 하나는 고성능 애플리케이션에 필수적인 극순도 금속을 생산할 수 있다는 점입니다.
- 정밀한 합금 구성: 이 공정을 통해 합금 원소를 정밀하게 제어할 수 있으므로 최종 제품이 정확한 사양을 충족합니다.
- 향상된 기계적 특성: VIM을 통해 생산된 금속은 강도, 인성, 피로 및 부식에 대한 저항성 증가와 같은 우수한 기계적 특성을 보이는 경우가 많습니다.
제한 사항
- 높은 비용: 진공 유도 용융의 설치 및 운영 비용은 모두 높기 때문에 소규모 기업이나 소량 생산에는 장벽이 될 수 있습니다.
- 복잡한 작업: 이 공정에는 고품질 생산에 필요한 조건을 유지하기 위해 고도로 숙련된 작업자와 정교한 제어 시스템이 필요합니다.
- 배치 크기: 생산할 수 있는 배치의 크기가 다른 용융 공정에 비해 작은 경우가 많기 때문에 생산 능력이 제한될 수 있습니다.
비교 진공 유도 용융 다른 용융 공정과 함께
| 매개변수 | 진공 유도 용융 | 전기 아크 용융 | 공기 유도 용융 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 순도 | 높음 | 보통 | 낮음 |
| 비용 | 높음 | 보통 | 낮음 |
| 구도 제어 | 우수 | 양호 | 공정 |
| 배치 크기 | 중소형 | 중대형 | 크기가 큰 |
| 기계적 특성 | 우수 | 양호 | 공정 |
자주 묻는 질문
| 질문 | 답변 |
|---|---|
| 진공 유도 용융이란 무엇인가요? | 진공 유도 용융은 전자기 유도를 사용하여 진공 밀폐된 환경에서 금속을 녹여 고순도 합금을 생산하는 공정입니다. |
| 이 과정에서 진공이 사용되는 이유는 무엇인가요? | 진공은 금속에 불순물과 결함을 일으킬 수 있는 산소, 질소, 수소와 같은 가스의 존재를 줄여줍니다. |
| VIM을 사용하여 녹일 수 있는 금속의 종류는 무엇인가요? | 니켈, 티타늄, 코발트, 스테인리스 스틸 등 다양한 금속을 VIM을 사용하여 녹일 수 있습니다. |
| 어떤 산업에서 주로 VIM을 사용하나요? | 항공우주, 의료, 자동차, 전자, 에너지 산업에서는 일반적으로 고성능 부품을 생산하기 위해 VIM을 사용합니다. |
| 다른 용융 공정에 비해 VIM을 사용하면 어떤 이점이 있나요? | VIM은 다른 용융 공정에 비해 순도가 높고 합금 조성을 더 잘 제어할 수 있으며 기계적 특성이 우수합니다. |
| VIM을 사용하는 데 제한이 있나요? | 예, VIM은 비용이 많이 들고 복잡할 수 있으며 숙련된 작업자와 정밀한 제어 시스템이 필요합니다. 또한 일반적으로 더 작은 배치 크기를 처리합니다. |
공유
중국 칭다오에 본사를 둔 선도적인 적층 제조 솔루션 제공업체인 MET3DP Technology Co. 당사는 산업용 3D 프린팅 장비와 고성능 금속 분말을 전문으로 합니다.
관련 기사
Met3DP 소개
최근 업데이트
제품

3D 프린팅 및 적층 제조용 금속 분말
문의 정보
- 칭다오시, 산둥성, 중국
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- +86 19116340731

















