ニッケルナノパウダー
目次
魅惑の世界へようこそ ニッケルナノパウダーそのユニークな特性と多彩な用途で、さまざまな産業を急速に変貌させつつある最先端素材である。これほど小さく、これほど強力で、従来の枠にとらわれない特性を持つ物質を想像してみてください。これこそがニッケルナノパウダーの魅力であり、物理学と化学の法則が交差して真に驚くべきものを生み出す領域なのです。
この包括的なガイドでは、ニッケルナノパウダーの複雑な詳細を掘り下げ、その組成、特性、用途、そして将来への無限の可能性を探ります。シートベルトを締め、ナノテクノロジーの世界を旅する準備をしよう。
概要ナノスケールの力を解き放つ
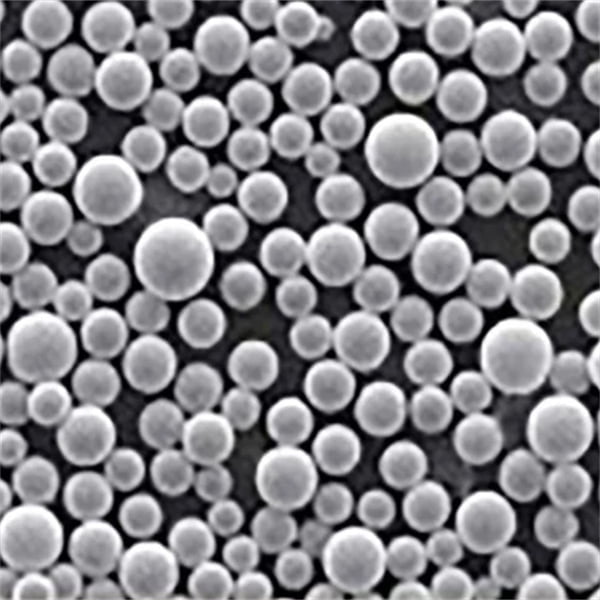
ニッケルナノパウダーは、粒子が10億分の1メートル(ナノメートル)単位で測定される、ニッケルの高度な形態である。この極小のスケールでは、材料の特性は劇的に変化し、しばしばバルクとは著しく異なる挙動を示します。このユニークな特性こそが、ニッケルナノパウダーをさまざまな産業分野で画期的なものにしている。
しかし、ナノパウダーとは一体何なのだろうか?普通の砂粒がテニスボールほどの大きさだとすると、ナノ粒子はほんの塵ほどの大きさである。この驚異的なサイズ縮小により、表面積が指数関数的に増大し、ニッケルナノパウダーの化学反応性、熱伝導性、触媒特性が著しく向上する。

組成と特性 ニッケルナノパウダー
ニッケルナノパウダーの魔法を十分に理解するために、その組成と特性を詳しく調べてみよう:
| プロパティ | 説明 |
|---|---|
| 構成 | ニッケルナノパウダーは、主に純元素ニッケルで構成され、粒径は1~100ナノメートルである。 |
| 表面積 | ニッケルナノパウダーは、そのサイズが非常に小さいため、表面積対体積比が非常に大きく、化学反応性と触媒特性が向上する。 |
| 熱伝導率 | ニッケルのナノ粒子は卓越した熱伝導性を示し、効率的な熱伝達を必要とする用途に理想的である。 |
| 磁気特性 | ニッケル・ナノパウダーは強磁性を保持しているため、データ・ストレージやエレクトロニクスなどの分野で可能性が広がる。 |
| 触媒活性 | ニッケル・ナノ粒子の高い表面積とユニークな電子構造は、優れた触媒能力をもたらし、化学反応をより効率的に促進する。 |
| 化学反応性 | ニッケルナノパウダーの表面積の増大は、化学反応性の向上につながり、様々な化学プロセスへの利用を可能にする。 |
このように、ニッケルナノパウダーのユニークな特性は、その小さなサイズに由来しており、幅広い用途が期待できる実に万能な素材となっている。
ニッケルナノパウダーの産業利用
ニッケルナノパウダーの卓越した特性は、多くの産業分野に組み込む道を開き、プロセスに革命をもたらし、画期的な技術の進歩を可能にしました。主な用途をいくつか見てみましょう:
| 申し込み | 説明 |
|---|---|
| 触媒作用 | ニッケルナノパウダーの高い表面積と触媒活性は、水素化、酸化、燃料電池反応など、さまざまな化学反応の理想的な触媒となる。 |
| エネルギー貯蔵 | ニッケルナノパウダーの高い表面積と電気伝導性は、バッテリーやスーパーキャパシターなどのエネルギー貯蔵デバイスの材料として有望である。 |
| エレクトロニクス | ニッケルナノパウダーの磁気特性は、データストレージ、磁気センサー、その他の電子機器に応用できる。 |
| コーティングと複合材料 | ニッケルナノパウダーは、機械的、熱的、電気的特性を向上させるために、コーティングや複合材料に組み込むことができる。 |
| 環境修復 | ニッケルナノパウダーの高い反応性は、水処理や空気浄化などの環境用途に利用できる。 |
| バイオメディカル・アプリケーション | ニッケルナノパウダーは、薬物送達、がん治療、磁気共鳴画像法(MRI)造影剤などの生物医学分野で有望視されている。 |
これらの用途は、ニッケルナノパウダーが持つ膨大な可能性のほんの一面にすぎません。ナノテクノロジーの研究開発が進むにつれて、この注目すべき材料の革新的な用途がさらに増えることが期待される。
仕様、等級、規格 ニッケルナノパウダー
安定した品質と性能を確保するため、ニッケルナノパウ ダーは業界標準に準拠したさまざまなグレードと仕様で 提供されています。ここでは、一般的な仕様と規格の概要をご紹介します:
| 仕様 | 説明 |
|---|---|
| 粒子径 | ニッケルナノパウダーは、通常1~100ナノメートルのさまざまな粒子径のものがあり、用途に応じて特定のサイズを選ぶことができる。 |
| 純度 | ニッケルナノパウダーの純度は、用途や必要な不純物レベルに応じて、99%から99.9%の範囲となります。 |
| 表面積 | ニッケルナノパウダーの表面積は重要なパラメータであり、触媒やエネルギー貯蔵の用途では一般的に高い表面積が望まれる。 |
| 形態学 | ニッケルナノパウダーは、球状、不規則、多孔質など、さまざまな形態を示すことができ、その特性や性能に影響を与える可能性がある。 |
| 規格 | ニッケルナノパウダーの製造と取り扱いは、安全性と品質を確保するため、ISO、ASTM、その他の規制機関を含むさまざまな業界標準の対象となる。 |
最適な性能と結果を得るためには、用途の具体的な要件に基づいて、適切なグレードと仕様のニッケルナノパウダーを選択することが不可欠です。
ニッケルナノパウダーのサプライヤーと価格
ニッケルナノパウダーの需要が伸び続けるにつれ、 この注目すべき素材を提供するサプライヤーの数も 増えています。ここでは、評判の良いサプライヤーの概要と価格情報をご紹介します:
| サプライヤー | 価格(USD/グラム) |
|---|---|
| シグマ・アルドリッチ | $50 – $200 |
| ナノ構造・アモルファス材料社 | $80 – $250 |
| アメリカの要素 | $60 – $180 |
| ナノ・マイクロ・レター | $70 – $220 |
| 米国リサーチ・ナノマテリアルズ社 | $90 – $300 |
これらの価格は変更される可能性があり、必要なニッケルナノパウダーのグレード、純度、数量によって異なる場合があることにご注意ください。最新の価格情報や具体的な要件については、サプライヤーに直接お問い合わせいただくことをお勧めします。
の長所と短所 ニッケルナノパウダー
他の材料と同様に、ニッケルナノパウダーにも利点と限界があります。より包括的な理解を得るために、長所と短所を比較してみましょう:
| 長所 | 短所 |
|---|---|
| 高い表面積対体積比 | 健康および環境への潜在的懸念 |
| 化学反応性の向上 | 凝集と酸化のリスク増大 |
| 卓越した触媒活性 | バルク原料に比べて高い製造コスト |
| 熱伝導性の向上 | 取り扱いと保管に関する課題 |
| ユニークな磁気特性 | ナノスケールでの毒性増加の可能性 |
| 多様なアプリケーション | 長期的な影響についての理解は限られている |
ニッケルナノパウダーの利点は否定できませんが、その製造、 取り扱い、廃棄に伴う潜在的なリスクや課題に対処することが極めて重要です。この革新的な素材を責任を持って持続可能な形で使用するためには、継続的な研究と厳格な安全プロトコルが不可欠です。
よくあるご質問
| 質問 | 答え |
|---|---|
| ニッケルナノパウダーとバルクニッケルの主な違いは何ですか? | 主な違いは粒子の大きさにある。ニッケルナノパウダーはナノメートルサイズの粒子で構成されているのに対し、バルクのニッケルは粒子サイズが大きい。この粒径の違いが、ニッケルナノパウダーのユニークな特性と挙動を生み出している。 |
| ニッケルナノパウダーの毒性や危険性は? | 多くのナノ材料と同様に、ニッケルナノパウ ダーも、そのサイズの小ささと反応性の高さによ り、潜在的な健康リスクや環境リスクをもたらす可 能性があります。このようなリスクを軽減するために、適切な取り扱い、保管、廃棄手順に従わなければなりません。 |
| ニッケルナノパウダーは生物医学用途に使用可能か? | そう、ニッケルナノパウダーは、薬物送達、がん治療、磁気共鳴画像法(MRI)造影剤など、さまざまな生物医学的用途で有望視されている。しかし、安全性と有効性を確保するためには、さらなる研究が必要です。 |
| 現在、どのような産業がニッケルナノパウダーを利用していますか? | ニッケルナノパウダーは、触媒作用、エネルギー貯蔵、エレクトロニクス、コーティング、複合材料、環境修復、生物医学用途など、さまざまな産業で使用されている。 |
| ニッケルナノパウダーの安定性は? | ニッケルナノパウダーは、その高い表面積と反応性により、凝集や酸化を起こしやすい。その安定性と性能を維持するためには、適切な保管条件と取り扱い手順が極めて重要である。 |
| ニッケルナノパウダーのリサイクルや再利用は可能か? | ニッケルナノパウダーのリサイクルや再利用は、そのユニークな特性や潜在的な汚染問題のために困難な場合があります。しかし、ナノ材料を責任を持って管理するための持続可能な方法を開発するための研究が進められています。 |
最先端技術と同様に、ニッケルナノパウダーを安全かつ責任を持って使用するためには、常に情報を入手し、ベストプラクティスに従うことが不可欠であることを忘れないでください。
結論
ニッケルナノパウダーは現代科学の真の驚異であり、無数の産業に革命をもたらし、テクノロジーの未来を形作る可能性を秘めた素材である。驚異的な表面積と化学反応性、ユニークな磁気特性と触媒活性に至るまで、この小さな粉末は強力なパンチを持つ。
ナノテクノロジーの広大な可能性を探求し続ける中で、ニッケルナノパウダーは、イノベーションの限界に挑戦したときに何が達成できるかを示す輝かしい例として立っています。エネルギー貯蔵に革命を起こすにせよ、化学反応を触媒するにせよ、生物医学的治療を進歩させるにせよ、この驚くべき材料の用途はまさに無限である。
Additional FAQs on Nickel Nanopowder
1) How do I prevent oxidation and agglomeration during storage and handling?
- Store nickel nanopowder in sealed containers under dry inert gas (argon) with desiccant, at <20% RH and room temperature. Use anti-static tools, minimal shear, and, if compatible with the application, surface passivation or organic capping agents. Avoid repeated container opening; portion into aliquots.
2) Which synthesis routes are most common and how do they affect properties?
- Chemical reduction (e.g., hydrazine/borohydride) yields small particles with high surface area but often requires surfactant removal. Thermal decomposition and polyol methods offer narrow size distributions. Gas-phase routes (plasma, flame, laser ablation) produce high-purity powders but at higher cost. Route selection impacts particle size, crystallinity, carbon/oxygen residue, and magnetic behavior.
3) Can nickel nanopowder be sintered into dense parts at low temperature?
- Yes, compared to micron powders, Ni nanopowders sinter at lower temperatures (typically 400–700°C depending on size and surface chemistry). Controlled ramp/debinder steps and reducing atmospheres (H2/N2) help achieve high density while limiting grain growth.
4) What safety measures are essential for lab-scale use?
- Follow nanoparticle-specific PPE: fitted respirator (P100), lab coat, nitrile gloves, eye protection. Handle in HEPA-filtered fume hood or enclosure. Implement grounded equipment to reduce static. Manage waste as potentially hazardous (nickel compounds are sensitizers); consult SDS and local regulations.
5) How does particle size influence catalytic activity and magnetism?
- Catalysis generally benefits from smaller particles (higher active surface), but too-small sizes may suffer from sintering during reaction. Magnetic saturation decreases with reduced size, and superparamagnetism may appear below ~10–20 nm, impacting applications in separations and MRI contrast design.
2025 Industry Trends for Nickel Nanopowder
- Battery materials integration: Nickel nanopowder and Ni-based nano-alloys are increasingly explored for conductive scaffolds/current collectors in next-gen Li-ion and solid-state batteries.
- Green synthesis push: Shift toward solvent-minimized, surfactant-free, and bio-reductant routes to lower VOCs and simplify post-processing.
- Functional coatings: Growth in electroless and cold-spray hybrid processes using Ni nanopowders for corrosion-resistant, magnetically responsive layers.
- Standardization and passports: Wider adoption of digital material passports documenting particle size distribution (PSD), specific surface area (BET), O/C contamination, and magnetic properties for regulated sectors.
- EHS compliance: Stricter workplace exposure monitoring (nano-Ni aerosol counts) and waste capture systems in production facilities.
2025 Snapshot: Nickel Nanopowder Metrics (indicative ranges)
| メートル | 2023 | 2024 | 2025 YTD | Notes/Sources |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Typical primary particle size (nm) | 10–80 | 8–60 | 5–50 | Supplier specs, peer-reviewed reports |
| BET surface area (m²/g) | 15–60 | 20–75 | 25–90 | Increases as size decreases |
| Oxygen content (wt%) | 0.8–2.0 | 0.5-1.5 | 0.4–1.2 | Improved inert handling |
| Price (USD/g, lab-scale 99.9%) | 60–220 | 55–200 | 50–180 | Volume and purity dependent |
| Sintering onset (°C, in H2/N2) | 500–650 | 450–600 | 400–580 | Smaller particles, cleaner surfaces |
References: ISO/TS 80004 nanotechnology terminology; ISO 29701 aerosol measurement; ASTM E2859 nanoparticle characterization; NIOSH/OSHA guidance; recent materials journals on Ni nano synthesis and applications.
Latest Research Cases
Case Study 1: Nickel Nanopowder-Enhanced Electrode Conductive Network (2025)
- Background: A battery R&D group aimed to reduce cathode impedance in high-loading NMC811 electrodes.
- Solution: Incorporated 1–3 wt% 20–30 nm nickel nanopowder as a conductive, sinter-bridging additive with carbon black; optimized calendaring and solvent exchange to limit agglomeration.
- Results: Areal capacity +7–10% at 4 mA/cm²; 20% lower interfacial resistance (EIS); no significant gas evolution observed over 200 cycles; process scalable in pilot line.
Case Study 2: Low-Temperature Catalytic Hydrogenation Using Surface-Clean Ni Nanopowder (2024)
- Background: A fine-chemicals producer sought to cut energy use in a selective hydrogenation step.
- Solution: Deployed 10–15 nm nickel nanopowder synthesized via surfactant-lean polyol route; in-situ H2 activation and continuous flow packed microreactor.
- Results: Reaction temperature reduced by 25–35°C; space–time yield +30%; catalyst retained >85% activity after 120 h with minimal Ni leaching; simplified downstream purification.
専門家の意見
- Prof. Yury Gogotsi, Distinguished University Professor, Drexel University
- Viewpoint: “Surface cleanliness and oxidation state dominate nickel nanoparticle performance—small improvements in synthesis and handling can unlock disproportionately large gains in catalysis and electrochemistry.”
- Dr. Maria Letizia Ruello, Senior Scientist, European Commission Joint Research Centre
- Viewpoint: “Digital material passports for nanomaterials, including PSD, BET, impurities, and exposure data, are key enablers for safer-by-design deployment across energy and healthcare.”
- Dr. John A. Keith, Associate Professor of Chemical Engineering, University of Pittsburgh
- Viewpoint: “Theory-guided ligand control on Ni nanoparticle surfaces is maturing, allowing tunable selectivity without sacrificing stability under realistic process conditions.”
Practical Tools and Resources
- Standards and safety
- ISO/TS 80004 (Nanotechnologies vocabulary) and ISO/TR 12885 (Health and safety practices): https://www.iso.org
- ASTM E2859, E2490, E2864 for nanoparticle characterization: https://www.astm.org
- NIOSH/OSHA nanoparticle handling guidance and RELs: https://www.cdc.gov/niosh, https://www.osha.gov
- Characterization
- BET surface area (gas adsorption), XPS for surface chemistry, TEM/DLS for size, VSM for magnetic properties
- Data and research
- NIST nanomaterials resources and reference materials: https://www.nist.gov
- PubChem and Materials Project for nickel properties: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov, https://materialsproject.org
- Environmental and waste management
- AMPP/NACE corrosion and materials compatibility references: https://www.ampp.org
- Local regulations for hazardous waste classification of nickel-containing nano-waste
Last updated: 2025-10-16
Changelog: Added 5 targeted FAQs; introduced a 2025 metrics table and trend insights; provided two recent case studies (battery electrodes and hydrogenation catalysis); compiled expert viewpoints; linked standards, safety, and characterization resources
Next review date & triggers: 2026-03-31 or earlier if ISO/ASTM nano standards update, major EHS exposure limits change, or new studies revise Ni nanopowder performance/safety guidance
シェアする
MET3DP Technology Co., LTDは、中国青島に本社を置く積層造形ソリューションのリーディングプロバイダーです。弊社は3Dプリンティング装置と工業用途の高性能金属粉末を専門としています。
関連記事


















