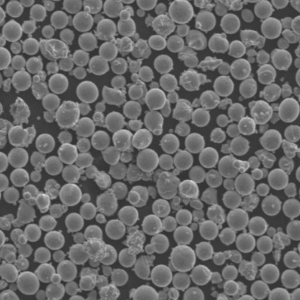
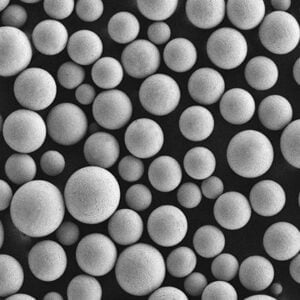
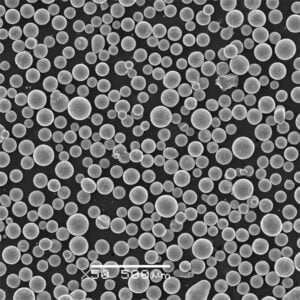
チタン合金粉末:組成、製造、応用
目次
チタン合金粉末 チタン合金は、チタンを主成分とし、アルミニウム、バナジウム、鉄などの他の金属と組み合わせたものである。この合金組成により、航空宇宙、医療機器など幅広い用途で強化された特性が得られます。
チタン合金粉末の種類
粉末状の一般的なチタン合金の配合:
| 合金 | Tiコンテンツ | その他の要素 | 主要物件 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ti-6Al-4V | 90% | 6% Al, 4% V | 高強度、低密度 |
| Ti-6Al-7Nb | 90% | 6% Al, 7% Nb | 生体適合性、耐食性 |
| Ti-10V-2Fe-3Al | 82% | 10% V, 2% Fe, 3% Al | 耐熱性、硬化 |
| Ti-3Al-2.5V | 93% | 3% Al、2.5% V | 高温強度 |
- アルミニウム、バナジウム、鉄、ニオブと合金化したチタンは、硬度、強度、密度のバランスがとれている。
- 特定元素は、機械的、物理的、生物学的特性を調整する。
- 混合物は、高温挙動、摩耗性能、溶接性などを最適化する。
- アルミニウムがチタンの結晶構造を安定させ、加工性を向上させる。
そのため、チタン合金の金属の組み合わせを調整することで、用途に応じた機能特性を実現することができる。

チタン合金粉末製造
チタン合金粉末を製造する一般的な技術:
| 方法 | プロセス | 説明 | 粒子特性 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ガス噴霧 | 溶融流がガスジェットに衝突 | 急速冷却により球状粒子を形成 | 優れた流動性 |
| プラズマ霧化 | 高温プラズマが合金を溶かす | 非常に微細な球状粉末の製造 | サブミクロンサイズ |
| ヒドリド脱水素 | 水素化物相粉砕 | 水素化物の不規則で脆い粒子 | 緩やかな流れ |
| メカニカルアロイング | パウダー粒子の変形溶接 | 微細粒径の複合構造 | 流れの悪さ |
- ガスアトマイズとプラズマアトマイズにより、積層造形に適した微細な球状合金粉が生成される
- ハイドライド脱水素法、脆いハイドライド相を小さな粒子に粉砕
- メカニカルアロイングは、変形を通じて小さな粒子を複合凝集体に溶接する。
そのため、さまざまな技術によって、チタン合金の粒子径、形状、内部微細構造を調整することができる。
の応用 チタン合金粉末
チタン合金粉末は、あらゆる分野で高性能部品を可能にします:
| セクター | 申し込み | 利用物件 |
|---|---|---|
| 航空宇宙 | タービンブレード、機体部品 | 高い比強度 |
| インダストリアル | 食品加工機器 | 耐食性 |
| 自動車 | コンロッド、バルブ | 耐熱性 |
| バイオメディカル | インプラント、補綴 | 生体適合性 |
| ディフェンス | アーマー素材 | 弾道保護 |
| 積層造形 | 3Dプリント部品 | 印刷適性 |
- 軽量強度により、チタン製部品を使用した航空機や車両の燃料節約を実現
- 生体中性チタン合金インプラントは人体による拒絶反応を回避する
- 工業プラントの侵食性化学薬品に適した耐食性
- 合金テーラーリングにより、用途に応じたチタングレードを提供
チタン合金粉末は、要求の厳しい様々な産業において高度な製造を可能にする。
チタン合金粉末の仕様
チタン合金粉末の主な品質指標:
| パラメータ | 代表値 | 試験方法 |
|---|---|---|
| 合金組成 | 元素の重量パーセント | ICP分光法 |
| 粒度分布 | 範囲と平均サイズ | レーザー回折 |
| 見かけ密度 | 最大85%の真密度 | スコット・ボリュメーター |
| タップ密度 | 最大95%の真密度 | タッピングによる測定 |
| 粒子形状 | 真球度、滑らかさ | SEMイメージング |
| 粉体流量 | 安息角、ホール流量計 | 標準テストファネル/容器 |
- 組成チェックでは、チタン、アルミニウム、バナジウムなどの含有率を確認する。
- 粒度分布は、意図した製造工程への適合性を保証します。
- 密度は充填効率と気孔率を示す
- 粒子形状はアプリケーションの性能と粉体の取り扱いに影響する
- 流量は、自動輸送と計量に適していることを証明する。
そのため、これらの指標は、購入したチタン合金粉末がアプリケーションの要件を満たしていることを確認するのに役立ちます。
チタン合金粉末の種類の比較
チタン合金の性能は?
| 合金 | Ti-6Al-4V | Ti-6Al-7Nb | Ti-10V-2Fe-3Al |
|---|---|---|---|
| 密度 | 4.43 g/cc | 4.52 g/cc | 4.38 g/cc |
| 引張強さ | 128キロ・シー | 126キロ・シー | 115キロ・シー |
| ヤング率 | 16 msi | 10 msi | 15 msi |
| 最高使用温度 | 700°F | 750°F | 800°F |
| 生体適合性 | 中程度 | 素晴らしい | 貧しい |
| コスト | 低い | 高い | 中程度 |
- Ti-6Al-4Vは、性能とコストを兼ね備えた主力チタン合金です。
- NbとTa合金は医療用途に優れた生体適合性を提供する
- より高いバナジウムと鉄は高温での安定性を可能にする。
- アルミニウムを含む合金は強度重量比が高い
そのため、それぞれのチタン合金の配合は、目標とする用途に特有の有利な特性を持っています。
チタン合金粉末のサプライヤー
チタン合金粉末の世界的大手メーカー:
| 会社概要 | 本社所在地 | グレード | 生産能力 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ATI粉末冶金 | 米国 | Ti-6Al-4V、カスタム合金 | 5,000トン/年 |
| テクナ | カナダ | Ti-6Al-4V 他 | 未発表 |
| ホガナスグループ | スウェーデン | Ti-6Al-4V | 3,000トン/年 |
| TLSテクニーク | ドイツ | TiAl、TiAlNb、Ti粉末 | 未発表 |
| CNPC パウダー | 中国 | Ti-6Al-4V, TiAl | 10,000トン/年 |
- 米国のATIパウダー・メタルズは、チタン合金粉末の世界的なリーディング・メーカーである。
- スウェーデンのHoganasグループもまた、チタン粉末の製造業を営んでいる。
- 中国は世界輸出を目指す複数の大手チタン合金粉末メーカーを抱える
- 中小企業も成長するチタン粉末業界に参入
そのため、チタン合金の需要拡大に対応するため、供給能力は拡大し続けている。
チタン合金粉末 価格
チタン合金粉末の概算価格
| 合金 | kgあたりの価格 | 粒子径範囲 |
|---|---|---|
| Ti-6Al-4V | $50 – $150 | 15~120ミクロン |
| Ti-6Al-7Nb | $250 – $500 | 5~45ミクロン |
| Ti-10V-2Fe-3Al | $75 – $200 | 15~63ミクロン |
| Ti-3Al-2.5V | $100 – $150 | 45~150ミクロン |
- 価格は購入量と粒度分布の仕様に大きく依存する。
- 特殊合金と高級医療用グレードは高値で取引される
- Ti-6Al-4Vは工業規模で最も経済的に生産される。
- 5~10トン以上の契約には割引料金が適用されます。
そのため、チタン合金粉末は依然として比較的高価であり、用途は主に航空宇宙と防衛分野に限られている。

チタン合金粉末に関するFAQ
| 質問 | 答え |
|---|---|
| チタン合金にはどんな色がありますか? | ナチュラルグレーが最も一般的。着色表面処理も施されている。 |
| パウダーは特別な取り扱いが必要ですか? | 取り扱い中の酸化を防ぐため、不活性ガス・ブランケットを使用することが望ましい。 |
| これらのパウダーでコールドスプレーは可能ですか? | そう、粒子の変形が高密着コーティングを可能にする。 |
| チタン合金は非磁性ですか? | どのグレードも透磁率は非常に低い。 |
| これらの粉体を安全に空輸できますか? | はい、非常に微細な反応性粉末を除き、輸送制限はありません。 |
そのためチタン合金粉末は、ほとんどの金属粉末の取り扱い、加工、コーティング作業に適しています。
結論
要約すると、チタン合金粉末は、密度、強度、弾性率、生体適合性のバランスをとる設計の柔軟性を提供し、産業界全体の高度なエンジニアリングの要求に応えます。製造技術はオーダーメイドの粒子特性を与えます。合金配合はカスタム特性のチューニングを可能にします。$50/kgを超える比較的高価な価格にもかかわらず、チタン合金粉末は、部品の性能がコスト面を上回る防衛、医療、航空宇宙、自動車用途において、より高い性能をもたらします。
Additional FAQs about Titanium Alloy Powders (5)
1) What powder characteristics most influence additive manufacturing quality?
- Particle size distribution (e.g., 15–45 µm for PBF), high sphericity (>0.9), low satellites, narrow D10–D90 spread, low interstitials (O, N, H), and good flow (Hall flow ≤25 s/50 g). These drive layer packing, laser absorption, density, and fatigue.
2) How many reuse cycles are acceptable for Ti-6Al-4V powder in PBF?
- Typically 5–15 cycles with sieving and 20–50% virgin top-up per cycle. Monitor O/N/H, PSD, and flowability per ISO/ASTM 52907; requalify if oxygen trends toward spec limits (e.g., ≤0.20 wt% O for many AM grades) or density/fatigue drifts.
3) Which production method is best for medical-grade titanium alloy powders?
- Plasma atomization and electrode/plasma rotating electrode (PREP) produce highly spherical, low-oxide powders favored for implants. They support tight PSDs and lower inclusion content compared to HDH for PBF applications.
4) What post-processing is typical for AM Ti-6Al-4V parts?
- Stress relief (e.g., 650–800°C), hot isostatic pressing (HIP 900–930°C/100–150 MPa/2–4 h), and heat treatment per ASTM F3001/AMS 4999 equivalents. HIP improves fatigue by closing internal porosity.
5) How do oxygen and nitrogen affect properties of Titanium Alloy Powders and parts?
- Interstitials increase strength/hardness but reduce ductility and fatigue life. Maintain low O/N in powder and control pickup during reuse and processing; use inert handling and dry environments.
2025 Industry Trends for Titanium Alloy Powders
- Tighter interstitial control: Aerospace/medical buyers specify lower O (≤0.12–0.18 wt%) and N (≤0.03 wt%) for fatigue- and implant-critical builds.
- Powder genealogy and EPDs: Digital material traceability from melt to build, plus Environmental Product Declarations covering recycle rates and energy per kg.
- AM allowables expansion: More published design allowables for Ti‑6Al‑4V (ELI) and Ti‑6Al‑7Nb across laser PBF and EBM, aligned to ASTM F42 frameworks.
- Binder Jetting and MIM convergence: Fine Ti and Ti alloy powders with tailored binders enable BJ/MIM routes for cost-sensitive components, with HIP to achieve fatigue targets.
- Capacity additions stabilize price: New atomization/PREP lines in NA/EU/Asia shorten lead times for aerospace PSDs (15–45 µm) and medical grades (10–38 µm).
2025 snapshot: Titanium Alloy Powders metrics
| メートル | 2023 | 2024 | 2025 YTD | Notes/Sources |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Typical PSD for PBF (µm, Ti-6Al-4V) | 15~53歳 | 15–45 | 15–45 | OEM datasets, supplier catalogs |
| Oxygen spec (wt%, AM grade) | ≤0.20 | ≤0.15–0.18 | ≤0.12–0.18 | ISO/ASTM 52907, buyer specs |
| As-built density (laser PBF, %) | 99.3–99.7 | 99.4–99.8 | 99.5–99.85 | Parameter/machine dependent |
| UTS after HIP (MPa, Ti-6Al-4V ELI) | 920–980 | 930–1000 | 940–1020 | ASTM F3001 ranges; vendor data |
| Powder price (USD/kg, Ti-6Al-4V AM grade) | 80–180 | 85–190 | 85–185 | PSD, sphericity, volume affect |
| Avg reuse cycles (with SPC) | 6–10 | 8~12歳 | 10-15 | With sieving and top-up |
References:
- ISO/ASTM 52907 (metal powder), 52900/52930 (AM fundamentals/qualification): https://www.iso.org
- ASTM F42 standards (F3001 for Ti‑6Al‑4V ELI, F2924 for Ti‑6Al‑4V): https://www.astm.org
- NIST AM resources and data programs: https://www.nist.gov
Latest Research Cases
Case Study 1: Low-Oxygen Ti‑6Al‑4V Powder Improves Fatigue of L-PBF Flight Brackets (2025)
Background: An aerospace Tier‑1 targeted longer HCF life on L‑PBF brackets without changing geometry.
Solution: Switched to low‑O AM powder (≤0.13 wt%), implemented closed-loop sieving/top-up tracking, HIP at 920°C/100 MPa/3 h, and surface finishing to Ra ≤1.5 µm.
Results: As-built density 99.8%; UTS 970–1005 MPa post‑HIP; HCF life +22% at R=0.1; powder oxygen remained ≤0.15 wt% after 12 reuse cycles; scrap reduced 8%.
Case Study 2: EBM Ti‑6Al‑7Nb Cups and Stems for Orthopedics with Validated Porous Lattices (2024)
Background: An implant OEM needed osseointegration and reproducible mechanicals for acetabular cups.
Solution: EBM-printed Ti‑6Al‑7Nb with controlled lattice porosity (55–65%), validated per ASTM F3001/F2924 analogs and ISO 10993 biocompatibility; final HIP to stabilize fatigue.
Results: Shear strength of porous interface +18% vs prior design; fatigue endurance at 10 million cycles met internal spec; CT-based porosity within ±3% of target; zero adverse biocompatibility outcomes.
専門家の意見
- Prof. Hamish L. Fraser, The Ohio State University
Key viewpoint: “Powder cleanliness and interstitial control dominate fatigue performance in AM titanium alloys—HIP helps porosity but not nonmetallic inclusions.” - Dr. Laura Ely, SVP Technology, 3D Systems
Key viewpoint: “Disciplined powder lifecycle management—oxygen trending, PSD control, and batch genealogy—underpins consistent properties for Titanium Alloy Powders in serial production.” - Prof. Peter D. Lee, University College London
Key viewpoint: “Process–structure modeling coupled with in-situ monitoring is making near-net prediction of defects and microstructure feasible for titanium AM routes.”
Citations: University/OEM publications and conference talks: https://mse.osu.edu, https://www.3dsystems.com, https://www.ucl.ac.uk
Practical Tools and Resources
- Standards and specifications:
- ASTM F3001 (Ti‑6Al‑4V ELI AM), ASTM F2924 (Ti‑6Al‑4V), ISO/ASTM 52907 (powder): https://www.astm.org, https://www.iso.org
- Property data and handbooks:
- ASM Handbooks Online (Ti alloys), MMPDS for aerospace allowables: https://www.asminternational.org, https://mmpds.org
- AM process control:
- ASTM F3301 (PBF process control), ISO/ASTM 52930 (qualification): standards portals above
- Powder and materials suppliers:
- Carpenter Additive, Sandvik Osprey, AP&C, Tekna—datasheets with PSD/interstitials
- Modeling and QA:
- Ansys Additive/Netfabb Simulation for distortion/HIP; CT NDE practice (ASTM E1441)
Notes on reliability and sourcing: Specify melt route (e.g., VAR for medical/aero), interstitial limits, PSD, and morphology. Implement SPC on O/N/H and flow, define reuse policies, and maintain lot/build traceability. For critical hardware, include HIP, CT acceptance criteria, and statistically planned coupon testing aligned to end-use standards.
Last updated: 2025-10-15
Changelog: Added 5 targeted FAQs, 2025 trend table with metrics/sources, two recent case studies, expert viewpoints with citations, and a practical tools/resources section specific to Titanium Alloy Powders
Next review date & triggers: 2026-02-15 or earlier if ISO/ASTM standards update, major suppliers change interstitial specs/prices, or new allowables for Ti-6Al-4V/Ti-6Al-7Nb AM are published
シェアする
MET3DP Technology Co., LTDは、中国青島に本社を置く積層造形ソリューションのリーディングプロバイダーです。弊社は3Dプリンティング装置と工業用途の高性能金属粉末を専門としています。
関連記事