Sfäriska pulver
Innehållsförteckning
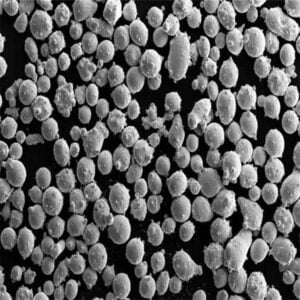
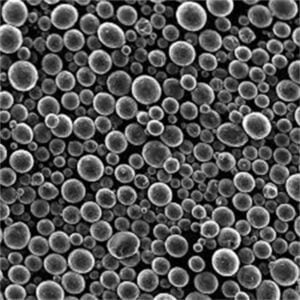
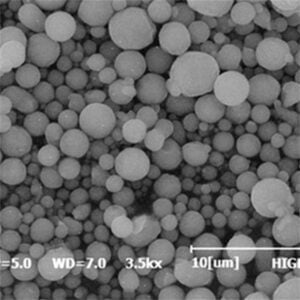
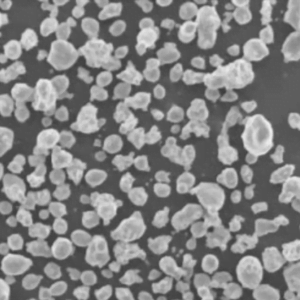
Sfäriska pulver avser finpartikulära material med rundad morfologi som används inom områden som additiv tillverkning av metallpulver, formsprutning av keramik och karbider, läkemedel och avancerad elektroniktillverkning. Deras förbättrade flödes- och packningsegenskaper ger prestandafördelar jämfört med pulver med oregelbunden form.
Översikt av sfäriskt pulver
Konstruerade sfäriska pulver ger överlägsen densitet, flytbarhet, spridningsförmåga, packningseffektivitet och reologiskt beteende, vilket är avgörande för tillverkningsprocesser som kräver homogena och stabila råmaterial.
En noggrann kontroll av partikelstorleksfördelning, enhetlig form, kemisk renhet, mikrostruktur och ytkemi gör det möjligt att skräddarsy prestanda för krävande applikationer inom områden som t.ex:
- Additiv tillverkning
- Formsprutning av metall
- Termiska sprutbeläggningar
- Avancerad keramikbearbetning
- Material för batterier
- Katalysatorer
- Kosmetiska och dentala formuleringar
- Kemisk mekanisk polering
Både submikrona och större sfäriska pulver spelar en avgörande roll i allt från nya produktionstekniker i nanoskala till pressning av stora volymer.

sfäriskt pulver Fastigheter
Den sfäriska morfologin och den släta ytan hos pulverpartiklar minimerar friktionen mellan partiklarna och maximerar densiteten jämfört med icke-sfäriska motsvarigheter. Detta ger upphov till önskvärda egenskaper.
Förbättrad flytbarhet och packningstäthet
Rundade partiklar omorganiseras och glider lättare förbi varandra under tyngdkraft, pneumatisk transport eller omrörning, vilket resulterar i förbättrade flödeshastigheter, mindre klumpbildning och enklare hantering. Bulkdensiteter som närmar sig den verkliga materialdensiteten uppnås också, vilket minimerar tomrummen.
Detta möjliggör snabbare fyllning av formar, matriser och bäddar, vilket är avgörande för ekonomin i pulverbaserade processer. Flödeshastigheter som överstiger 15 s/50 g med hjälp av ett standardtest med Hall-apparaten förväntas.
Smal partikelstorleksfördelning
Kontrollerade produktionstekniker möjliggör sfäriska pulverpartier med snäva storleksfördelningar som sträcker sig från 10-99% och passerar inom 5 μm avvikelser. Denna jämnhet säkerställer ett förutsägbart beteende vid dispensering, blandning, uppvärmning och konsolidering.
Hög sintrad densitet
Sfäriska morfologier möjliggör större förtätning under sintrings- eller fusionsprocesser med mindre porer mellan partiklarna. Detta maximerar uppnåeliga mekaniska egenskaper i färdiga delar. Densiteter över 90% av teoretiska nivåer är typiska.
Förbättrad dispersion
Det lägre förhållandet mellan yta och volym hos sfäriska pulver minskar aggregeringen i förhållande till oregelbundna former när de dispergeras i vätskor för deponering över termisk sprutning, bläckstråleskrivning, glidgjutning eller andra våtrutor. Detta bidrar till jämnhet och stabilitet i beläggningen.
Övriga attribut
- Bättre bibehållen flytbarhet efter exponering för förhöjd temperatur
- Minskad nötning och minskat slitage på utrustningen över tid
- Mer kontrollerade elektriska resistiviteter och defekter
- Jämn krympning och dimensionell precision
sfäriskt pulver Produktionsmetoder
Genom att tillföra tillräcklig kinetisk energi till smälta materialströmmar möjliggörs ytspänningsdriven uppdelning i finfördelade droppar som stelnar till pulverpartiklar. Styrning av processförhållandena avgör de slutliga sfäriska pulveregenskaperna.
Atomisering av gas
Höghastighetsstrålar av inert gas träffar metallsmältor och sönderdelar dem i fina droppar som snabbt kyls till rundade fasta pulver när de lämnar finfördelningskammaren. Används för reaktiva legeringar som titan, nickel och järnbaserade material.
Atomisering av vatten
Liknande koncept men med vatten som smältbrytande medium. Lägre kylhastigheter än gasmetoder men högre utbyte och lägre driftskostnader passar bättre för legeringar med högre smältpunkt som stål och superlegeringar när lägre pulverkvalitet kan accepteras.
Process med roterande elektrod och plasma (PREP)
En elektrisk båge smälter spetsarna på roterande trådar med hög renhetsgrad som sönderdelas till sfärer som kyls i en ström av inert gas som dras in i plasmastrålen. Högt kontrollerade förhållanden möjliggör täta fördelningar. Används för reaktiva metaller som aluminium och magnesium.
Smältgasatomisering med elektrodinduktion (EIGA)
Kombinerar smältning av trådelektroder med induktionsspole med tätt placerade gasmunstycken som möjliggör mycket snabb släckning av framväxande droppar. Bäst för att producera mycket enhetliga sfäriska metallpulver i nano- och submikronstorlek med skräddarsydda legeringskemier.
Sol-gel-behandling
Kemiska metoder gör det möjligt att fälla ut ultrafina partiklar från flytande prekursorer, som sedan kalcineras och mals till formoptimerade pulver. Används för keramik, oxider och karbider som kräver renhet och dimensioner i nanoskala.
Andra metoder
Spraytorkning, kondensationsreaktioner, emulgering, kavitationsbaserad teknik, kemisk ångdeponering, elektrodeponering och solid state-reaktioner erbjuder specialiserade metoder för sfäriska metall-, keramik- och polymerpartiklar.
sfäriskt pulver Material och storlekar
De vanligaste sfäriska pulvermaterialen omfattar metaller, keramer, polymerer och speciallegeringar - med partikelstorlekar från nanometerskala till över 100 mikrometer.
| Materialklass | Material | Storleksintervall |
|---|---|---|
| Metaller | Rostfria stål, verktygsstål, superlegeringar, titan, volfram, kobolt, krom, koppar, aluminium | 0,5 μm - 150 μm |
| Keramik | Aluminiumoxid, zirkoniumoxid, karbider som WC eller SiC | 0,01 μm - 45 μm |
| Polymerer | Nylon, PEEK, PEKK, Ultem | 5 μm - 100 μm |
| Övriga | Glas, magnetiska legeringar, legeringar med formminne, legeringar med hög entropi | 0,1 μm - 50 μm |
Dyrare legerings-, keramik- och specialpulver tenderar att få mindre partikeldimensioner för högpresterande additiv tillverkning, medan processer med högre genomströmning fungerar bättre med större, nästan enkla storleksfördelningar.
Klassificering av storlek
| Grupp | Intervall för partikeldiameter |
|---|---|
| Ultrafin | < 20 μm |
| Fina | 20-45 μm |
| Medium | 45-105 μm |
| Grov | 105-150 μm |
Egenskaper som medelstorlek, sfäriskhet, kemisk renhet, morfologi, mikrostruktur, flöde och tappdensitet bekräftas mot applikationskrav och bearbetningsbehov.
sfäriskt pulver av Viktiga tillämpningar
Additiv tillverkning
Selektiv lasersmältning, elektronstrålesmältning och bindemedelsstrålning ger ultrafina sfäriska pulver med kontrollerade storleksfördelningar och sammansättningar som möjliggör tillverkning av komplexa metalldelar direkt från CAD-data.
Formsprutning av metall (MIM)
Sfäriska pulver blandade med bindemedel formsprutas och sintras sedan för att tillverka små, komplicerade detaljer i stora volymer. Här kombineras plastgjutningens möjligheter till nära nog nätform och ytbehandling med högpresterande egenskaper hos material som rostfritt stål, verktygsstål och superlegeringar.
Termiska sprutbeläggningar
Sfäriska pulver av metall, karbid, oxid och polymer matas genom uppvärmda plasma- eller förbränningsstrålar och skapar beläggningar som är motståndskraftiga mot korrosion, slitage och värme med skräddarsydda mekaniska eller dielektriska egenskaper.
Avancerad keramik
Sfäriska keramiska pulver med snäv storleksfördelning används som utgångsmaterial för tillverkning av högpresterande elektriska, strukturella och eldfasta komponenter via isostatisk kallpressning, glidgjutning, tejpformuleringar och avancerade sintringstekniker som kräver optimerade pulverbäddar.
Andra nischapplikationer
Kosmetiska foundations, dentalpolymerer, lödpastor, bärarpartiklar för katalysatorer, slurry för kemisk mekanisk polering, pulversmidesledare, metalliska glasprekursorer etc. är beroende av sfäriska specialpulver som uppfyller högt ställda krav.
Globala leverantörer av sfäriskt pulver
Ledande materialtillverkare och pulverförädlare i Nord- och Sydamerika, Europa och Asien levererar sfäriska pulver till köpare inom både FoU och kommersiell skala. Priserna varierar mycket beroende på renhet, enhetlighet, storlek, sammansättning och inköpsvolym.
Alternativ för metall och legering
| Företag | Plats |
|---|---|
| Sandvik | Tyskland |
| Rio Tinto Metallpulver | Kanada |
| Höganäs | Sverige |
| Mitsubishi Material | Japan |
| BÖHLER Edelstahl | Österrike |
| AMETEK | USA |
| Tekna | Kanada |
Keramik-, karbid- och oxidpulver
| Företag | Plats |
|---|---|
| HC Starck | Tyskland |
| Reade Avancerade Material | USA |
| Inframat Avancerade Material | USA |
| Stanford Avancerade Material | USA |
| Nanoshel | USA |
Andra leverantörer av sfäriska pulver tillgodose tillämpningar inom läkemedel, polymerer, magnetiska material, batterimaterial, katalysatorer och elektroniska prekursorer.
sfäriskt pulver Kostnadsanalys
Sfäriska pulver av metall och legeringar varierar från $5/kg för vanligt aluminium och järn till $500/kg för specialkvaliteter.
Kostnaden beror i hög grad på:
- Grundsammansättning (t.ex. rostfritt stål kostar 2-4x kolstål)
- Produktionsmetod (gas- vs. vattenatomisering, plasma vs. förbränning)
- Enhetlig storleksfördelning
- Morfologi och partikelstruktur
- Inköpskvantitet och önskade ledtider
- Renhetsnivåer och konsistens
Priserna på sfäriskt pulver av keramik/karbid varierar från $50/kg till $5000/kg baserat på:
- Material (kiseldioxid vs litiumaluminat, WC vs HfC)
- Renhet - Från 98 till 99,999%
- Partikeldimensioner - nanoskala kostar 100 gånger mer
- Ordervolym
- Yta
- Kalcinering/malningsgrad
- Agglomerationstendenser
- Fuktkänslighet
Stordriftsfördelar gäller för bulkbeställningar medan kundanpassade partier ger en premie. Lägre pulverkonsistens minskar också kostnaderna.
Standarder och specifikationer
Konstruerade sfäriska pulver måste uppfylla applikationsbehov och standardiserade testmetoder som kontrollerar egenskaper som:
| Parameter | Vanliga metoder |
|---|---|
| Fördelning av partikelstorlek | Laserdiffraktion, sedimentering, siktning |
| Partikelns form | Svepelektronmikroskopi, optisk utvärdering |
| Flödbarhet för pulver | Hall flödesmätare tratt |
| Tappdensitet | Standardapparat för droppdensitet |
| Verifiering av sammansättning | ICP-OES/MS, FTIR, XRF, GDMS |
| Morfologi | SEM, TEM |
| Specifik ytarea | BET kväveadsorption |
| Pulverbäddens densitet | Geometriska mätningar |
| Termisk analys | TGA, DSC |
Internationella (ISO), nationella (ASTM) och branschorganens riktlinjer omfattar godtagbara mättekniker som är tillämpliga på metalliska, keramiska, elektroniska och andra Sfäriska pulver.
Genom att använda konsekventa metoder mot standardiserade krav säkerställs tillförlitlig prestanda när de används i strikta tillverkningsprocesser och livskritiska applikationer.
Fördelar kontra begränsningar
| Fördelar | Nackdelar |
|---|---|
| - Förutsägbart packnings- och flödesbeteende | - Högre kostnad jämfört med krossat/oregelbundet pulver |
| - Förbättrad produktkvalitet och processutbyte | - Begränsad förmåga att klara extremt höga temperaturer för metaller |
| - Bättre kontroll över mikrostruktur och prestanda | - Agglomerationstendens i vissa fall |
| - Anpassningsbar storleksfördelning | - Kontaminerings- och konsistenrisker |
| - Flexibilitet i sammansättningen med legeringar | - Partikelinbäddning under deponeringsstegen |
| - Högre uppnåelig sintrad densitet | - Särskilda försiktighetsåtgärder vid hantering |
| - Minskad porositet | - Siktning eller klassificering behövs ofta |
| - Gäller för komponenter i flera material | - Utmaningar med bibehållen form i de minsta storlekarna |
| - Lämpar sig för tillverkning av små dimensioner och tunna skikt |
Balansera fördelar mot begränsningar baserat på bearbetningsväg och avsedd pulverapplikation.

VANLIGA FRÅGOR
F: Vad är den största fördelen med sfäriska pulver jämfört med oregelbundet formade pulver?
S: Sfäriska pulver flyter mycket lättare på grund av lägre friktion mellan partiklarna, vilket möjliggör snabbare formfyllning, tryckning, sprutning och komprimering, vilket är avgörande för precisionstillverkning - vilket ökar produktionstakten, kvaliteten och tillförlitligheten. Deras rundade form möjliggör också högre sintrad densitet.
F: Hur små sfäriska metallpulver kan tillverkas?
S: Atomiseringstekniker med inert gas gör det möjligt att tillverka pulver av rostfritt stål ned till 10 mikrometer, medan kopparlegeringar med gasatomisering kan nå en diameter på 5 mikrometer. Specialiserade legeringsblandningar med flera komponenter har tillverkats under 20 nm via mini-emulsionskemi.
F: Vad bestämmer sfäriska pulverstorleksfördelningar?
A: Munstycksdesign, gasflödesdynamik, instabilitet i smältströmmen och snabbkylningskinetik styr droppbildning och stelningsfysik i gasatomiseringsprocesser - vilket kräver modellering och noggrann parametertestning för att optimera fördelningen.
F: Vilket är billigast - gas- eller vattenatomiserade sfäriska pulver?
S: Vattenatomisering har 5-10 gånger lägre driftskostnader än gasatomisering men ger mer oregelbundna pulver som kräver efterföljande bearbetning för att förbättra sfäriskhet och fördelning. Kostnadsfördelen beror alltså på vilken kvalitetsnivå som är acceptabel för applikationen.
F: Kan du göra sfäriska pulverpartiklar i en storlek?
S: Våta kemiska produktionsvägar tillåter mycket snäva fördelningar ner till relativa standardavvikelser under 5% av medelpartikelstorleken men kvarvarande satellitfraktioner leder till viss spridning. Specialiserad klassificering eller siktning hjälper till att isolera primära modala fraktioner om det behövs.
Dela på
MET3DP Technology Co, LTD är en ledande leverantör av lösningar för additiv tillverkning med huvudkontor i Qingdao, Kina. Vårt företag är specialiserat på 3D-utskriftsutrustning och högpresterande metallpulver för industriella tillämpningar.
Förfrågan för att få bästa pris och anpassad lösning för ditt företag!
Relaterade artiklar

Högpresterande segment för munstycksvingar: Revolutionerande turbineffektivitet med 3D-utskrift i metall
Läs mer "Om Met3DP
Senaste uppdateringen
Vår produkt
KONTAKTA OSS
Har du några frågor? Skicka oss meddelande nu! Vi kommer att betjäna din begäran med ett helt team efter att ha fått ditt meddelande.

Metallpulver för 3D-printing och additiv tillverkning
FÖRETAG
PRODUKT
cONTACT INFO
- Qingdao City, Shandong, Kina
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- +86 19116340731