ASTM F136: 究極のガイド
目次
読者の皆さん、ようこそ!本日は、この魅惑的な世界を深く掘り下げていこう。 ASTM F136.さて、"ASTM F136っていったい何?"と思われるかもしれません。ご心配なく。この広範なガイドを読み終える頃には、この注目すべき素材について知っておくべきことがすべてわかるでしょう。
ASTM F136の概要
ASTM F136は、チタン6Al-4V ELI(Extra Low Interstitial)としても知られ、医療分野での使用が広く認められているチタン合金です。この合金は生体適合性、耐食性、優れた機械的特性により際立っており、医療用インプラント、手術器具、その他の重要な用途に最適な材料となっています。
ASTM F136の主な詳細
- 構成:チタン、アルミニウム、バナジウム
- プロパティ:高強度、軽量、耐食性、生体適合性
- アプリケーション:医療用インプラント、手術器具、航空宇宙部品
- 仕様:ASTM F136規格は、合金の品質と特性を定義している。
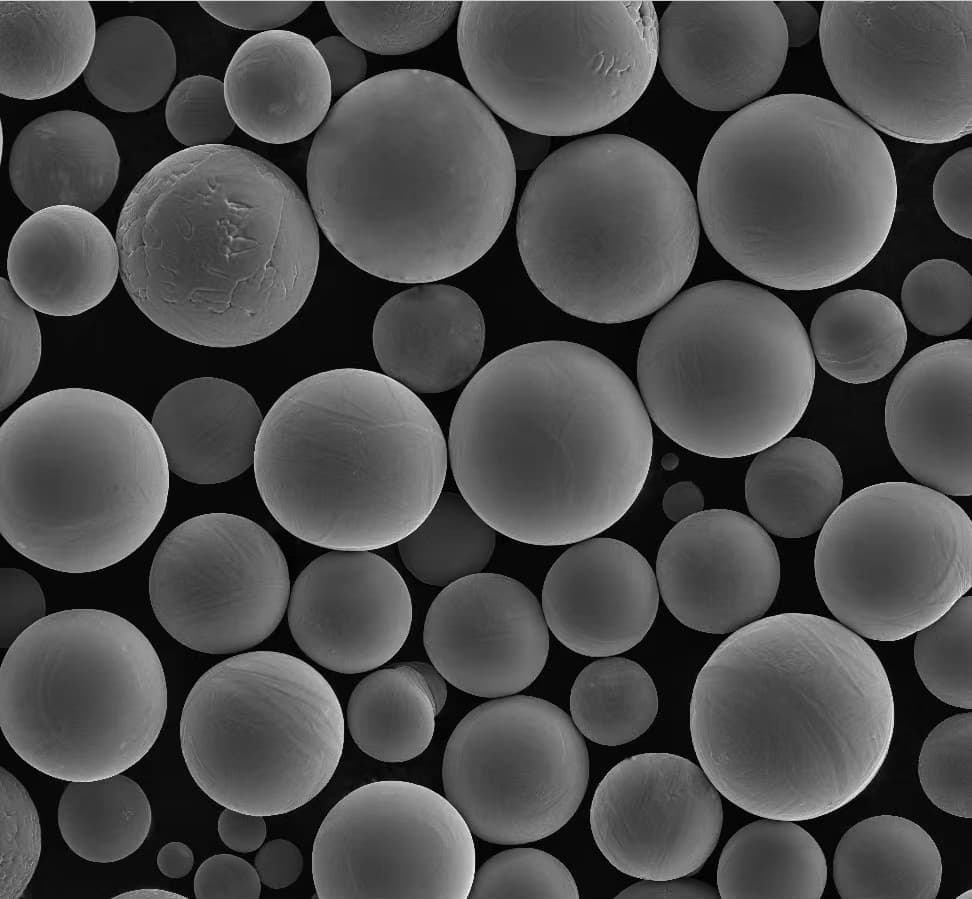
種類、組成、特性、特徴
ASTM F136を真に理解するためには、その組成、特性、特徴を理解することが不可欠です。それを分解してみよう:
ASTM F136の組成
| エレメント | パーセント |
|---|---|
| チタン(Ti) | 88 – 90% |
| アルミニウム(Al) | 5.5 – 6.75% |
| バナジウム (V) | 3.5 – 4.5% |
| 酸素 (O) | ≤ 0.13% |
| カーボン(C) | ≤ 0.08% |
| 窒素(N) | ≤ 0.05% |
| 水素(H) | ≤ 0.0125% |
| 鉄(Fe) | ≤ 0.25% |
ASTM F136の特性と特徴
| プロパティ | 説明 |
|---|---|
| 密度 | 4.43 g/cm³ |
| ヤング率 | 110 GPa |
| 極限引張強さ | 860 MPa |
| 降伏強度 | 795 MPa |
| 破断伸度 | 15% |
| 硬度 | 300 HV |
| 熱伝導率 | 6.7 W/m-K |
| 電気抵抗率 | 1.7 µΩ-m |
| 生体適合性 | 優秀(ASTM F136規格に適合) |
| 耐食性 | 高い(体液や化学薬品に強い) |
の応用 ASTM F136
ASTM F136は、主に医療分野で使用されているが、そのユニークな特性により他の産業にも応用されている。
医療用途
| 申し込み | 説明 |
|---|---|
| 整形外科インプラント | 人工股関節、膝関節、脊椎インプラント |
| 歯科インプラント | 歯根、支台、ブリッジ |
| 手術器具 | メス、鉗子、リトラクタ |
| 頭蓋顔面インプラント | 再建手術用プレート、スクリュー |
| 心臓血管インプラント | 心臓弁、ステント |
航空宇宙用途
| 申し込み | 説明 |
|---|---|
| 航空宇宙用ファスナー | 航空機組立用ボルト、ナット、ネジ |
| 構造部品 | 機体構造、着陸装置 |
| エンジン部品 | タービンブレード、コンプレッサーディスク |
産業用途
| 申し込み | 説明 |
|---|---|
| 化学処理 | 化学プラント用機器、リアクター |
| マリンアプリケーション | 造船、海洋掘削部品 |
| スポーツ用品 | 高性能自転車、ゴルフクラブ |
仕様、サイズ、等級、規格
ASTM F136を使用する場合、材料の完全性と性能を保証するために、指定された規格を遵守することが極めて重要です。
仕様と規格
| スタンダード | 説明 |
|---|---|
| ASTM F136 | 外科用インプラント用のチタン-6アルミニウム-4バナジウムELI(超低間充てん)合金の標準仕様。 |
サイズと等級
| サイズ範囲 | 説明 |
|---|---|
| バー | 直径:6mm~150mm |
| シーツ | 厚さ:0.5mm~5mm |
| プレート | 厚さ:5mm~100mm |
| ワイヤー | 直径:0.1mm~10mm |
| グレード | グレード23(Ti 6Al-4V ELI) |
サプライヤーと価格詳細
高品質のASTM F136材料を確実に入手するには、適切なサプライヤーを見つけることが重要です。ここでは、評判の良いサプライヤーとその価格詳細をご紹介します。
トップサプライヤー
| サプライヤー | 説明 | 価格(概算) |
|---|---|---|
| ATIメタルズ | チタンをはじめとする特殊素材の製造・供給で世界をリード。 | $50〜$100/kg |
| ティメット(チタン金属株式会社) | 航空宇宙および医療用途を中心としたチタン系製品の大手メーカー。 | 1kgあたり$60~$110 |
| VSMPO-AVISMA | 世界最大のチタンメーカーで、高品質のチタン合金を供給。 | 1kgあたり$55~$105 |
| 東邦チタニウム | 高純度で先進的なチタン製品で知られる日本のサプライヤー。 | 1kgあたり$65~$115 |
| アルカムAB(GEアディティブ) | アディティブ・マニュファクチャリング(積層造形)および医療・航空宇宙分野向け先端材料の専門メーカー。 | 1kgあたり$70~$120 |
長所と短所を比較する
ASTM F136をお客様の用途に使用することを検討する際には、その利点と限界を比較検討することが不可欠です。
ASTM F136の利点
| メリット | 説明 |
|---|---|
| 生体適合性 | 人体組織との適合性に優れ、医療用インプラントに最適。 |
| 耐食性 | 体液や化学薬品に対する耐性が高く、長期間使用できる。 |
| 機械的特性 | 強度重量比が高く、丈夫でありながら軽量。 |
| 汎用性 | 医療から航空宇宙まで幅広い用途に適している。 |
ASTM F136の限界
| 制限 | 説明 |
|---|---|
| コスト | 他の素材に比べて比較的高価。 |
| 加工性 | 機械加工には特殊な設備と技術が必要。 |
| 空室状況 | 需要が高く、製造工程が特殊なため、リードタイムが長くなる場合がある。 |
特定金属粉末モデル
アディティブ・マニュファクチャリングと先端アプリケーションの領域では、ASTM F136のいくつかの金属粉末モデルが際立っている。以下はその顕著な例である:
メタルパウダーのトップモデル
| モデル | 説明 |
|---|---|
| Arcam ABによるTi64 ELI | 電子ビーム溶解(EBM)技術用の高純度チタン粉末。 |
| TLSテクニックのTLS Ti6Al4V ELI | 選択的レーザー溶融(SLM)およびその他の積層造形プロセス用の高品質粉末。 |
| GEアディティブのAP&C Ti-6Al-4V ELI | 付加製造における最適な流動性と充填密度を実現するために設計された球状チタン粉末。 |
| カーペンターアディティブ製Ti-6Al-4V ELI | 様々な3Dプリンティング技術に対応する高性能パウダーで、安定した品質と特性を保証します。 |
| テクナ製AMTi-6Al-4V ELI | アディティブ・マニュファクチャリングで優れた性能を発揮するプラズマアトマイズされたチタン粉末。 |
| エリコン・メトコ製Ti-6Al-4V ELI | レーザークラッディング、アディティブマニュファクチャリング、その他の先端プロセス用の高品質パウダー。 |
| LPWテクノロジーによるTi-6Al-4V ELI | 航空宇宙および医療分野での高強度、軽量用途のために設計された粉末。 |
| プラクセア・サーフェス・テクノロジーズ社のTi-6Al-4V ELI | 要求の厳しい積層造形用途向けの安定した高純度パウダー。 |
| サンドビック製Ti-6Al-4V ELI | 優れた機械的特性と生体適合性を保証する積層造形用プレミアムチタン粉末。 |
| レニショーによる Ti-6Al-4V ELI | 幅広い積層造形技術に対応し、高い性能と信頼性を提供する万能粉末。 |
金属粉末モデルの比較分析
十分な情報に基づいた決断をするために、これらの金属粉モデルをさまざまなパラメーターに基づいて比較してみよう。
パフォーマンス比較
| モデル | 流動性 | 梱包密度 | 純度レベル | 価格帯 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arcam ABによるTi64 ELI | 素晴らしい | 高い | ウルトラハイ | $100〜$150/kg |
| TLSテクニックのTLS Ti6Al4V ELI | 非常に良い | 高い | 高い | $90〜$140/kg |
| GEアディティブのAP&C Ti-6Al-4V ELI | 素晴らしい | 非常に高い | ウルトラハイ | $110〜$160/kg |
| カーペンターアディティブ製Ti-6Al-4V ELI | 非常に良い | 高い | 高い | $95〜$145/kg |
| テクナ製AMTi-6Al-4V ELI | 素晴らしい | 高い | ウルトラハイ | $105〜$155/kg |
| エリコン・メトコ製Ti-6Al-4V ELI | 非常に良い | 高い | 高い | $100〜$150/kg |
| LPWテクノロジーによるTi-6Al-4V ELI | 素晴らしい | 非常に高い | ウルトラハイ | $110〜$160/kg |
| プラクセア・サーフェス・テクノロジーズ社のTi-6Al-4V ELI | 非常に良い | 高い | 高い | $95〜$145/kg |
| サンドビック製Ti-6Al-4V ELI | 素晴らしい | 非常に高い | ウルトラハイ | $110〜$160/kg |
| レニショーによる Ti-6Al-4V ELI | 素晴らしい | 高い | 高い | $100〜$150/kg |
長所と短所の比較
| モデル | 長所 | 短所 |
|---|---|---|
| Arcam ABによるTi64 ELI | 高純度、優れた流動性、信頼性の高い性能 | いくつかの代替品に比べ高コスト |
| TLSテクニックのTLS Ti6Al4V ELI | 安定した品質、優れた価格性能比 | 他社製品に比べ、充填密度がやや低い |
| GEアディティブのAP&C Ti-6Al-4V ELI | 超高純度、高充填密度 | 高価格帯 |
| カーペンターアディティブ製Ti-6Al-4V ELI | 高性能、安定した特性 | 中~高価格帯 |
| テクナ製AMTi-6Al-4V ELI | 優れた性能、高純度、積層造形に最適 | より高いコスト |
| エリコン・メトコ製Ti-6Al-4V ELI | 信頼できる性能、良好な流動性 | 中~高価格帯 |
| LPWテクノロジーによるTi-6Al-4V ELI | 超高純度、優れた充填密度 | 高価格帯 |
| プラクセア・サーフェス・テクノロジーズ社のTi-6Al-4V ELI | 安定した品質、優れたパフォーマンス | 中~高価格帯 |
| サンドビック製Ti-6Al-4V ELI | プレミアム品質、優れた機械的特性 | より高いコスト |
| レニショーによる Ti-6Al-4V ELI | 高い信頼性、多彩なアプリケーション | 中~高価格帯 |
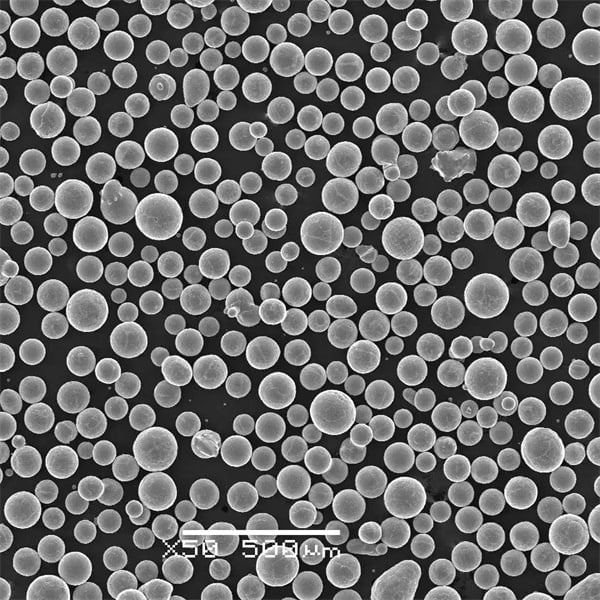
よくあるご質問
ASTM F136とは何の略ですか?
ASTM F136は、主に外科用インプラントに使用されるチタン-6アルミニウム-4バナジウム(ELI)合金の標準仕様です。
なぜASTM F136が医療用インプラントに好まれるのですか?
ASTM F136は、その優れた生体適合性、耐食性、高い機械的強度により、医療用インプラントに好まれています。これらの特性により、この材料は人体の過酷な環境に耐え、長期間にわたって機能を維持することができます。
ASTM F136の主要要素は何ですか?
ASTM F136の主要元素は、チタン(Ti)、アルミニウム(Al)、バナジウム(V)であり、チタンが主成分である。
ASTM F136は通常どのように製造されるのですか?
ASTM F136は、鍛造、圧延、熱処理を含む様々な工程を経て製造され、所望の機械的特性を達成し、規格仕様に適合することを保証する。
医療用以外にASTM F136が使用されている場所はありますか?
ASTM F136は医療分野だけでなく、航空宇宙分野の構造部品、ファスナー、エンジン部品や、化学処理、海洋工学などの工業用途にも使用されています。
ASTM F136は3Dプリントに適していますか?
ASTM F136は積層造形、特に電子ビーム溶解(EBM)や選択的レーザー溶解(SLM)のような3Dプリンティング技術用のチタン粉末として広く使用されています。
ASTM F136は高価ですか?
ASTM F136は、その高い性能と特殊な用途のため、他の材料よりも比較的高価であり、価格は通常、供給業者と形状(棒、シート、パウダーなど)に応じて、1kgあたり$50から$160の範囲である。
結論
これで完成だ。 ASTM F136!このガイドでは、ASTM F136の組成や特性から、その用途、仕様、さらには高度な製造のための様々な金属粉末モデルについて深く掘り下げています。ASTM F136を医療用インプラント、航空宇宙部品、その他あらゆる高性能用途に使用することを検討されている場合、本ガイドブックはあなたの頼りになる情報源となるはずです。
シェアする
MET3DP Technology Co., LTDは、中国青島に本社を置く積層造形ソリューションのリーディングプロバイダーです。弊社は3Dプリンティング装置と工業用途の高性能金属粉末を専門としています。
関連記事
Met3DPについて
最新情報
製品

3Dプリンティングと積層造形用金属粉末