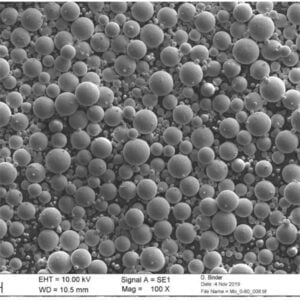
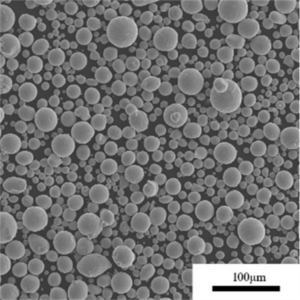
チタンモリブデン合金粉末
目次
チタンモリブデン合金粉 このガイドでは、TiMo合金粉末の組成、主要特性、製造方法、適切な用途、仕様、購入に関する検討事項、サプライヤーの比較、および長所と短所について説明します。このガイドでは、TiMo合金粉末の組成、主な特性、製造方法、適切な用途、仕様、購入上の注意点、サプライヤーの比較、長所/短所について説明します。
チタンモリブデン合金粉 典型的な構成
| 合金グレード | チタン(%) | モリブデン (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Ti-6Al-7Nb (IMI 550) | バランス | 7% |
| Ti-15Mo-3Nb-3Al-0.2Si | バランス | 15% |
| Ti-11.5Mo-6Zr-4.5Sn (Ti-11) | バランス | 11.5% |
| Ti-15Mo-5Zr-3Al | バランス | 15% |
モリブデンのレベルは7%から15%で、高温強化に効果的。ニオブ、ジルコニウム、スズなどの他の元素は、クリープ特性をさらに高める。
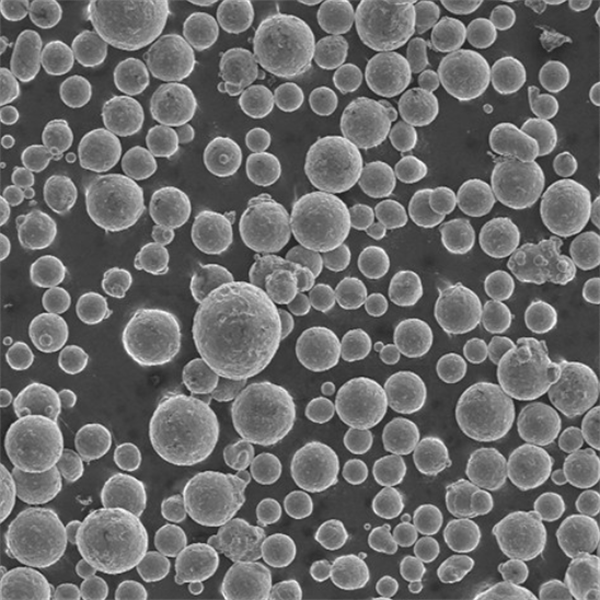

特徴と特性
| 属性 | 詳細 |
|---|---|
| 粒子形状 | 不活性ガスアトマイズによる球状化 |
| 酸素ppm | 500ppm以下 |
| 標準密度 | 4.5g/cc |
| 熱伝導率 | 4-6 W/mK |
| 高温強度 | 500°C で 100 MPa |
| 耐食性 | TiO2保護膜を形成 |
粒子状で酸素含有量が低く、組成が調整された合金粉末は、積層造形や高性能部品の焼結に適している。
生産方法
| 方法 | プロセス説明 |
|---|---|
| ガス噴霧 | 不活性ガスが溶融合金の流れを粉末に分解する |
| プラズマ霧化 | 非常にクリーンだが、ガス噴霧に比べて粉体出力が低い |
| 準備 | 再溶解による既存粉末の球状化 |
| ヒドリド脱水素 | 粉砕用脆性TiH2中間体 |
プラズマとガスアトマイゼーションは最高の品質を提供するが、PREPやHDHのような二次ルートに比べて高価である。
TiMo合金粉末の用途
| 産業 | コンポーネント例 |
|---|---|
| 航空宇宙 | タービンブレード、ケーシング、ランディングギア |
| 発電 | 熱交換器、蒸気配管 |
| 化学処理 | バイオリアクター、反応容器 |
| マリン | プロペラシャフト、ソナードーム |
| 石油・ガス掘削 | 地熱坑井用ツールとシャフト |
高強度、軽量、耐食性の組み合わせは、航空機エンジンや海洋掘削のような厳しい環境に適したTiMo合金です。
仕様
| スタンダード | 対象学年 |
|---|---|
| ASTM B862 | Ti-6Al-2Sn-4Zr-6Mo, Ti-8Al-1Mo-1V, Ti-6Al-2Nb-1Ta-0.8Mo |
| ASTM B348 | チタンおよびチタン合金の棒材および鋼片 |
| AIMS 04-18 | AMチタン部品の標準 |
AMPM(米国粉末冶金)協会、IPS(国際粉末冶金標準化機構)も各種Tiグレードをカバーしている。
世界のサプライヤーと価格帯
| 会社概要 | リードタイム | 価格 |
|---|---|---|
| TLSテクニーク | 16週間 | $300〜$900/kg |
| サンドビック | 12週間 | $350〜$1000/kg |
| アトランティック・エクイップメント | 14週間 | $320〜$850/kg |
100kg以上のバッチ価格。低酸素・球状パウダーはプレミアム。500kg以上の場合は20%+の割引があります。
長所と短所
| メリット | 課題 |
|---|---|
| 優れた高温強度 | 高い原材料費 |
| 様々な環境下での耐食性 | カスタム合金のリードタイムが長い |
| カスタム合金設計の柔軟性 | 限られたグローバル・サプライチェーン |
| 粉末AM法との互換性 | AM後に後処理が必要になることが多い |
| 優れた耐クリープ性 | 酸素/窒素に関する厳しい要件 |
TiMo粉末は、新しい部品設計と軽量構造を可能にしますが、チタン合金を使用することは、粉末の製造と取り扱いに独特の課題をもたらします。

よくあるご質問
バインダージェット3Dプリンティングに最適な粒子径範囲は?
30ミクロンから50ミクロン程度であれば、パウダーベッドの密度が高くなり、層を適切に結合させるために必要な液体の飽和を効率的に行うことができる。粉末が細かすぎると性能が低下する。
Ti合金ガスアトマイズ時のコンタミネーションの原因は何ですか?
空気漏れからの酸素ピックアップは粉末の純度を低下させるため、厳格なプロセス管理が必要となる。高純度の消耗品を必要とする他の汚染源として、炉のパーティング剤と溶融るつぼがあります。
なぜTi基合金では高Mo含有が難しいのか?
モリブデンの過度の蒸発損失は、真空誘導溶解とそれに続く再溶解工程で、25%レベルを超えて発生する。緩和策には、溶融プールを覆うか、低温るつぼ技術を使用することが含まれる。
チタンパウダーはどのように保管すべきですか?
不活性カバーガスまたは真空下の密閉容器内。腐敗の原因となる吸湿を避け、オシゲンや窒素の不純物が多くならないように取り扱い、保管する。
チタン合金をAMプリントする際によくある欠陥とは?
捕捉されたガス原子によるポロシティ、融合欠陥の欠如、残留応力クラック、密閉された容積内に捕捉された未融合の粉末。スキャン戦略、エネルギー入力などを考慮した統合パラメータの最適化が必要。
結論
要約すると チタンモリブデン合金粉 は、粉末冶金または積層造形により、航空宇宙、エネルギー、その他要求の厳しい産業における次世代部品の製造に不可欠な、カスタマイズされた高温特性と耐食性を提供します。
シェアする
MET3DP Technology Co., LTDは、中国青島に本社を置く積層造形ソリューションのリーディングプロバイダーです。弊社は3Dプリンティング装置と工業用途の高性能金属粉末を専門としています。
関連記事
Met3DPについて
最新情報
製品

3Dプリンティングと積層造形用金属粉末