ニッケルアルミ合金粉
目次
概要
ニッケルアルミニウム合金粉 は、ニッケル、アルミニウム、その他の合金元素を微粉末状に加工した材料である。高強度、耐食性、熱安定性などの特性を持ち、積層造形、表面コーティング、溶接などの用途に適している。
ニッケル・アルミニウム合金粉末に関するいくつかの重要な詳細:
- 組成 - 主にニッケルとアルミニウムで、チタン、鉄、クロムなどの元素を含む。
- 製造プロセス - 溶融合金のガスまたは水アトマイズ
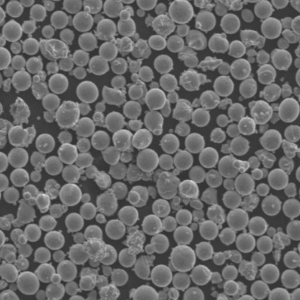
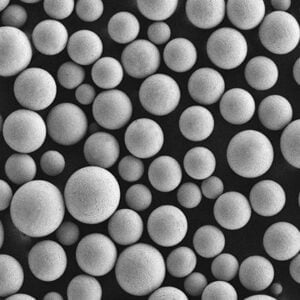
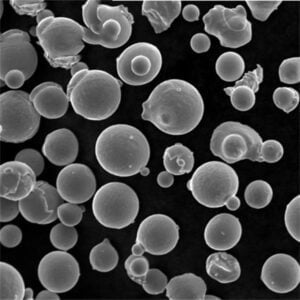
- 粒子形状 - 球状または不規則な形態
- サイズ範囲 - 10ミクロンから150ミクロンまで
- 一般商品名 - NiAl、ニクロム、インコネル、ハステロイ

構成 ニッケルアルミ合金粉
| エレメント | 重量 % |
|---|---|
| ニッケル(Ni) | 30-80% |
| アルミニウム(Al) | 10-50% |
| クロム(Cr) | 5-25% |
| 鉄(Fe) | 0-20% |
| チタン(Ti) | 0-10% |
| コバルト | 0-5% |
| タングステン(W) | 0-5% |
| カーボン(C) | 0-2% |
ニッケル含有量は、耐食性と高温での熱的/構造的安定性をもたらす。アルミニウムは強度と溶接性を向上させる。その他の元素は、硬度、引張強さなどの特定の特性を向上させます。
ニッケルアルミニウム合金粉末の特性
| プロパティ | 特徴 |
|---|---|
| 密度 | 3~8g/cm3前後 |
| 融点 | 1000 - 1400°C |
| 熱伝導率 | 10 - 30 W/mK |
| 電気抵抗率 | 500 - 1000 nΩ.m |
| 熱膨張係数 | 10 - 20 μm/mK |
| 耐酸化性 | 良好、1100℃まで |
| 耐食性 | 様々な媒体で活躍 |
| 透磁率 | 非常に低い |
ニッケル・アルミニウム合金を有用なものにしている主な特性には、高温での高強度、優れた耐食性と耐酸化性、優れた熱伝導性と低膨張性、非磁性などがある。
ニッケルアルミニウム合金粉末の特徴
粒子の形態学
- 球状、不規則、樹枝状粒子
- 衛星粒子が存在する可能性がある
- 多孔質表面構造
粒度分布
- 10ミクロンから150ミクロンまで対応可能
- 一般的なサイズ等級-15-45μm、45-106μmなど。
- 狭い分布が均一な特性を保証
フロー特性
- 一般的に流動性のある粉末
- 球状粒子と不規則な粒子の違い
- カー指数15~25%
パッケージング
- 容器 - プラスチックの瓶/ボトル、ホイルパウチ
- アルゴンまたは窒素雰囲気下で包装
- 含水率 <0.5%
粒子形状、粒度分布、流動特性を制御し、空隙率/サテライトを最小限に抑えることで、信頼性の高い加工と性能を実現します。適切な包装により、取り扱いや保管中の粉体の品質を維持します。
の応用 ニッケルアルミ合金粉
| 産業 | アプリケーション |
|---|---|
| アディティブ・マニュファクチャリング | レーザー焼結、バインダージェッティング |
| 溶接 | ハードフェーシング、補修、磨耗保護 |
| 表面コーティング | 溶射、レーザークラッディング |
| 金属射出成形 | 航空宇宙、自動車部品 |
| ろう付け | 高温ジョイント |
| インベストメント鋳造 | タービンブレード、船舶用部品 |
優れた耐熱性と粉末としての加工性により、ニッケル・アルミニウム合金は、あらゆる産業分野の過酷な環境において、強靭で耐久性のある部品/コーティングの製造に適している。
ニッケルアルミニウムパウダー仕様
| 仕様 | 詳細 |
|---|---|
| 利用可能なグレード | IN718、IN625、HX、ヘインズ214、ヘインズ242 |
| 粒度分布 | -325メッシュ、-100メッシュ、+325メッシュなど |
| 粒子の形態学 | 主に球形 |
| ルース見掛け密度 | 2~5g/cm3前後 |
| タップ密度 | 4~7g/cm3前後 |
| 真の密度 | 7~9g/cm3前後 |
| カスタム合金粉末 | リクエストに応じて |
ニッケル合金粉末は、用途に応じて組成、粒子特性、粒度分布をカスタマイズすることができます。標準グレードは容易に入手可能です。
サプライヤーと価格
| サプライヤー | 価格見積もり |
|---|---|
| サンドビック | kgあたり$50-150 |
| カーペンター・パウダー製品 | kgあたり$40-250 |
| ホーガナス | 1kgあたり$60-220 |
| リオ・ティント・メタル・パウダーズ | $80-350 kgあたり |
| CNPC 粉末グループ | 1kgあたり$35-125 |
価格は、合金グレード、粒度分布、注文量、純度によって異なります。カスタマイズもコストに影響します。大手の多国籍企業や中国のメーカーは、標準および特注のニッケル合金粉末を提供しています。
ニッケル・アルミニウム合金粉末の長所と短所
| メリット | デメリット |
|---|---|
| 優れた高温強度 | 高い材料費 |
| 良好な耐食性 | 一部の合金では成形性に限界がある |
| 高い硬度と耐摩耗性 | 管理された雰囲気での処理が必要 |
| 代替品に比べ軽量 | 析出硬化しやすい |
| 合金添加によるカスタマイズが可能 | リサイクルや再利用が難しい |
ニッケル・アルミニウム粉末は、軽量で耐久性のある金属部品を可能にするが、特殊な粉末加工法の専門知識を必要とする。用途に応じて組成を調整することができます。

ニッケルアルミニウムパウダーと代替品の比較
| プロパティ | ニッケル・アルミニウム合金 | ステンレス鋼 | チタン合金 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 密度 | 低い | より高い | ミディアム |
| コスト | ミディアム | 低い | 高い |
| 最高使用温度 | 1100°C | 850°C | 600°C |
| 耐食性 | 素晴らしい | グッド | 素晴らしい |
| 熱伝導率 | 高い | ミディアム | 低い |
| リードタイム | ミディアム | 低い | 高い |
ニッケルアルミニウムパウダーは、ほとんどの用途において、耐熱性、耐食性、コストのバランスが最も優れています。ステンレス鋼粉末は安価ですが、極端な温度では使用できません。チタン合金粉末はコストが高いが、使用温度が低い。
よくあるご質問
Q: それは何ですか? ニッケルアルミ合金粉 何のために?
A: ニッケルアルミニウム合金粉末は、アディティブ・マニュファクチャリング、溶射、溶接、表面コーティング、インベストメント鋳造などに応用され、高温強度、硬度、耐食性に優れた部品を製造します。
Q: ニッケル・アルミニウム合金粉末は磁性がありますか?
A: いいえ、ニッケル・アルミニウム合金はフェライト系合金とは異なり、透磁率が非常に低く、非磁性であると考えられています。そのため、特定の用途には有利です。
Q: ニッケル・アルミニウム合金粉末の組成は?
A: これらの粉末は30-80%のニッケルと10-50%のアルミニウムをバランスよく含み、要求される特性に基づいてクロム、鉄、チタンなどの元素と合金化されています。
Q: このパウダーにはどのような粒径がありますか?
A: ニッケル・アルミニウム合金粉末は約10ミクロンから150ミクロンまであります。一般的なサイズカットは-325メッシュ(45ミクロン未満)、-100/+325メッシュ(45~150ミクロン)などです。
Q: ニッケルアルミ合金は環境に優しいのですか?
A:ニッケル自体は摂取すると有毒ですが、アルミニウムとその合金は、代替品と比較して環境に優しい素材と考えられており、固体の状態では危険性はありません。再利用とリサイクルにより、環境への影響を最小限に抑えることができます。
Additional FAQs about Nickel Aluminium Alloy Powder
1) What oxygen/nitrogen limits should be specified for AM-grade Nickel Aluminium Alloy Powder?
- Typical gates: O ≤ 0.04–0.06 wt%, N ≤ 0.03 wt%, H ≤ 0.005 wt%. Tighter interstitial control improves weldability, ductility, and reduces cracking in LPBF/DED.
2) Which particle size distribution (PSD) is best for different processes?
- LPBF: 15–45 µm (sometimes 20–63 µm) with high sphericity (≥0.95). Binder Jetting: 20–80 µm for spreadability and green density. DED/Cladding: 45–125 µm for stable feed and larger melt pools.
3) Do Ni–Al powders require special heat treatment after AM?
- Yes. Many Ni–Al systems benefit from solution + aging to precipitate strengthening phases (e.g., γ′/β-NiAl depending on chemistry). Post-build stress relief (800–980°C) and, where applicable, HIP can close porosity and stabilize properties.
4) How much recycled powder can be blended without degrading properties?
- Common practice allows 20–40% recycled powder with PSD re-screening, magnetic separation, and O/N/H tracking per ISO/ASTM 52907. Validate with witness coupons and NDE.
5) Are Ni–Al powders suitable for high-temperature coatings via thermal spray?
- Yes. HVOF/APS using NiAl and NiCrAl (and MCrAlY variants) produce oxidation- and wear-resistant coatings up to ~1000–1100°C, widely used for turbine and exhaust components.
2025 Industry Trends: Nickel Aluminium Alloy Powder
- Productivity-focused PSDs: LPBF platforms increasingly qualify 20–63 µm PSD to boost layer thickness and laser utilization without sacrificing density.
- Oxidation-resistant chemistries: Broader adoption of NiCrAl and MCrAlY derivatives for hot-section coatings and AM/hybrid repairs in aerospace and energy.
- Closed-loop powder reuse: Inline O/N/H sensors and automated sieving raise reuse ratios and lower cost per part.
- Qualification momentum: More OEM material allowables and process windows for Ni–Al and NiCrAl powders in serial production of hot tooling and exhaust components.
- Sustainability: Recycled Ni/Al feedstocks with traceability gain share; EHS programs strengthen powder handling and explosion mitigation.
Table: Indicative 2025 benchmarks for Nickel Aluminium Alloy Powder and AM/Coating performance
| メートル | 2023 Typical | 2025 Typical | 備考 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Powder oxygen (wt%) | 0.05–0.08 | 0.03–0.06 | Improved atomization/packaging |
| Mean sphericity | 0.92–0.95 | 0.94–0.97 | Better melt flow control |
| LPBF as-built density (%) | 99.3–99.6 | 99.5–99.8 | Optimized scan vectors/preheat |
| Post-HIP density (%) | 99.7–99.95 | 99.8–99.99 | For critical fatigue service |
| Oxidation mass gain at 1000°C (mg/cm², 100 h, NiCrAl) | 1.5–2.2 | 0.9–1.4 | Composition + coating process |
| Powder price (USD/kg) | 40–350 | 45–380 | Alloy/cert scope dependent |
Selected references and standards:
- ISO/ASTM 52907 (metal powders for AM), ISO/ASTM 52908 (post-processing)
- ASTM B214 (sieve analysis), ASTM E1409/E1019 (O/N/H)
- Thermal spray: ISO 14919 (feedstock), ISO 14918 (coating qualification); MCrAlY application notes from OEMs
Latest Research Cases
Case Study 1: High-Throughput LPBF of NiCrAl Exhaust Collectors (2025)
Background: An aerospace Tier-1 needed corrosion-/oxidation-resistant exhaust components with shorter lead time.
Solution: Qualified NiCrAl powder (20–63 µm, O=0.035 wt%); 120–150 µm layers with multi-laser stripe strategy; stress relief at 900°C; selective HIP for fatigue-critical zones; final aging.
Results: Build time reduced 18–24% vs 15–45 µm PSD; as-built density 99.6%, post-HIP 99.93%; 1000°C oxidation mass gain 1.1 mg/cm² (100 h); unit cost down 17% at 300 pcs/year.
Case Study 2: HVOF NiAl/NiCrAl Duplex Coating for Turbine Shrouds (2024)
Background: A power-gen operator sought longer maintenance intervals for shrouds exposed to thermal cycling.
Solution: Applied bond coat NiAl followed by NiCrAl top layer via HVOF; surface prep Sa 3; optimized particle size 15–53 µm; post-spray sealing.
Results: TGO growth reduced 22% vs legacy single-coat; erosion resistance improved 30%; outage interval extended from 18 to 24 months; NDE showed porosity <1.5% vol.
専門家の意見
- Dr. Christopher Berndt, Distinguished Professor, Surface Engineering (Swinburne University of Technology)
Viewpoint: “Duplex NiAl/NiCrAl architectures deposited by HVOF deliver superior oxidation and erosion performance—critical for hot-section longevity.” - Dr. Laura Cotterell, AM Materials Lead, Aerospace OEM
Viewpoint: “Careful control of interstitials and PSD—paired with elevated plate preheats—enables thicker LPBF layers for Ni–Al alloys without density penalties, unlocking real throughput gains.” - Prof. David R. Clarke, Materials Scientist, Harvard University
Viewpoint: “The balance between β-NiAl and protective alumina formation remains central—chemistry and heat treatment must be tuned to stabilize the desired oxide scale.”
Practical Tools and Resources
- ISO/ASTM AM standards (52907, 52908) – https://www.astm.org/
- Thermal spray standards (ISO 14919, 14918) – https://www.iso.org/
- NIST AM-Bench data and materials resources – https://www.nist.gov/ambench
- MPIF powder handling and safety guidance – https://www.mpif.org/
- OEM technical notes for MCrAlY/NiAl coatings (GE, Siemens Energy) – https://www.ge.com/ | https://www.siemens-energy.com/
- Porosity/CT analysis toolkits (ITK-SNAP, pyVista) – https://www.itksnap.org/ | https://github.com/pyvista/pyvista
- Powder property measurement methods (Hall/Carney flow, tap density): ASTM B213/B212/B527 – https://www.astm.org/
SEO tip: Use keyword variations such as “Nickel Aluminium Alloy Powder for LPBF,” “NiCrAl thermal spray powder,” and “β‑NiAl oxidation-resistant coatings” in subheadings and internal links to strengthen topical relevance.
Last updated: 2025-10-14
Changelog: Added 5 FAQs; inserted 2025 benchmarks/trends table; provided two recent case studies; included expert viewpoints; curated standards/resources; added SEO keyword usage tip
Next review date & triggers: 2026-04-15 or earlier if ISO/ASTM standards update, major Ni/Al price shifts (>15%), or new OEM allowables/oxidation data change recommended PSD/heat-treatment/coating practices
シェアする
MET3DP Technology Co., LTDは、中国青島に本社を置く積層造形ソリューションのリーディングプロバイダーです。弊社は3Dプリンティング装置と工業用途の高性能金属粉末を専門としています。
関連記事