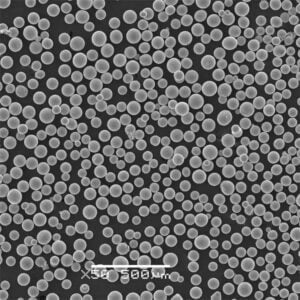
高密度タングステン粉
目次
高密度タングステン粉 タングステンは金属粉末の中で最も密度が高く、その固有密度は金に匹敵します。このユニークな特性は、重い粉末のプレスや焼結の方法論を利用して、様々な分野でコンパクトで重量効率の高い部品の高度な設計を可能にします。
概要 タングステン粉
固体の形で19.3 g / cm3の密度で、タングステンは小さなボリュームに巨大な重量をパックします。このおかげで、タングステン粉末は、圧縮されたときに他の材料を使用して達成できない比類のない密度レベルを提供します。高密度タングステン粉末から作られた部品は、要求の厳しい環境で数多くのアプリケーションを見つける。
高密度タングステン粉末を利用する主な促進要因は以下の通り:
- 金やプラチナのような貴金属に似た高い密度
- 鉛やスチールに比べ、使用可能な密度が2倍
- 重くてもコンパクトなサイズと形状が可能
- シンプルな粉末冶金による最終製品へのルート
- 合金元素の混合によるテーラーメイドの特性
- 高価なタングステンのリサイクル性
密度スパン安定器、放射線遮断、慣性、複合材料の加重、振動減衰、部品の小型化などを利用したアプリケーション。

高密度タングステン粉末の種類
すべてのタングステン粉末の品種は、高密度を提供していますが、特定のグレードと組成は、成形および焼結後に最適な密度レベルを付与します:
| タイプ | 説明 | 典型的な密度 |
|---|---|---|
| 純タングステン | 99.95%以上の高純度により、信頼性の高い密度を実現 | ≥18g/cm以上 |
| ドープ・タングステン | Y2O3のような微量の希土類酸化物の添加は、焼結密度を向上させる。 | ≥18.5g/cm以上 |
| タングステン-ニッケル-鉄 | Ni-Fe合金化により優れた最終密度を実現 | ≥18g/cm以上 |
| タングステン重合金 | 90-97% W、Ni-Cu-Fe 結合相付き | ≥17.5 g/cm 以上 |
| タングステン複合材料 | 金、タンタル、劣化ウラン等と混合。 | 21g/cmまで |
これらの強化された配合は、純粋なタングステンだけでなく、カスタマイズされた特性の組み合わせまで、高性能の選択肢を広げます。
構成 タングステン粉
高純度タングステン粉末は、99.95%以上のタングステンを含み、不純物はわずかです:
| エレメント | 最大コンテンツ | 役割 |
|---|---|---|
| タングステン(W) | 99.95% | 主成分 |
| カーボン(C) | 100ppm | 穀物成長抑制剤 |
| 酸素 (O) | 100ppm | 表面酸化物 |
| 銅(Cu) | 10 ppm | 残留微量不純物 |
| シリカ(Si) | 20 ppm | 不純物 |
特殊な重合金グレードは、タングステンとともにニッケル、銅、鉄などの合金を意図的に添加し、特性をさらに向上させている。
プロパティ タングステン粉
高密度タングステン粉末は、有用な強度、硬度、熱特性と相まって、極端な密度を誇るニアネットシェイプ部品の製造を可能にします。
物理的性質
| プロパティ | 価値 |
|---|---|
| 密度 | ≥18g/cm以上3。 |
| 融点 | 3380-3410°C |
| 強さ | 最大1000MPa |
| 硬度 | ≥400VPN以上 |
| 熱伝導率 | ∼約175W/(m・K) |
| 熱膨張係数 | ∼4.5 μm/(m-K) |
これらの特性は、タングステンの本質的な原子構造に由来するもので、熱的・機械的完全性を必要とする高密度用途に最適です。
機械的特性
入念な粉末プレスと焼結により、有利な機械的特性が得られる:
| プロパティ | 価値 |
|---|---|
| 硬度 | 最大550VPN |
| 降伏強度 | ∼約900MPa |
| 引張強度 | 最大1000MPa |
| 伸び | ∼約10%~15% |
| 破壊靭性 | ∼約20 MPa√m |
| 疲労強度 | 500 MPa |
ニッケル、鉄などの合金元素は、延性、靭性、加工特性を調整するのに役立つ。
身体的特徴
設計者に有用な高密度タングステン粉末の顕著な物理的属性:
| パラメータ | 価値 | 単位 |
|---|---|---|
| 密度 | 18から19.3 | g/cm3</sup |
| 電気抵抗率 | 5.5 | μΩ-cm |
| 熱伝導率 | 170 | W/(m-K) |
| 融点 | 3410 | °C |
| 沸点 | 5930 | °C |
| 比熱 | 132 | J/(kg-K) |
超高融点と熱伝導性により、極端な温度下でも強度と寸法を維持できる。
製造 タングステン粉
| ステージ | 説明 | キーポイント |
|---|---|---|
| 1.原材料の入手 | そのプロセスは、主に鉄マンガン鉱と輝石からなるタングステン鉱石の採掘から始まる。 | * タングステン鉱石は世界中で採掘されているが、主な産地は中国、ペルー、ボリビアなど。 * 採掘方法は鉱床によって異なるが、一般的な手法としては露天掘りや地下採掘がある。 * 採掘された鉱石は、破砕、粉砕、濃縮の工程を経て、不純物を取り除き、タングステンの含有量を濃縮する。 |
| 2.化学処理 | 濃縮された鉱石は、さらなる精製と還元に適した中間化合物に変換される。 | * パラタングステン酸アンモニウム(APT)は、最も広く使用されている中間体である。浸出、ろ過、沈殿を含む一連の化学反応によって製造される。 * APTは高純度でハンドリングが良いという利点がある。 * タングステン酸や酸化タングステンのような他の中間化合物も、特定の製造工程に応じて使用することができる。 |
| 3.高純度酸化物の製造 | さらに精製工程を行うことで、残存する不純物を確実に除去し、還元に必要な酸化タングステンのレベルを達成する。 | * APTは、タングステン粉末製造のための厳しい純度要件を満たすために、再結晶や溶媒抽出のような追加の精製工程を経る。 * WO3(三酸化タングステン)やWO2(二酸化タングステン)のような酸化タングステンは、多くの場合、この段階の最終製品です。 * 酸化物の選択とその特性は、最終的なタングステン粉末の特性に影響を与えます。 |
| 4.水素還元 | 精製された酸化タングステンは、制御された炉内で水素ガスを用いて金属タングステン粉末に還元される。 | * この段階は、タングステン粉末の生産の中心です。水素が還元剤として働き、酸化タングステンから酸素を奪い、純粋なタングステン金属粒子を残します。 * 還元プロセスは、プッシャー炉または回転炉で、温度(通常600℃~1100℃)と水素ガス流量を精密に制御して行われる。 * これらのパラメータを注意深く制御することは、粒子径、形態、純度など、望ましいタングステン粉末の特性を達成するために非常に重要です。 |
| 5.粉体の分類と仕上げ | 還元炉で作られたタングステン粉末は、最終的な特性を得るためにさらに加工されます。 | * 粉体は特定の粒度分布を得るために選別・分級されます。様々な用途には、様々な粒子径と形態のパウダーが必要です。 * 粉砕や造粒のような工程を追加することで、粒子径や形状をさらに細かくすることができる。 * 粉末は、還元処理で残留する水素を除去するために脱ガス処理に付されることもある。 |
| 6. 品質管理 | 生産工程では、最終的なタングステン粉が要求される仕様をすべて満たしていることを確認するため、厳格な品質管理措置が実施される。 | * 化学分析は、粉末の元素組成と純度を決定する。 * 粒度分布と形態は、レーザー回折や電子顕微鏡などの技術を用いて分析される。 * その他の試験では、密度、流動性、焼結挙動などの特性を評価することができる。 * 一貫した品質を維持することは、粉末から作られるタングステン製品の性能に不可欠です。 |
アプリケーション タングステン粉
| カテゴリー | 申し込み | レバレッジ物件 | 例 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 工業・製造業 | 機械加工と切削工具 | 極めて高い硬度、耐摩耗性 | - ドリルビット - フライスチップ - エンドミル - 旋削工具 |
| 金型 | 高融点、熱安定性 | - ワイヤー・フィラメント用押出金型 - ホットスタンピング金型 - プラスチック射出成形金型 | |
| 電極 | 高融点、良好な電気伝導性 | - 不活性ガス溶接(TIG)電極 - 抵抗溶接電極 | |
| フィラメントと発熱体 | 高融点、良好な電気伝導性 | - 白熱電球のフィラメント - 炉の発熱体 | |
| 触媒 | 高い表面積、化学反応を促進する能力 | - アンモニア製造用触媒 - 炭化水素処理用触媒 | |
| 顔料・コーティング | 高密度、X線に対する不透明性 | - 医療機器の放射線遮蔽 - X線造影剤 | |
| 電気・電子 | 電気接点およびスイッチ | 高融点、良好な導電性、耐アーク性 | - リレー接点 - サーキットブレーカー接点 - 高圧スイッチギア接点 |
| ヒートシンク | 高い熱伝導性 | - 電子部品の放熱 | |
| 半導体製造 | 高密度、耐エッチング性 | - 集積回路のタングステンプラグとビア - トランジスタのゲート電極 | |
| 消費財 | スポーツ用品 (ゴルフクラブ、釣りのおもり) | 重量配分のための高密度 | - ゴルフクラブのウエイトでスイングを改善 - より深く、より速く沈むためのフィッシング・ウエイト |
| 振動減衰 | 高密度 | - テニスラケットやアーチェリー用具のダンパー - 機械装置の振動ダンパー | |
| 高度なアプリケーション | アディティブ・マニュファクチャリング(3Dプリンティング) | 粒径が細かく、流動性が良い | - 航空宇宙および自動車産業向け3Dプリント部品 - 医療用インプラント |
| 原子力 | 高融点、中性子吸収 | - 原子炉の制御棒 - 核廃棄物の遮蔽 | |
| 軍事・防衛 | 徹甲弾 | 高密度、高硬度 |
仕様
高密度タングステン粉末の主要パラメータを定義:
タングステン粉末の等級
| グレード指定 | 平均粒子径(ミクロン) | 純度(最低%タングステン) | アプリケーション |
|---|---|---|---|
| 超微粒子タングステンパウダー | < 1.0 | ≥ 99.95 | - 優れた焼結性と流動性により、タービンブレードやその他の高摩耗用途に使用される溶射皮膜。 |
| 1.0 – 3.0 | ≥ 99.95 | - 耐摩耗性と切れ味に優れ、硬質材料の切断や研削に使用されるダイヤモンド工具。 | |
| 3.0 – 5.0 | ≥ 99.9 | - 集積回路の高い導電性と熱安定性のために、不純物を最小限に抑えた電子基板。 | |
| 微粉タングステン | 5.0 – 10.0 | ≥ 99.5 | - 超硬合金製切削工具は、硬度、靭性、耐欠損性のバランスが良く、様々な材料の加工に適しています。 |
| 10.0 – 15.0 | ≥ 99.0 | - 電力スイッチング用途で高い融点、耐アーク性、導電性が要求される重負荷用電気接点。 | |
| 15.0 – 22.0 | ≥ 98.5 | - タングステン・イナート・ガス(TIG)溶接用電極は、安定したアークと集中した熱を発生させる能力がある。 | |
| ミディアム・タングステン・パウダー | 22.0 – 32.0 | ≥ 98.0 | - タングステンの高密度を利用した貫通弾と運動エネルギー弾は、優れた装甲貫通力を発揮します。 |
| 32.0 – 45.0 | ≥ 97.0 | - X線やガンマ線を吸収するタングステンの特性により、医療機器や原子力施設における放射線遮蔽材料。 | |
| 粗タングステン粉 | 45.0 – 75.0 | ≥ 96.0 | - タングステンの高密度を利用したカウンターウエイトや制振ダンパー用のバラストウエイトです。 |
| > 75.0 | ≥ 95.0 | - 冷間加工プロセスで金属部品の表面を強化するためのショットピーニングメディア。 |
タングステン粉末の規格
| プロパティ | 説明 | 重要性 | 代表的な規格 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 純度 | タングステン粉末の純度は、重量で粉末中に存在するタングステン金属(W)の割合を指します。不純物は大幅にタングステン製品の物理的および機械的特性に影響を与える可能性があります。 | 一般に、導電性、融点、強度などの特性に依存する用途では、純度が高いほど性能が向上する。しかし、極めて高純度であることが必ずしも必要であったり、費用対効果が高いとは限りません。 | – 高純度(99.9% W以上): 優れた導電性が重要な電子機器、フィラメント、電極に使用される。 – 標準純度(99.5% W - 99.9% W): 超硬切削工具、ヒートシンク、放射線遮蔽など様々な用途に適している。 – 低純度(99.5% W以下): プラスチック充填材や、さらに精製するための原料など、特定の用途に使用される。 |
| 粒子径と分布 | 粒子径とは、粉末中の個々のタングステン粒子の平均直径を指します。粒度分布は、粉末サンプル内の粒子径のばらつきを表します。 | 粒径と粒度分布は、タングステン製品の加工挙動と最終的な特性に大きく影響する。例えば、粒子が細かいほど焼結性は良くなりますが、取り扱いが難しくなります。 | – ミクロンサイズの粉末(1~50ミクロン): 超硬合金製造、溶射、積層造形によく使用される。 – サブミクロン粉末(1ミクロン以下): 触媒や導電性コーティングなど、高い表面積を必要とする用途に使用される。 – ナノ粉末(100ナノメートル以下): エレクトロニクスや複合材料への応用が期待される新分野。 |
| 見かけ密度 | 見掛け密度は、粒子間の空間を考慮した単位体積あたりのタングステン粉末の重量を表します。金型に充填できる粉末の量や焼結製品の最終密度に影響します。 | 見かけ密度を高くすることで、パウダーをより効率的に使用することができ、機械的特性が改善された高密度の最終製品につながります。 | – 高密度粉体(>10 g/cm³): 超硬工具のように高い強度と耐摩耗性を必要とする用途に使用される。 – 標準密度の粉末(7~10 g/cm³): 密度と加工のしやすさのバランスが求められる様々な用途によく使用される。 – 低密度粉体(<7 g/cm³): 一部の溶射工程など、ルースパッキングや流動性が重要な用途に使用できる。 |
| 流動性 | 流動性は、タングステン粉末が移動し、注ぐことができる容易さを指します。様々な用途で効率的に取り扱い、加工するために非常に重要です。 | 流動性が良いため、機械への粉体の供給がスムーズで、粉体内の異なる粒径の偏析を最小限に抑えることができる。 | – 自由に流動する粉末: 粒子間相互作用を最小化するための特定の粒度分布と表面処理によって達成される。 – 添加物: 粒子間の摩擦を減らして流動性を向上させるために使用できる。 |
| 形態学 | モルフォロジーとは、個々のタングステン粒子の形状や形態を指す。 | 粒子形態は、充填挙動、焼結特性、およびタングステン製品の最終的な微細構造に影響を与える可能性がある。 | – 球状粉末: 良好な充填密度と流動性を提供する。 – 角のある粉: 焼結時に網目状のネットワークが形成され、強度が向上する可能性がある。 – 樹枝状粉末: 分岐構造が有利な特定の用途に使用できる。 |
| 酸素含有量 | 酸素含有量とは、タングステン粉末に含まれる酸素の量を指し、一般的には酸化物として含まれる。過剰な酸素は、タングステン製品の最終的な特性に影響を与える可能性があります。 | - ほとんどの用途では、最適な性能を確保するために酸素含有量を低くすることが一般的に望まれている。 – 厳しい酸素制限 は、エレクトロニクスやフィラメントのような高性能用途に指定されることが多い。 | |
| タップ密度 | タップ密度は、標準化されたタッピングプロセスによって達成されたタングステン粉末の充填密度の尺度です。流動性と見かけ密度の間接的な指標となります。 | - タップ密度が高いほど充填効率が良く、品質管理パラメータとして使用できる。 | - 業界標準では、異なるタングステン粉末グレードの最小タップ密度要件を指定することがよくあります。 |
価格
高密度用途に適したタングステン粉末の代表的な価格:
| グレード | 価格 |
|---|---|
| ウルトラファイン | 1kgあたり$800~$1200 |
| サブミクロン | 1kgあたり$500~$900 |
| ファイン | 1kgあたり$100~$250 |
| ミディアム | 1kgあたり$50~$150 |
| 重合金 | 1kgあたり$40~$100 |
粒径が小さく、純度が高く、特殊なドーパントが使われ、量が少ないとコストが高くなる。リサイクルされたスクラップパウダーの方が安い。
長所と短所
| メリット | デメリット |
|---|---|
| 比類なき高融点: タングステン粉末は、あらゆる金属の中で最も高い融点を誇り、その温度は驚異的な3,422℃に達します。この優れた特性により、炉の内張り、ロケットのノズル、宇宙船の再突入用遮熱板など、極端な高温にさらされる用途で優れた性能を発揮します。 | 高額な投資: タングステンの抽出と加工は複雑な手順で行われるため、一般的な金属に比べて価格が高くなります。これは、コストが大きな要因となる用途にとっては大きなハードルとなり得る。 |
| 優れた熱伝導性と電気伝導性: タングステン粉末は、熱と電気の両方を効率的に伝導することに優れています。これは、電子機器のヒートシンク、または白熱灯のフィラメントや溶接用電極のような電気部品のように、効率的な熱管理を必要とするアプリケーションに最適です。 | 密度が濃く、要求が高い: タングステンの顕著な密度は、その密に詰まった原子構造の直接的な結果であり、粉末の形態にも適用されます。この高密度は、加工中に課題を提起することができます。タングステン粉末を効果的に取り扱い、成形するためには、特殊な技術や設備が必要になる場合があります。 |
| 卓越した耐摩耗性と耐食性: タングステン粉末は、卓越した耐摩耗性と耐食性を示します。これは、徹甲弾のような過酷な環境での卓越した耐久性を必要とするアプリケーション、タフな材料のためのドリルビット、および化学処理プラントで使用されるコンポーネントに最適です。 | 潜在的な健康リスク: タングステン粉を吸い込むと、肺を刺激し、健康上の合併症を引き起こす可能性があります。タングステン粉を扱う際には、厳格な安全プロトコルと適切な換気が曝露リスクを最小限に抑えるために非常に重要です。 |
| 調整可能な合金化の可能性: タングステン粉末は、様々な金属と容易に合金を形成し、その特性を大幅に向上させます。これにより、エンジニアは、高性能切削工具やジェットエンジン部品のような用途向けに、強度、硬度、耐熱性の特定の組み合わせを持つカスタム設計の材料を作成することができます。 | 限られた世界供給: タングステンの主な供給源は地理的に集中しており、中国が世界生産の大半を占めている。これはサプライチェーンの脆弱性と潜在的な価格変動につながる可能性がある。 |
| 生体適合アプリケーション: タングステンは良好な生体親和性を示し、その粉末は特定の医療用途に適しています。例えば、タングステンベースのインプラントは、その卓越した強度と耐摩耗性により、人工股関節に使用することができます。 | 専門サプライヤー: タングステン粉末のユニークな特性と潜在的な安全性の懸念のため、評判が高く経験豊富なサプライヤーからの調達が不可欠です。このようなサプライヤーは、安全な取り扱いと目的の用途における最適な性能を保証する技術サポートとともに、高品質で十分に特性化された粉末を提供することができます。 |
| 3Dプリンティングの新たな応用: タングステン粉末は、3Dプリンティングとしても知られる積層造形の分野で、急速に進展する新たな用途を見出している。そのユニークな特性の組み合わせは、航空宇宙、自動車、医療産業向けの高性能金属部品の印刷に適しています。 | 偽造品の懸念: タングステンパウダーは高価であるため、偽造品の製造業者を惹きつける可能性があります。厳格な品質管理を実施している優良サプライヤーと協力することで、粗悪品や不純物を受け取るリスクを軽減することができます。 |
サプライヤー
高密度タングステンおよびタングステン合金粉末を世界的に供給している著名な商社やメーカーには以下のものがあります:
| 会社概要 | 所在地 |
|---|---|
| バッファロー・タングステン | 米国 |
| ウルフラム社 | オーストリア |
| プランゼーグループ | ヨーロッパ |
| 中西部タングステン | 米国 |
| 厦門タングステン | 中国 |
| JXニッポン | 日本 |
| 東芝マテリアル | 日本 |
| GTPシェーファー | ドイツ |
これらの企業は、信頼できるワールドクラスのパウダーを商業市場に供給している。

よくあるご質問
| 質問 | 答え |
|---|---|
| 高密度タングステン粉とは? | 密度が18~19.3g/cm3のタングステン粉末。 |
| 高密度タングステン粉の製造方法は? | 精製された酸化タングステンの還元と特殊な粉砕を組み合わせ、希望する粒子径にする。 |
| 高密度タングステン粉末は何に使われるのか? | カウンターウェイト、放射線シールド、バラスト、ウェイトコンパウンド、制振部品などの製造 |
| 高密度パウダーにはどのような種類がありますか? | 純タングステン、希土類酸化物をドープしたタングステン、タングステン-ニッケル-鉄合金、タングステン重合金など。 |
| 高密度タングステン粉末の利点は何ですか? | 他の粉体とは比較にならないコンパクトな体積で極めて高い密度を実現、複雑な部品へのネットシェイプ加工が可能 |
| タングステンパウダーを使用する際の限界は? | タングステンカーバイドよりも硬度が比較的低く、靭性と延性が限られているため、加工上の課題がある。 |
| 高密度タングステンパウダーは、鉛のような従来の高密度材料と比較してどうですか? | 有毒な鉛よりも安全、鉛よりも融点が高い、同程度の密度の貴金属に対して経済的な価格 |
概要
元素金属の中でも並外れた密度を持つ高純度タングステン粉末は、以前には実現不可能だったコンパクトなプロファイルを必要とする重量重視のアプリケーションのためのユニークな機能を設計者に提供します。粉末の製造、プレス、焼結、二次加工の進歩は、より広い使用のロックを解除脆性の制限を克服する。ブレンドと合金は、高密度が強度、硬度、熱血統と決定的に結合する要求の厳しい電気、原子力、自動車、航空宇宙分野での物理的特性の追加調整を提供します。
持続可能な供給源が信頼できるグローバルサプライチェーンを支えているため、設計者は現在、タングステン粉末の極限密度を利用し、重さとコンパクトさが一体となって価値を生み出す各産業の精密工学的機能性を追求しています。タングステンの戦略的重要性が高まるにつれ、大手メーカーは今後10年で、20g/cm3を超える密度のしきい値を超えることを追求するでしょう。
シェアする
MET3DP Technology Co., LTDは、中国青島に本社を置く積層造形ソリューションのリーディングプロバイダーです。弊社は3Dプリンティング装置と工業用途の高性能金属粉末を専門としています。
関連記事
Met3DPについて
最新情報
製品

3Dプリンティングと積層造形用金属粉末