Advanced Material Powders
Table of Contents
In the ever-evolving world of materials science and engineering, advanced material powders play a crucial role. These powders are at the heart of many technological advancements, contributing to innovations in various industries, from aerospace to biomedical engineering. But what exactly are these powders, and why are they so important? Let’s dive into the world of advanced material powders, exploring their types, compositions, properties, applications, and more.
Overview of Advanced Material Powders
Advanced material powders are finely divided solid particles that exhibit unique properties and are used in a variety of high-tech applications. These powders can be metallic, ceramic, polymeric, or composite in nature, and they are engineered to have specific properties that make them ideal for advanced manufacturing processes like additive manufacturing (3D printing), powder metallurgy, and surface coating.
Key Characteristics:
- High Surface Area: Due to their fine particle size, these powders have a large surface area which can enhance chemical reactivity and mechanical properties.
- Uniform Particle Size Distribution: Consistency in particle size ensures uniformity in the final product.
- Controlled Purity Levels: High purity levels are often required to achieve the desired properties and performance.
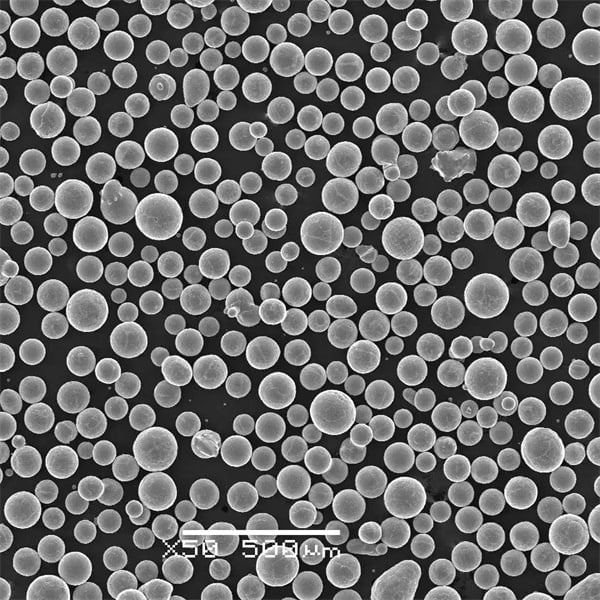
Types of Advanced Material Powders
Metallic Powders
Metallic powders are widely used in various industries due to their excellent mechanical properties, electrical conductivity, and thermal stability. Here are some specific models:
1. Titanium Alloy Powder (Ti-6Al-4V)
Composition: Titanium (90%), Aluminum (6%), Vanadium (4%)
Properties: High strength-to-weight ratio, excellent corrosion resistance, and good biocompatibility.
Applications: Aerospace components, medical implants, and high-performance automotive parts.
2. Stainless Steel Powder (316L)
Composition: Iron (65-70%), Chromium (16-18%), Nickel (10-14%), Molybdenum (2-3%)
Properties: Excellent corrosion resistance, high strength, and good weldability.
Applications: Medical devices, food processing equipment, and marine applications.
3. Nickel Alloy Powder (Inconel 718)
Composition: Nickel (50-55%), Chromium (17-21%), Iron (balance), Niobium (4.75-5.5%), Molybdenum (2.8-3.3%)
Properties: High-temperature strength, oxidation resistance, and good fatigue resistance.
Applications: Turbine blades, rocket engines, and high-temperature fasteners.
Ceramic Powders
Ceramic powders are used for their exceptional thermal stability, wear resistance, and electrical insulation properties. Here are a few notable ones:
4. Alumina Powder (Al2O3)
Composition: Aluminum oxide
Properties: High hardness, excellent thermal stability, and good electrical insulation.
Applications: Cutting tools, electronic substrates, and refractory materials.
5. Zirconia Powder (ZrO2)
Composition: Zirconium dioxide
Properties: High fracture toughness, thermal insulation, and good wear resistance.
Applications: Dental implants, thermal barrier coatings, and fuel cell components.
Polymeric Powders
Polymeric powders are known for their lightweight nature and versatility. They are widely used in industries requiring specific mechanical and chemical properties.
6. Nylon Powder (PA12)
Composition: Polyamide 12
Properties: High impact resistance, good chemical resistance, and flexibility.
Applications: Rapid prototyping, automotive components, and consumer goods.
Composite Powders
Composite powders combine different materials to achieve enhanced properties. They are used in applications where unique combinations of properties are required.
7. Tungsten Carbide-Cobalt Powder (WC-Co)
Composition: Tungsten carbide (90%), Cobalt (10%)
Properties: Exceptional hardness, high wear resistance, and good toughness.
Applications: Cutting tools, wear-resistant coatings, and mining equipment.
Rare Earth Metal Powders
These powders are essential in high-tech applications due to their unique magnetic, optical, and electronic properties.
8. Neodymium-Iron-Boron Powder (NdFeB)
Composition: Neodymium (29-32%), Iron (64-68%), Boron (1-2%)
Properties: Strongest magnetic properties, high resistance to demagnetization.
Applications: Permanent magnets in motors, wind turbines, and electronic devices.
Nano Powders
Nano powders are ultra-fine powders with particle sizes in the nanometer range. They exhibit unique properties due to their small size and high surface area.
9. Silver Nano Powder (Ag)
Composition: Silver
Properties: High electrical conductivity, antibacterial properties, and optical characteristics.
Applications: Conductive inks, medical devices, and electronic components.
10. Silicon Carbide Nano Powder (SiC)
Composition: Silicon carbide
Properties: High hardness, excellent thermal conductivity, and chemical stability.
Applications: High-performance ceramics, electronic devices, and composite materials.
Composition and Properties of Advanced Material Powders
| Type | Composition | Properties |
|---|---|---|
| Titanium Alloy (Ti-6Al-4V) | Ti (90%), Al (6%), V (4%) | High strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, biocompatibility |
| Stainless Steel (316L) | Fe (65-70%), Cr (16-18%), Ni (10-14%), Mo (2-3%) | Corrosion resistance, high strength, weldability |
| Nickel Alloy (Inconel 718) | Ni (50-55%), Cr (17-21%), Fe (balance), Nb (4.75-5.5%), Mo (2.8-3.3%) | High-temperature strength, oxidation resistance, fatigue resistance |
| Alumina (Al2O3) | Aluminum oxide | High hardness, thermal stability, electrical insulation |
| Zirconia (ZrO2) | Zirconium dioxide | Fracture toughness, thermal insulation, wear resistance |
| Nylon (PA12) | Polyamide 12 | Impact resistance, chemical resistance, flexibility |
| Tungsten Carbide-Cobalt (WC-Co) | WC (90%), Co (10%) | Hardness, wear resistance, toughness |
| Neodymium-Iron-Boron (NdFeB) | Nd (29-32%), Fe (64-68%), B (1-2%) | Strong magnetic properties, demagnetization resistance |
| Silver Nano Powder (Ag) | Silver | Electrical conductivity, antibacterial, optical properties |
| Silicon Carbide Nano Powder (SiC) | Silicon carbide | Hardness, thermal conductivity, chemical stability |
Applications of Advanced Material Powders
Advanced material powders are indispensable in a variety of high-tech applications. Their unique properties enable innovations across multiple industries.
| Powder Type | Applications |
|---|---|
| Titanium Alloy (Ti-6Al-4V) | Aerospace components, medical implants, automotive parts |
| Stainless Steel (316L) | Medical devices, food processing equipment, marine applications |
| Nickel Alloy (Inconel 718) | Turbine blades, rocket engines, high-temperature fasteners |
| Alumina (Al2O3) | Cutting tools, electronic substrates, refractory materials |
| Zirconia (ZrO2) | Dental implants, thermal barrier coatings, fuel cell components |
| Nylon (PA12) | Rapid prototyping, automotive components, consumer goods |
| Tungsten Carbide-Cobalt (WC-Co) | Cutting tools, wear-resistant coatings, mining equipment |
| Neodymium-Iron-Boron (NdFeB) | Permanent magnets in motors, wind turbines, electronic devices |
| Silver Nano Powder (Ag) | Conductive inks, medical devices, electronic components |
| Silicon Carbide Nano Powder (SiC) | High-performance ceramics, electronic devices, composite materials |
Specifications, Sizes, Grades, and Standards
| Powder Type | Sizes (µm) | Grades | Standards |
|---|---|---|---|
| Titanium Alloy (Ti-6Al-4V) | 15-45 | Grade 5 | ASTM F136, ASTM B348 |
| Stainless Steel (316L) | 10-50 | Grade 316L | ASTM A240, ASTM A276 |
| Nickel Alloy (Inconel 718) | 20-60 | Grade 718 | AMS 5662, ASTM B637 |
| Alumina (Al2O3) | 0.5-20 | Grade A | ISO 6474-1 |
| Zirconia (ZrO2) | 0.1-10 | Grade Y-TZP | ISO 13356 |
| Nylon (PA12) | 20-100 | Grade PA12 | ISO 1874-1 |
| Tungsten Carbide-Cobalt (WC-Co) | 0.2-10 | Grade K10 | ISO 513 |
| Neodymium-Iron-Boron (NdFeB) | 2-5 | Grade N42 | IEC 60404-8-1 |
| Silver Nano Powder (Ag) | 20-50 nm | Nano grade | ISO/TS 80004-2 |
| Silicon Carbide Nano Powder (SiC) | 10-100 nm | Nano grade | ISO/TS 80004-4 |
Suppliers and Pricing Details
Finding reliable suppliers of advanced material powders is crucial for ensuring quality and consistency in manufacturing processes. Here are some reputable suppliers along with indicative pricing information:
| Powder Type | Suppliers | Pricing (per kg, USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Titanium Alloy (Ti-6Al-4V) | ATI Specialty Materials, Arconic, Carpenter | $200 – $300 |
| Stainless Steel (316L) | Sandvik, Carpenter, EOS | $50 – $80 |
| Nickel Alloy (Inconel 718) | Special Metals Corporation, Carpenter | $300 – $400 |
| Alumina (Al2O3) | Almatis, CoorsTek, Saint-Gobain | $10 – $20 |
| Zirconia (ZrO2) | Tosoh Corporation, Saint-Gobain | $50 – $100 |
| Nylon (PA12) | Evonik, BASF, Arkema | $20 – $40 |
| Tungsten Carbide-Cobalt (WC-Co) | Kennametal, Sandvik, Ceratizit | $100 – $150 |
| Neodymium-Iron-Boron (NdFeB) | Hitachi Metals, Shin-Etsu Chemical | $80 – $120 |
| Silver Nano Powder (Ag) | Ames Goldsmith, American Elements | $300 – $500 |
| Silicon Carbide Nano Powder (SiC) | Sigma-Aldrich, US Research Nanomaterials | $100 – $200 |
Pros and Cons of Advanced Material Powders
When considering the use of advanced material powders, it’s essential to weigh their advantages and limitations to make informed decisions.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| High strength-to-weight ratio | High cost compared to conventional materials |
| Tailored properties for specific applications | Challenges in powder handling and storage |
| Enhanced performance in extreme environments | Post-processing complexities in additive manufacturing |
| Design flexibility in complex geometries | Potential for contamination in powder feedstocks |
| Improved efficiency in material usage | Limited availability of certain specialized powders |
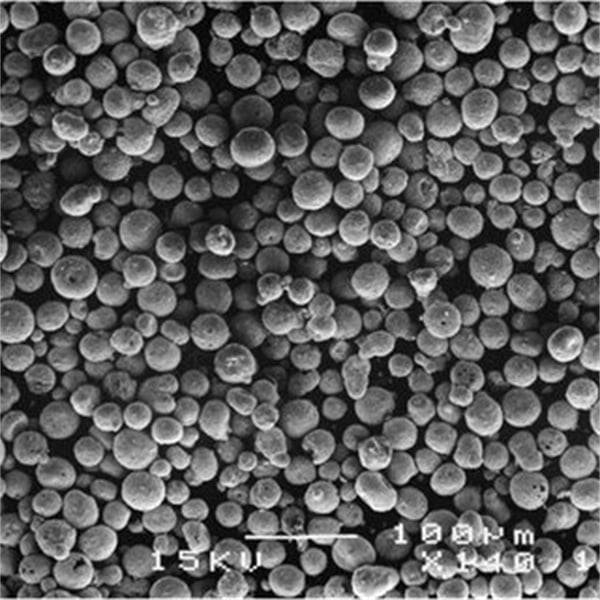
FAQs
What are the primary applications of titanium alloy powder (Ti-6Al-4V)?
Titanium alloy powder (Ti-6Al-4V) is extensively used in aerospace components due to its high strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility. It’s also employed in medical implants and high-performance automotive parts.
How does stainless steel powder (316L) compare to other alloys in terms of corrosion resistance?
Stainless steel powder (316L) offers superior corrosion resistance compared to many other alloys, making it suitable for demanding applications in medical devices, food processing equipment, and marine environments.
What are the advantages of using silver nano powder (Ag) in conductive inks?
Silver nano powder (Ag) exhibits high electrical conductivity, making it ideal for conductive inks used in printed electronics. Its nano-sized particles enable smooth printing and excellent adhesion to substrates.
How can advanced material powders contribute to sustainable manufacturing practices?
By enabling precise material usage and reducing waste in manufacturing processes, advanced material powders contribute to sustainable practices. Their efficiency in energy consumption and resource utilization supports environmental conservation efforts.
What are the challenges associated with using tungsten carbide-cobalt powder (WC-Co) in cutting tools?
Tungsten carbide-cobalt powder (WC-Co) offers exceptional hardness and wear resistance but can be challenging to machine due to its high hardness. Proper handling and tooling are crucial to maximize its performance in cutting applications.
Conclusion
Advanced material powders represent the forefront of materials science, offering tailored solutions to meet the demanding requirements of modern technology. Whether in aerospace, medical, automotive, or consumer goods industries, these powders continue to push the boundaries of innovation. By understanding their compositions, properties, applications, and challenges, manufacturers can harness their full potential to drive forward in their respective fields.
For more detailed technical specifications and procurement guidance, consulting with trusted suppliers and keeping abreast of advancements in materials research are essential. Embracing these advanced powders not only enhances product performance but also fosters sustainable practices in manufacturing. As technology evolves, so too will the capabilities and applications of these remarkable materials.
Share On
MET3DP Technology Co., LTD is a leading provider of additive manufacturing solutions headquartered in Qingdao, China. Our company specializes in 3D printing equipment and high-performance metal powders for industrial applications.
Inquiry to get best price and customized Solution for your business!
Related Articles
About Met3DP
Recent Update
Our Product
CONTACT US
Any questions? Send us message now! We’ll serve your request with a whole team after receiving your message.

Metal Powders for 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing
COMPANY
PRODUCT
cONTACT INFO
- Qingdao City, Shandong, China
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- +86 19116340731