System depozytowy
Spis treści
Produkcja addytywna, bardziej znana jako druk 3D, szturmem zdobyła świat. Od prototypowania po produkcję na pełną skalę, oferuje bezprecedensową elastyczność i wydajność. Jednym z kluczowych, ale często pomijanych aspektów tego procesu jest depowdering. Zanurzmy się głęboko w świat systemy depowderinguZapoznanie się z różnymi proszkami metali, ich specyficznymi modelami oraz zrozumienie zastosowań, zalet i ograniczeń tych systemów.
Przegląd systemów depowderingu
Systemy usuwania nadmiaru proszku są niezbędne do usuwania nadmiaru proszku z części drukowanych w 3D, zapewniając czysty, gotowy produkt. Proces ten jest szczególnie istotny w branżach, w których precyzja i czystość są najważniejsze, takich jak przemysł lotniczy, medyczny i motoryzacyjny. Systemy te pomagają zmniejszyć nakład pracy ręcznej, zwiększyć wydajność i poprawić ogólną jakość drukowanych części.
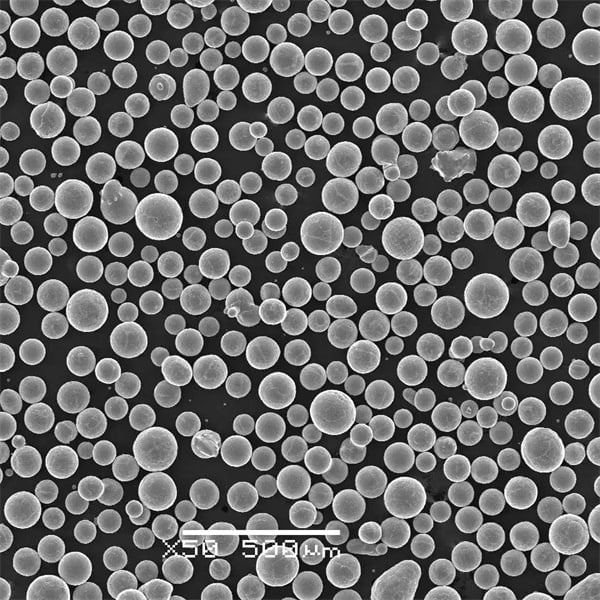
Rodzaje proszków metali dla Depowdering Systems
W produkcji addytywnej wykorzystywane są różne proszki metali, z których każdy ma unikalne właściwości i zastosowania. Poniżej przedstawiamy kilka konkretnych modeli i ich właściwości:
| Model proszku metalowego | Skład | Właściwości | Charakterystyka |
|---|---|---|---|
| AlSi10Mg | Aluminium, krzem, magnez | Lekkość i wysoka wytrzymałość | Doskonałe właściwości termiczne, odporność na korozję |
| Ti6Al4V | Tytan, aluminium, wanad | Wysoka wytrzymałość, lekkość | Biokompatybilny, stosowany w implantach medycznych |
| Inconel 718 | Nikiel, chrom, żelazo | Odporność na wysokie temperatury, odporność na korozję | Używany w przemyśle lotniczym, w środowiskach o wysokim obciążeniu |
| Stal nierdzewna 316L | Żelazo, chrom, nikiel | Wysoka odporność na korozję, wytrzymałość | Idealny do zastosowań medycznych i spożywczych |
| CoCr | Kobalt, chrom | Wysoka odporność na zużycie, biokompatybilność | Stosowany w implantach dentystycznych i medycznych |
| Stal maraging | Żelazo, nikiel, kobalt, molibden | Wysoka wytrzymałość, twardość | Stosowany w oprzyrządowaniu i częściach o wysokiej wydajności |
| Miedź C18150 | Miedź, chrom, cyrkon | Doskonała przewodność elektryczna | Używany w zastosowaniach elektrycznych i termicznych |
| AlSi7Mg | Aluminium, krzem, magnez | Lekki, wytrzymały | Używany w komponentach motoryzacyjnych i lotniczych |
| Hastelloy X | Nikiel, chrom, molibden | Odporność na utlenianie, wysoka wytrzymałość | Używany w urządzeniach do przetwarzania chemicznego |
| Stal nierdzewna 17-4 PH | Żelazo, chrom, nikiel, miedź | Wysoka wytrzymałość, odporność na korozję | Używany w przemyśle lotniczym i petrochemicznym |
Zastosowania systemów depowderingu
Systemy depowderingu są wykorzystywane w różnych branżach, poprawiając jakość i funkcjonalność części drukowanych w 3D. Przyjrzyjmy się bliżej ich zastosowaniom:
| Zastosowanie | Przemysł | Szczegóły |
|---|---|---|
| Komponenty lotnicze i kosmiczne | Lotnictwo i kosmonautyka | Precyzyjne części, takie jak łopatki turbin i elementy konstrukcyjne. |
| Implanty medyczne | Medyczny | Czyste i biokompatybilne implanty, takie jak stawy biodrowe i korony dentystyczne. |
| Części samochodowe | Motoryzacja | Wytrzymałe i lekkie części do silników, układów wydechowych i elementów podwozia. |
| Przewody elektryczne | Elektronika | Wydajne części o wysokiej przewodności do zarządzania elektrycznego i termicznego. |
| Oprzyrządowanie i prototypowanie | Produkcja | Narzędzia o wysokiej wytrzymałości i szybkie prototypy do rozwoju produktów. |
| Sprzęt do przetwarzania chemicznego | Przetwarzanie chemiczne | Odporne na korozję i wytrzymałe części do reaktorów i systemów rurowych. |
| Sprzęt do przetwarzania żywności | Przemysł spożywczy | Higieniczne i odporne na korozję komponenty do produkcji i pakowania żywności. |
| Implanty dentystyczne | Stomatologia | Precyzyjne korony dentystyczne, mosty i aparaty ortodontyczne. |
| Zastosowania wysokotemperaturowe | Energia | Komponenty do turbin i innych środowisk o wysokim obciążeniu i wysokiej temperaturze. |
| Części odporne na zużycie | Maszyny przemysłowe | Części o wysokiej odporności na zużycie do ciężkich maszyn i urządzeń. |
Specyfikacje, rozmiary, gatunki i normy proszków metali
Każdy proszek metalowy stosowany w produkcji addytywnej ma określone standardy i specyfikacje, które zapewniają optymalną wydajność i jakość.
| Model proszku metalowego | Zakres wielkości (mikrony) | Klasa | Standardy |
|---|---|---|---|
| AlSi10Mg | 15-45 | Klasy AM | ASTM F3318 |
| Ti6Al4V | 15-53 | Klasa 23 (ELI) | ASTM F1472, ASTM F2924 |
| Inconel 718 | 15-45 | UNS N07718 | ASTM F3055 |
| Stal nierdzewna 316L | 15-45 | UNS S31603 | ASTM F3184 |
| CoCr | 10-50 | Stop CoCrMo | ASTM F75, ASTM F1537 |
| Stal maraging | 15-45 | 18Ni300 | AMS 6514, ASTM A538 |
| Miedź C18150 | 15-45 | C18150 | ASTM B631 |
| AlSi7Mg | 15-45 | Klasy AM | DIN EN 1706 |
| Hastelloy X | 15-45 | UNS N06002 | ASTM F3055 |
| Stal nierdzewna 17-4 PH | 15-45 | UNS S17400 | ASTM A564, AMS 5604 |
Dostawcy i szczegóły dotyczące cen
Pozyskując proszki metali do produkcji addytywnej, należy wziąć pod uwagę dostawców i ceny. Oto szczegółowe spojrzenie na niektórych znanych dostawców i ich struktury cenowe:
| Dostawca | Model proszku metalowego | Zakres cen (za kg) | Usługi dodatkowe |
|---|---|---|---|
| Praxair Surface Technologies | AlSi10Mg | $70 – $90 | Niestandardowe mieszanki proszków, wsparcie techniczne |
| Technologia Carpenter | Ti6Al4V | $300 – $400 | Obróbka cieplna, testowanie materiałów |
| Sandvik | Inconel 718 | $200 – $250 | Niestandardowe rozmiary proszku, opcje dostawy |
| Oerlikon | Stal nierdzewna 316L | $100 – $150 | Powlekanie powierzchni, wsparcie aplikacji |
| Arcam | CoCr | $200 – $300 | Rozwój procesów, pomoc w certyfikacji |
| EOS GmbH | Stal maraging | $150 – $200 | Wszechstronne biblioteki materiałów, wsparcie |
| Höganäs | Miedź C18150 | $90 – $120 | Dostosowane właściwości proszku, wsparcie logistyczne |
| Renishaw | AlSi7Mg | $70 – $90 | Inżynieria aplikacji, rozwiązania programowe |
| VDM Metals | Hastelloy X | $250 – $300 | Specjalistyczne mieszanki proszkowe, doradztwo techniczne |
| GKN Additive | Stal nierdzewna 17-4 PH | $120 – $160 | Zaawansowane rozwiązania metalurgii proszków |
Porównanie zalet i wad Depowdering Systems
Systemy depowderingu oferują liczne zalety, ale mają też pewne ograniczenia. Porównajmy ich wady i zalety:
| Zalety | Ograniczenia |
|---|---|
| Zwiększona wydajność | Wysoka inwestycja początkowa |
| Lepsza jakość części | Wymagania dotyczące konserwacji |
| Mniej pracy ręcznej | Wymagania dotyczące przestrzeni |
| Zwiększone bezpieczeństwo | Potrzebna wiedza techniczna |
| Spójne wyniki | Możliwe przestoje na naprawy |
| Nadaje się do złożonych geometrii | Specyficzne dla niektórych proszków metali |
| Zmniejszone zanieczyszczenie | Krzywa uczenia się dla operatorów |
| Skalowalność | Możliwość uszkodzenia części |
| Opłacalność w perspektywie długoterminowej | Generowanie hałasu i pyłu |
| Korzyści dla środowiska | Ograniczona dostępność niektórych systemów |
Zrozumienie systemów depozytowych: Szczegółowe informacje
Jak działają systemy depowderingu?
Systemy depowderingu wykorzystują różne techniki usuwania nadmiaru proszku z drukowanych części 3D. Należą do nich:
- Nadmuch powietrza: Strumienie powietrza pod wysokim ciśnieniem usuwają luźny proszek z części.
- Wibracje: Wibracje mechaniczne usuwają nadmiar proszku.
- Próżnia: Systemy ssące usuwają proszek, często używane w połączeniu z nadmuchem powietrza.
- Zautomatyzowane szczotki: Szczotki mechaniczne delikatnie usuwają proszek z powierzchni.
- Czyszczenie ultradźwiękowe: Fale ultradźwiękowe mieszają i usuwają cząsteczki proszku.
Zalety systemów depowderingu
Systemy depowderingu przynoszą szereg korzyści w procesie produkcji addytywnej:
- Wydajność: Automatyzacja procesu pozbywania się zanieczyszczeń znacznie skraca wymagany czas w porównaniu z czyszczeniem ręcznym.
- Precyzja: Zapewnia dokładne czyszczenie skomplikowanych i złożonych geometrii bez uszkadzania części.
- Bezpieczeństwo: Zmniejsza narażenie operatorów na potencjalnie niebezpieczne proszki, zwiększając bezpieczeństwo w miejscu pracy.
- Spójność: Zapewnia jednolite wyniki dla różnych części, gwarantując wysoką jakość.
- Skalowalność: Idealny do produkcji na dużą skalę, gdzie spójność i szybkość mają kluczowe znaczenie.
Wady systemów depoweringu
Systemy te mają jednak również swoje wady:
- Koszt: Wysokie początkowe koszty inwestycji i bieżącego utrzymania mogą stanowić barierę dla małych firm.
- Wiedza techniczna: Wymaga wykwalifikowanych operatorów do skutecznego zarządzania systemami i rozwiązywania problemów.
- Przestrzeń: Niektóre systemy wymagają znacznej powierzchni
- Projektowanie systemu: Dobrze zaprojektowany system pozbawiania proszku będzie zawierał takie funkcje, jak regulowany przepływ powietrza, konfigurowalne ustawienia wibracji i precyzyjne mechanizmy zbierania proszku. Funkcje te pomagają w dostosowaniu systemu do różnych geometrii części i rodzajów proszku.
- Integracja technologii: Zaawansowane systemy depowderingu często integrują technologie, takie jak automatyczne szczotkowanie, wysokowydajne odkurzacze i myjki ultradźwiękowe, aby zapewnić dokładny i wydajny proces czyszczenia.
- Konserwacja i trwałość: Regularna konserwacja ma kluczowe znaczenie dla utrzymania maksymalnej wydajności systemu. Trwałe komponenty i łatwo dostępne punkty konserwacji mogą skrócić czas przestojów i wydłużyć żywotność systemu.
- Względy środowiskowe: Efektywne systemy są projektowane z myślą o ochronie środowiska. Obejmuje to takie funkcje, jak systemy zbierania pyłu, środki redukcji hałasu i energooszczędne operacje.
Wybór systemu depowderingu odpowiedniego do potrzeb
Wybór systemu depowderingu zależy od różnych czynników, w tym wielkości serii produkcyjnych, złożoności drukowanych części i budżetu. Oto kilka wskazówek, które pomogą Ci wybrać odpowiedni system:
- Złożoność części: W przypadku skomplikowanych części z drobnymi szczegółami należy wybrać system z wysoce precyzyjnymi możliwościami czyszczenia, takimi jak myjki ultradźwiękowe lub zaawansowane systemy nadmuchu powietrza.
- Wielkość produkcji: W przypadku produkcji wielkoseryjnej należy wybrać zautomatyzowane systemy, które oferują skalowalność i wydajność, takie jak wielkoskalowe systemy wibracyjne lub szybkie systemy próżniowe.
- Ograniczenia budżetowe: Jeśli masz ograniczony budżet, rozważ systemy klasy podstawowej, które zapewniają podstawowe funkcje depowderingu, ale nadal spełniają Twoje potrzeby.
Zastosowania i przypadki użycia systemów depowderingu
Przeanalizujmy kilka konkretnych przypadków użycia i scenariuszy, w których stosowane są systemy depowderingu.
Przemysł lotniczy
W przemyśle lotniczym komponenty takie jak łopatki turbin i części konstrukcyjne muszą być wolne od nadmiaru proszku, aby spełniać surowe normy bezpieczeństwa i wydajności. Systemy usuwania nadmiaru zapewniają, że komponenty te są dokładnie czyszczone przed poddaniem ich dalszej obróbce.
Przykład: Czyszczenie łopatek turbiny
- Wyzwanie: Łopatki turbin mają skomplikowane kanały chłodzące i drobne elementy, które wymagają starannego czyszczenia.
- Rozwiązanie: Precyzyjne systemy usuwania proszku wykorzystują połączenie nadmuchu powietrza i odsysania próżniowego w celu usunięcia proszku bez uszkodzenia ostrza.
Dziedzina medycyny
W przypadku implantów i urządzeń medycznych czystość i biokompatybilność mają ogromne znaczenie. Systemy depowderingu pomagają osiągnąć wymagane standardy dla implantów, takich jak stawy biodrowe, korony dentystyczne i urządzenia ortodontyczne.
Przykład: Implanty stawu biodrowego
- Wyzwanie: Implanty muszą być wolne od zanieczyszczeń, aby były bezpieczne dla ludzi.
- Rozwiązanie: Specjalistyczne systemy z filtracją drobnych cząstek i ostrożnymi procesami obsługi są stosowane w celu zapewnienia, że implanty są czyste i gotowe do sterylizacji.
Produkcja motoryzacyjna
W produkcji motoryzacyjnej, części takie jak komponenty silnika i elementy podwozia muszą być zarówno lekkie, jak i wytrzymałe. Systemy depowderingu przyczyniają się do produkcji wysokiej jakości części, które spełniają wymagające specyfikacje przemysłu motoryzacyjnego.
Przykład: Komponenty silnika
- Wyzwanie: Części muszą być skutecznie czyszczone, aby usunąć nadmiar proszku ze złożonych geometrii.
- Rozwiązanie: Zautomatyzowane systemy oczyszczania z regulowanymi parametrami radzą sobie z czyszczeniem różnych części silnika.
Elektronika
W przypadku komponentów elektronicznych, takich jak złącza i płytki drukowane, usunięcie nadmiaru proszku ma kluczowe znaczenie dla zapewnienia prawidłowych połączeń elektrycznych i funkcjonalności urządzenia.
Przykład: Złącza elektryczne
- Wyzwanie: Nadmiar proszku może zakłócać połączenia elektryczne.
- Rozwiązanie: Systemy usuwania proszku z precyzyjnymi dyszami powietrznymi i systemami próżniowymi usuwają proszek bez wpływu na złącza.
Przetwarzanie żywności
W przemyśle spożywczym części i urządzenia używane do przetwarzania żywności muszą spełniać surowe normy higieny i bezpieczeństwa. Systemy depowderingu pomagają utrzymać te standardy.
Przykład: Urządzenia do pakowania żywności
- Wyzwanie: Sprzęt musi być czysty i wolny od zanieczyszczeń, aby zapewnić bezpieczeństwo żywności.
- Rozwiązanie: Systemy zaprojektowane z higienicznych materiałów i łatwych do czyszczenia powierzchni są stosowane w urządzeniach do pakowania żywności.
Zalety i wady różnych technik depowderingu
Przyjrzyjmy się bliżej różnym technikom depowderingu, porównując ich zalety i wady.
Nadmuch powietrza a systemy próżniowe
| Technika | Plusy | Wady |
|---|---|---|
| Nadmuch powietrza | - Szybki i wydajny w przypadku większych części. | - Może być mniej skuteczny w przypadku drobnych lub złożonych geometrii. |
| - Prosta i łatwa konfiguracja. | - Potencjalne rozprzestrzenianie się pyłu w środowisku. | |
| Systemy próżniowe | - Skuteczny w usuwaniu drobnych proszków. | - Może być droższy. |
| - Minimalizuje dyspersję proszku i wpływ na środowisko. | - Może wymagać częstej konserwacji i wymiany filtrów. |
Czyszczenie ultradźwiękowe a systemy wibracyjne
| Technika | Plusy | Wady |
|---|---|---|
| Czyszczenie ultradźwiękowe | - Wysoka precyzja dla złożonych części. | - Wyższe koszty i wymagania konserwacyjne. |
| - Skutecznie dociera do skomplikowanych elementów. | - Wymaga ostrożnej obsługi w celu uniknięcia uszkodzeń. | |
| Systemy wibracyjne | - Skalowalność na potrzeby produkcji wielkoseryjnej. | - Może nie być tak precyzyjna w przypadku bardzo delikatnych części. |
| - Może obsługiwać różne kształty i rozmiary części. | - Może generować hałas i pył. |

Najczęściej zadawane pytania
Oto obszerna sekcja FAQ zawierająca odpowiedzi na najczęściej zadawane pytania dotyczące systemy depowderingu:
| Pytanie | Odpowiedź |
|---|---|
| Co to jest system depowderingu? | System usuwania proszku to narzędzie służące do usuwania nadmiaru proszku z drukowanych części 3D w celu zapewnienia czystego wykończenia. |
| Dlaczego depowdering jest ważny w produkcji addytywnej? | Depowdering zapewnia, że produkt końcowy jest czysty, funkcjonalny i spełnia standardy jakości wymagane dla jego zastosowania. |
| Jakie są główne metody stosowane w depowderingu? | Typowe metody obejmują przedmuchiwanie powietrzem, odsysanie próżniowe, czyszczenie ultradźwiękowe i systemy wibracyjne. |
| Jak wybrać system depowderingu odpowiedni do moich potrzeb? | Przy wyborze systemu depowderingu należy wziąć pod uwagę takie czynniki, jak złożoność części, wielkość produkcji i budżet. |
| Czy systemy depowderingu są przyjazne dla środowiska? | Owszem, rozpraszanie pyłu i zużycie energii budzą obawy, ale nowoczesne systemy zawierają funkcje, które rozwiązują te kwestie. |
| Czy systemy proszkowe mogą obsługiwać wszystkie rodzaje proszków metali? | Większość systemów jest uniwersalna, ale należy sprawdzić kompatybilność z określonymi proszkami i geometrią części. |
| Jak często system depoweringu wymaga konserwacji? | Częstotliwość konserwacji różni się w zależności od systemu i sposobu użytkowania, ale zazwyczaj obejmuje czyszczenie filtrów, kontrolę komponentów i sprawdzanie wydajności. |
| Jakie są przykłady zaawansowanych systemów depowderingu? | Zaawansowane systemy obejmują te z automatycznym szczotkowaniem, wysokowydajnymi odkurzaczami i zintegrowanymi funkcjami czyszczenia ultradźwiękowego. |
Wnioski
Systemy depowderingu odgrywają kluczową rolę w procesie produkcji addytywnej, oferując szereg rozwiązań zapewniających, że części drukowane w 3D spełniają najwyższe standardy jakości i wydajności. Od przemysłu lotniczego po zastosowania medyczne, systemy te są niezbędne do produkcji niezawodnych i precyzyjnych komponentów.
Niezależnie od tego, czy chcesz zainwestować w nowy system, czy ulepszyć istniejącą konfigurację, zrozumienie różnych rodzajów proszków metali, ich zastosowań i różnych technik usuwania proszków pomoże Ci podjąć świadomą decyzję. Weź pod uwagę takie czynniki jak wydajność, koszty i wymagania techniczne, aby wybrać najlepsze rozwiązanie dla swoich konkretnych potrzeb.
Udostępnij
MET3DP Technology Co., LTD jest wiodącym dostawcą rozwiązań w zakresie produkcji addytywnej z siedzibą w Qingdao w Chinach. Nasza firma specjalizuje się w sprzęcie do druku 3D i wysokowydajnych proszkach metali do zastosowań przemysłowych.
Zapytaj o najlepszą cenę i spersonalizowane rozwiązanie dla Twojej firmy!
Powiązane artykuły

Wysokowydajne segmenty łopatek dysz: Rewolucja w wydajności turbin dzięki drukowi 3D w metalu
Czytaj więcej "
Drukowane w 3D mocowania dla samochodowych czujników radarowych: Precyzja i wydajność
Czytaj więcej "Informacje o Met3DP
Ostatnia aktualizacja
Nasz produkt
KONTAKT
Masz pytania? Wyślij nam wiadomość teraz! Po otrzymaniu wiadomości obsłużymy Twoją prośbę całym zespołem.

Proszki metali do druku 3D i produkcji addytywnej
PRODUKT
cONTACT INFO
- Miasto Qingdao, Shandong, Chiny
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- +86 19116340731