ニッケル超合金: 種類, 価格, 供給者
目次
ジェットエンジンの灼熱やガスタービンの強烈な圧力に耐えうるほど強い素材を想像してみてほしい。この同じ材料が、比類のない精度で複雑な部品に成形されることを想像してみてください。これはSFではなく、ニッケル超合金の現実なのです。 3Dプリンティング.
ニッケル超合金は、高温での卓越した特性で有名な金属材料の一種です。強度、耐酸化性、耐クリープ性を独自にブレンドしているため、航空宇宙、エネルギー生産、その他の高性能産業における要求の厳しい用途に最適です。3Dプリンティング技術は、この驚くべき材料の真の可能性を解き放ち、これまでにない自由な設計で複雑かつ軽量なコンポーネントを作成することを可能にしています。

3Dプリンティング用ニッケル超合金のパワーを解き明かす
ニッケル超合金は、同じようには作られていません。それぞれの配合は、元素の特定の組み合わせを誇り、その結果、ユニークな一連の特性が得られます。3Dプリンティングにおけるニッケル超合金の能力を理解するために、その詳細を掘り下げてみよう:
3Dプリンティング用ニッケル超合金の組成と特性
| エレメント | 機能 | 物件への影響 |
|---|---|---|
| ニッケル(Ni) | ベースメタル | 強度と延性の基礎を提供する |
| クロム(Cr) | 主な強化要素 | 耐酸化性と高温強度を高める |
| コバルト | ソリッド・ソリューション強化 | 高温性能と耐クリープ性を向上 |
| アルミニウム(Al) | 軽量化剤 | 強度を維持しながら軽量化 |
| チタン(Ti) | 穀物精製 | 機械的特性を向上させるために微細構造を制御 |
| タンタル (Ta) | 超硬フォーマー | 高温強度と耐酸化性の向上 |
| タングステン(W) | 超硬フォーマー | 高温で素材を強化する |
3Dプリンティングにおけるニッケル超合金の用途
| 産業 | 申し込み | 3Dプリンティングのメリット |
|---|---|---|
| 航空宇宙 | タービンブレード、燃焼器ライナー、熱交換器 | エンジンの効率と性能を向上させる軽量で複雑な設計 |
| エネルギー生産 | ガスタービン部品、ヒートシールド | 軽量化と設計の柔軟性で効率的な発電を実現 |
| 化学処理 | リアクター、熱交換器 | 過酷な環境に対応する耐腐食性カスタム設計コンポーネント |
| 医療機器 | インプラント、手術器具 | 複雑な形状の個別化医療ソリューションのための生体適合性オプション |
3Dプリンティング用ニッケル超合金の仕様、サイズ、グレードおよび規格
ニッケル超合金粉末は、その用途の多様性から、様々な仕様があります。以下は、考慮すべき主な要因の内訳です:
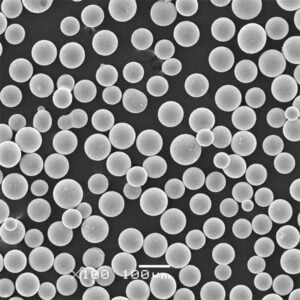
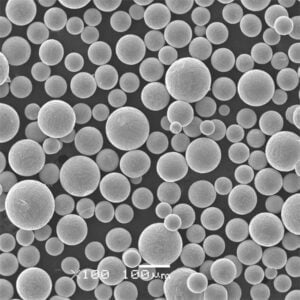
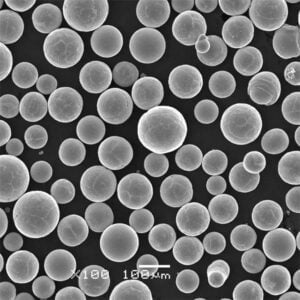
- 粒度分布: 流動性、印刷適性、最終部品の特性に影響する。一般的な範囲は15-45ミクロンと45-90ミクロンである。
- 粉体の流動性: 印刷工程でパウダーが均一に広がる能力に影響する。良好な流動性は、安定した層形成を保証する。
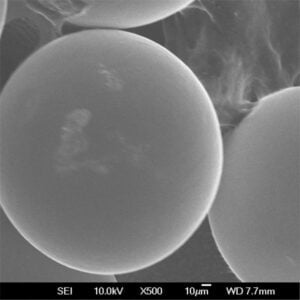
- 球形性と形態性: パウダーの形状は、充填密度と印刷中のレーザー吸収に影響する。最適な結果を得るには球形が好ましい。
- 化学組成: 印刷部品の最終的な特性を決定します。ASTM International (ASTM)やAerospace Material Specifications (AMS)のような特定の規格が、許容される組成を定義しています。
3Dプリンティング用の一般的なニッケル超合金粉末
- AM260S: アディティブ・マニュファクチャリング専用に開発されたAM260S粉末は、卓越した印刷適性と高温能力を備えています。IN718と比較して、AM260Sは高温での優れた耐クリープ性と強度を誇り、要求の厳しい航空宇宙用途の強力な候補となります。
- MarM247 LC: この先進的な合金粉末は、極端な温度での卓越した耐クリープ性と耐酸化性で知られています。MarM247 LCは、これらの点でRene 41をも凌駕しており、ジェットエンジンの次世代タービンブレードや熱間セクション部品に最適です。
- ニッケル合金ヘインズ282 高温強度と良好な溶接性のユニークな組み合わせを提供するヘインズ282パウダーは、性能と加工の容易さの両方を必要とする用途に適した貴重な選択肢です。この材料は、熱交換器、排気システム、およびその他の高温部品に使用されています。
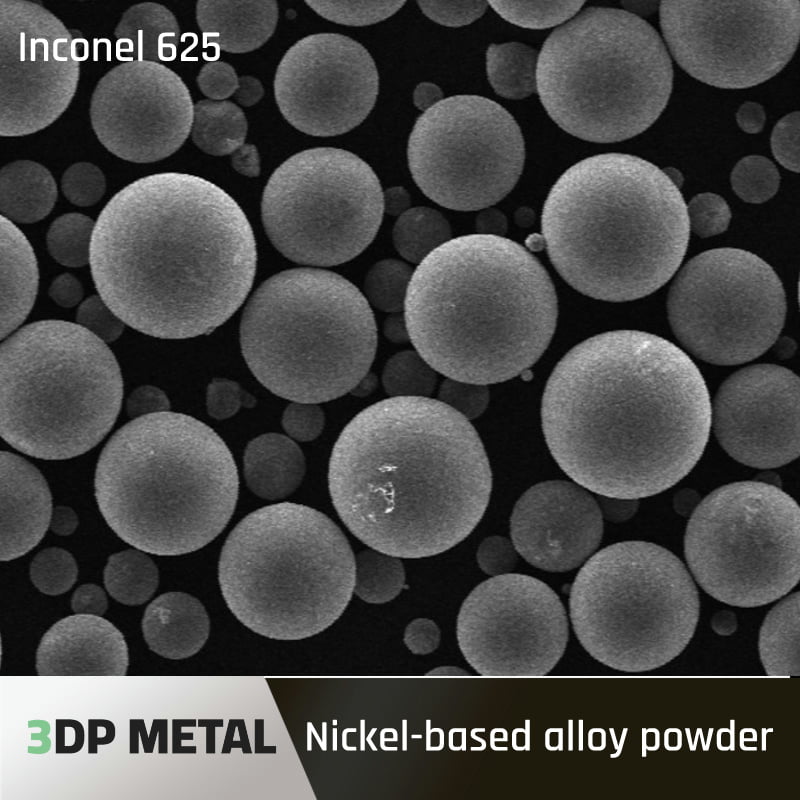
- Met3DP ニッケル超合金粉末: 3Dプリンティング用金属粉末のトップメーカーであるMet3DPは、様々な用途に最適化された高品質のニッケル超合金粉末を提供しています。そのポートフォリオには、IN718やインコネル625のような確立されたオプションに加え、特定の性能ニーズに合わせたより革新的な合金も含まれています。
3Dプリンティング用ニッケル超合金粉末の価格とサプライヤー
ニッケル超合金粉末のコストは、特定の合金、粒径、供給元によって異なります。一般的に、これらの粉末は、複雑な製造工程を伴うため、従来の金属粉末に比べて高価です。ここでは、価格設定の状況を垣間見ることができます:
- 価格帯 IN718やインコネル625のような一般的に使用される合金は、キログラム当たり$100-300の価格帯を見込んでください。MarM247 LCのようなより高度なオプションは、その特殊な特性のため、より高い価格帯に達する可能性があります。
- サプライヤー 3Dプリンティング用の高品質ニッケル超合金粉末を供給しているのは、評判の高い企業数社です。著名なところでは、EOS GmbH、Elementum 3D、SLM Solutions、そして前述のMet3DPなどがある。
3Dプリンティング用ニッケル超合金の長所と短所
メリット
- 卓越した高温性能: ニッケル超合金は、他の材料では破損するような温度でも強度と完全性を維持するため、要求の厳しい用途に最適です。
- デザインの自由と軽量化: 3Dプリンティングは、軽量化された複雑な形状の可能性を解き放ち、航空宇宙やその他の重量が重要な産業における効率向上につながる。
- 廃棄物の削減とニアネットシェイプ製造: 従来の減法的製造技術と比較して、3Dプリンティングは材料の無駄を最小限に抑え、ほぼネットシェイプの製造を可能にし、機械加工の必要性を低減します。
- 部品機能の向上: 3Dプリンティングで複雑な内部形状を作成する能力は、ニッケル超合金製の部品の機能性と性能を向上させる。
デメリット
- 高い材料費: ニッケル超合金粉末は一般に、積層造形に使用される他の金属粉末よりも高価である。
- 限られた材料しか入手できない: 利用可能なニッケル超合金粉末の範囲は拡大していますが、特定の用途に必要な特定の合金組成をすべて網羅しているわけではありません。
- プロセスの最適化が必要: ニッケル超合金の3Dプリントを成功させるには、良好なプリント性を確保し、最終コンポーネントで望ましい材料特性を達成するために、注意深くパラメータを最適化する必要がある。
- 後処理に関する考察: ニッケル超合金部品の中には、最終的な特性を最 適化するために、熱処理や熱間等方圧加圧(HIP)など の後処理工程を追加する必要があるものもあります。
3Dプリンティング用ニッケル超合金に関するFAQ
Q: 3Dプリンティングでニッケル超合金を使うメリットは何ですか?
A: ニッケル超合金は、卓越した高温性能、軽量化のための設計の自由度、ニアネットシェイプ製造による廃棄物の削減、複雑な内部形状による部品の機能性向上の可能性を提供します。
Q: ニッケル超合金の3Dプリントに関連する課題にはどのようなものがありますか?
A: 主な課題としては、材料費の高騰、標準的なオプションと比較した場合の材料入手の制限、印刷を成功させるためのプロセス最適化の必要性、後処理の必要性などが挙げられます。
Q: 3Dプリンターで造形されるニッケル超合金の代表的な用途にはどのようなものがありますか?
A:一般的な用途としては、タービンブレード、燃焼器ライナー、熱交換器(航空宇宙)、ガスタービン部品、遮熱板(エネルギー生産)、原子炉、熱交換器(化学処理)、インプラント、手術器具(医療機器)などがある。
Q: 3Dプリント用のニッケル超合金粉末はどこで購入できますか?
A: EOS GmbH、Elementum 3D、SLM Solutions、Met3DPなど、信頼できるサプライヤーがニッケル超合金粉末を提供しています。 メット3DP具体的には、レーザーおよび電子ビーム粉末床融合用に最適化された高品質の金属粉末を幅広く製造している。同社のポートフォリオには、TiNi、TiTa、TiAl、TiNbZr、CoCrMo、ステンレス鋼、超合金などの革新的な合金が含まれ、さまざまな3Dプリンティングのニーズに対応するワンストップショップとなっている。
3Dプリンティングにおけるニッケル超合金の未来
3Dプリンティングにおけるニッケル超合金の未来は、可能性に燃えている。研究開発が進むにつれて、私たちは次のことを期待できる:
- 新合金の開発: 材料科学者は、3Dプリンティング用に最適化された新しいニッケル超合金の配合を常に革新しています。これらの合金は性能の限界を押し広げ、さらに高い強度、耐酸化性、高温能力を提供する。
- 3Dプリンティング技術の進歩: より高いレーザー出力やより厳密なプロセス制御といった3Dプリンティング技術の向上により、ニッケル超合金からさらに複雑で高性能な部品を作り出すことが可能になる。
- コスト削減と幅広い利用可能性: 技術が成熟し、生産量が増加するにつれて、ニッケル超合金粉末のコストは低下すると予想される。これによって、より幅広い用途でニッケル超合金粉末を利用できるようになる。
- クリティカルなアプリケーションのための資格: ニッケル超合金3Dプリンティング部品を重要な航空宇宙およびエネルギー用途に使用するための厳しい認定プロセスが進行中である。これにより、これらの要求の厳しい業界でこの技術が広く採用される道が開かれることになります。
結論として、ニッケル超合金は、3Dプリンティングの未来に変革的な役割を果たす用意がある。高温性能、設計の自由度、軽量化の可能性など、そのユニークな組み合わせは、要求の厳しい様々な用途に理想的です。技術の進歩が進むにつれて、ニッケル超合金は間違いなく、3Dプリンティングで可能なことの限界を押し広げるための礎となる材料になるでしょう。
シェアする
MET3DP Technology Co., LTDは、中国青島に本社を置く積層造形ソリューションのリーディングプロバイダーです。弊社は3Dプリンティング装置と工業用途の高性能金属粉末を専門としています。
関連記事
Met3DPについて
最新情報
製品

3Dプリンティングと積層造形用金属粉末