純ニッケル粉
目次
純ニッケル粉 は、ユニークな特性を持つ汎用性の高い金属粉で、様々な産業分野の高度な用途に適しています。この記事では、純ニッケル粉について詳しくご紹介します。
純ニッケル粉末の概要
純ニッケルパウダーは、その名の通り99%以上の純度を持つニッケルの粉末です。合金元素を含まないため、ニッケル合金とは異なる特性を持っています。
純ニッケル粉の主な特徴をいくつか挙げる:
- 粒径が細かいため、圧縮や焼結が容易
- 高純度であるため、冶金特性に一貫性がある。
- 球状であるため流動性が良い。
- カルボニル、電解、カルボニル鉄フリーなどのグレードがある。
- 多くのニッケル合金よりも低コスト
高強度、延性、耐食性、磁性などの特性を持つ純ニッケル粉末は、代替品では実現できないニッチな用途に対応します。
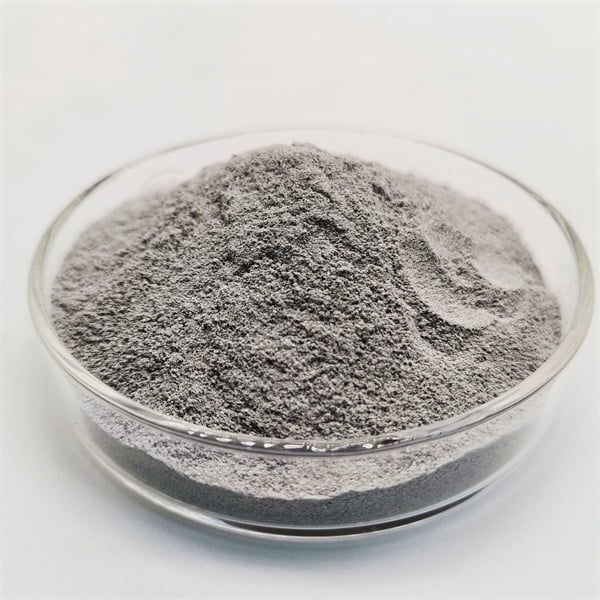

典型的な構成 純ニッケル粉
| エレメント | 重量 % |
|---|---|
| ニッケル(Ni) | 99.0分 |
| カーボン(C) | 最大0.1 |
| 酸素 (O) | 最大0.4 |
| 硫黄(S) | 最大0.01 |
| 鉄(Fe) | 最大0.5 |
| 銅(Cu) | 最大0.2 |
純ニッケル粉末の主な特性
| プロパティ | 詳細 |
|---|---|
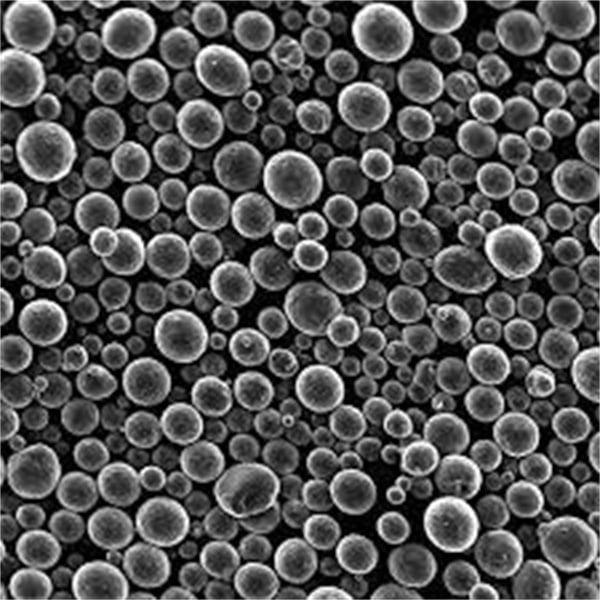
| 粒子形状 | 球状、鎖状 |
| タップ密度 | 最大4.2 g/cc |
| 見かけ密度 | 最大2.5 g/cc |
| 比表面積 | 0.1 - 10 m2/g |
| 粒子径 | 0.5ミクロン~75ミクロン |
| 純度 | 最大99.8% |
| 融点 | 1453°C |
純ニッケル粉末の用途と使用法
純ニッケル粉末は汎用性が高いため、以下のようなニッチな用途に適している:
積層セラミックコンデンサ(MLCC)
温度安定性、高導電性、耐酸化性などの特性により、純ニッケル粉末は電子機器や自動車産業におけるMLCCの内部電極に最適である。
軟磁性アプリケーション
透磁率が良く、保磁力が低いため、純ニッケル粉末は磁性コア、チョークコイル、フィルターなどに使用できる。
製造業
圧縮性と焼結性は、粉末冶金技術による純ニッケル部品の経済的な製造に役立つ。
触媒
大きな表面積は、化学、製薬、石油化学産業で利用される高い触媒活性を提供する。
バッテリー
純度と電気化学的特性は、ニッケル系電池の負極材料として有用である。
その他の用途
導電性コーティングおよびフィルム、溶接製品、ダイヤモンド工具、導電性接着剤/インク、ろう付け合金に特化した用途。
純ニッケル粉末の種類と仕様
純ニッケル粉末は、様々な用途に適した様々なタイプ、サイズ、形態、グレードで市販されています:
純ニッケル粉末の種類と代表的な仕様
| タイプ | 粒子径 | 見かけ密度 | タップ密度 | 比表面積 | 純度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| カルボニルニッケル | 2~12 μm | 1.5~2.2 g/cc | 最大4 g/cc | 0.15~0.6 m2/g | 最大99.8% |
| 電解ニッケル | 15~75 μm | 2~3 g/cc | 最大4.2 g/cc | 0.08~1.2 m2/g | 最大99.9% |
| カルボニル鉄フリー | 2~5 μm | 1.8~2.5 g/cc | 3.2~4 g/cc | 0.4~1 m2/g | 最大99.9% |
利用可能な粒子形状
- 球形
- チェーン状
- 樹状突起
サイズ
- サブミクロン(1ミクロン以下)
- 1~5ミクロン
- 10~15ミクロン
- 20~75ミクロン
グレード
- 標準純度 (99%以上)
- 高純度(99.8%以上)
- 超高純度(99.9%以上)
主要サプライヤーと価格
高度な用途向けの特殊粉末である純ニッケル粉末は、世界的に供給元が限られている。価格は数量とグレードによって異なります。
主要サプライヤー 純ニッケル粉
| サプライヤー | 所在地 | 生産能力 |
|---|---|---|
| ヴェール | カナダ | 年間50,000トン |
| ジエン ニッケル | 中国 | 年間20,000トン |
| MICグループ | 韓国 | 年間10,000トン |
価格見積もり
| タイプ | 純度 | 価格帯 |
|---|---|---|
| カルボニルニッケル | 99.8% | Kgあたり$15~$30 |
| 電解ニッケル | 99.5% | Kgあたり$10~$25 |
*参考価格。グレード、数量、用途に基づく正確な見積もりについては、サプライヤーにお問い合わせください。
比較分析
純ニッケルパウダーの利点
- 高純度による安定した特性
- 良好な耐食性
- ニッケル合金に比べて経済的
- 特性を生かした特殊用途
純ニッケル粉末の限界
- 世界的な生産能力の限界 -ベースメタルより高いSEG価格
- 高温での酸化感受性
- 多くの合金より強度が低い
| パラメータ | 純ニッケル | ニッケル合金 |
|---|---|---|
| コスト | より低い | より高い |
| 空室状況 | 中程度 | 高い |
| 電気伝導度 | 高い | 変動あり |
| 透磁率 | 高い | 変動あり |
| 耐食性 | グッド | 非常に良い |
| 耐酸化性 | 中程度 | グッド |
| 機械的強度 | 中程度 | 高い |
上記で見たように、ニッケル合金は強度や耐酸化性などの分野で優れていますが、純ニッケル粉末は、ニッケルに期待される優れた腐食特性を維持しながら、電気、磁気、その他のニッチ用途に手頃な価格のソリューションを提供します。
よくあるご質問
純ニッケル粉の最も一般的な用途は何ですか?
最も一般的な用途は、積層セラミックコンデンサー(MLCC)、軟磁性部品、ダイヤモンド工具、溶接製品、電池、触媒コンバーターの製造である。純ニッケルは、温度安定性、磁性、耐食性、圧縮性、コストなどの特性を兼ね備えているため、これらの用途に適している。
なぜニッケル合金ではなく純ニッケル粉末を選ぶのですか?
純ニッケル粉末は、合金元素が少ない、または全く含 まないニッケル合金に比べてはるかに低コストで、高 い電気伝導性、熱伝導性、磁性、圧縮性、適度な 腐食特性を提供します。そのため、これらの特性が必要であるがコストに制約があるニッチな用途に使用することができます。しかし、ニッケル合金は高温での強度に優れ ているため、特定の構造用途に使用する必要が ある。
カルボニルニッケル粉とは?
カルボニルニッケル粉末は、ニッケルカルボニルガスの分解による化学気相成長法によって製造され、適度な表面積を持つ均一な球状粒子を与えるため、粉末冶金法による焼結部品に適している。また、高純度で不純物が少ないため、触媒や電池材料としても利用できます。
純ニッケル粉末の価格は、ニッケル金属の価格と比較してどうですか?
純ニッケル粉 LMEニッケル価格の1.5倍から4倍/トンである。つまり、ニッケルがトン当たり$20,000 で取引されている場合、パウダーはおよそトン当たり $30,000から$80,000になる。金属粉末の特殊な製造工程が、金属に対するこの価格プレミアムの理由である。
結論
市販の高純度ニッケル粉末は、その手頃な価格と、代替品では得られない望ましい熱的、電気的、磁気的、腐食的特性を兼ね備えているため、アプリケーションの課題に対応するため、産業界全体で高度なエンジニアリング製品の開発を後押ししています。
シェアする
MET3DP Technology Co., LTDは、中国青島に本社を置く積層造形ソリューションのリーディングプロバイダーです。弊社は3Dプリンティング装置と工業用途の高性能金属粉末を専門としています。
関連記事
Met3DPについて
最新情報
製品

3Dプリンティングと積層造形用金属粉末
















