The Intricacies of Bonded Powder
Table of Contents
Bonded powder, a crucial material in various industrial applications, offers unique properties and advantages. This article delves into the specifics of bonded powder, discussing its types, composition, applications, and much more. We’ll also look at specific metal powder models, providing detailed descriptions and comparisons to help you understand their utility and performance.
Overview of Bonded Powder
Bonded powder technology involves combining different types of powders to create a composite material with enhanced properties. These powders can include metals, ceramics, or other substances, and they are bonded using various methods such as mechanical alloying, thermal spray, or sintering. The resulting materials exhibit improved characteristics like increased strength, corrosion resistance, and thermal stability.
Key Features of Bonded Powder
- Enhanced Properties: Bonded powders are designed to leverage the best characteristics of their constituent materials.
- Versatility: Used in numerous industries including aerospace, automotive, electronics, and medical devices.
- Customizability: Powders can be tailored to specific applications by adjusting their composition and bonding techniques.
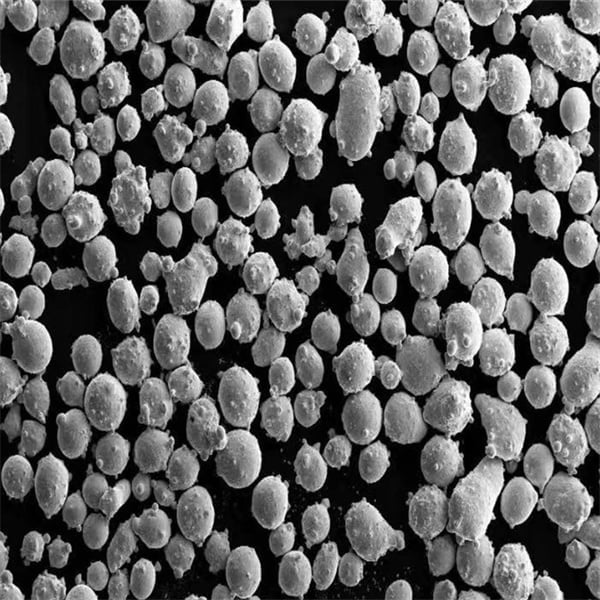
Types and Properties of Bonded Powders
Below is a table summarizing the types, composition, properties, and characteristics of various bonded powders.
| Type | Composition | Properties | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Metal-Ceramic Bonded Powder | Metal (e.g., Aluminum) + Ceramic (e.g., Alumina) | High strength, wear resistance | Suitable for high-stress environments |
| Thermal Spray Powders | Nickel, Chromium, Cobalt alloys | Thermal stability, corrosion resistance | Used in coating applications |
| Sintered Powders | Iron, Copper, Tungsten alloys | Enhanced mechanical properties | Common in automotive components |
| Composite Powders | Metal matrix composites (MMCs) | Superior wear resistance, lightweight | Aerospace and structural applications |
| Additive Manufacturing Powders | Titanium, Stainless Steel, Aluminum | High precision, strength | 3D printing and rapid prototyping |
Applications of Bonded Powder
Bonded powders find applications in various fields due to their enhanced properties. Here’s a table showcasing their typical uses:
| Application | Examples | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Turbine blades, structural components | High strength-to-weight ratio, thermal stability |
| Automotive | Engine parts, brake components | Wear resistance, durability |
| Electronics | Conductive pastes, heat sinks | Thermal conductivity, electrical properties |
| Medical Devices | Implants, prosthetics | Biocompatibility, corrosion resistance |
| Industrial Coatings | Protective coatings, thermal barriers | Corrosion protection, thermal insulation |
Specifications and Standards for Bonded Powder
The following table lists various specifications, sizes, grades, and standards for bonded powders:
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Particle Size | Ranges from nano to micrometer scales depending on application |
| Grades | Vary by alloy and application (e.g., Ti-6Al-4V for titanium powders) |
| Standards | ISO, ASTM standards specific to material type and use case |
| Purity Levels | High purity (99.9%+) for critical applications |
| Density | Tailored to meet specific mechanical requirements |
Suppliers and Pricing Details for Bonded Powder
Here’s a table summarizing key suppliers and indicative pricing details:
| Supplier | Location | Materials Supplied | Price Range (per kg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Höganäs AB | Sweden | Iron, Steel, Stainless Steel Powders | $30 – $100 |
| Carpenter Technology | USA | Nickel, Titanium, Cobalt Powders | $100 – $500 |
| Sandvik | Global | Metal-Ceramic Composites | $50 – $200 |
| Oerlikon Metco | Switzerland | Thermal Spray Powders | $200 – $800 |
| GKN Additive | UK | Additive Manufacturing Powders | $150 – $600 |
Comparing Pros and Cons of Bonded Powder Types
Below is a table comparing the advantages and limitations of different bonded powders:
| Type | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Metal-Ceramic | High strength, wear resistance | Higher cost, processing complexity |
| Thermal Spray | Excellent thermal and corrosion resistance | Requires specialized equipment |
| Sintered | Good mechanical properties, cost-effective | Limited to certain geometries |
| Composite | Lightweight, superior wear resistance | Expensive raw materials |
| Additive Manufacturing | High precision, customizable | High initial setup cost, slower production speed |
Specific Metal Powder Models
Here’s a detailed look at ten specific metal powder models, highlighting their unique properties and applications:
1. Höganäs Ancorsteel 1000
A versatile iron-based powder, ideal for structural parts in automotive applications due to its excellent compressibility and high green strength.
2. Carpenter 20Cb-3
A nickel-based superalloy powder known for its exceptional corrosion resistance and high-temperature performance, commonly used in aerospace and chemical processing industries.
3. Sandvik Osprey 17-4 PH
A stainless steel powder that combines high strength, good corrosion resistance, and excellent weldability, making it suitable for additive manufacturing and tooling applications.
4. Oerlikon Metco 73F-NS
A thermal spray powder composed of nickel and chromium, providing outstanding thermal and oxidation resistance, ideal for coating turbine components.
5. GKN Titanium Ti-6Al-4V
A widely used titanium alloy powder for additive manufacturing, known for its high strength-to-weight ratio and biocompatibility, extensively used in medical implants and aerospace parts.
6. Höganäs Astaloy CrM
An iron-chromium-molybdenum alloy powder offering high hardenability and good wear resistance, often used in high-performance gears and automotive parts.
7. Carpenter Custom 465
A martensitic stainless steel powder with excellent toughness and strength, utilized in aerospace components and high-performance sporting goods.
8. Sandvik Osprey 625
A nickel-based superalloy powder with superb corrosion and oxidation resistance, perfect for marine and chemical processing environments.
9. Oerlikon Metco 307NS
A cobalt-based alloy powder for thermal spray applications, known for its high wear resistance and good high-temperature strength, used in industrial gas turbines.
10. GKN Aluminum AlSi10Mg
An aluminum alloy powder suitable for additive manufacturing, offering a good balance of mechanical properties and lightweight, ideal for aerospace and automotive applications.
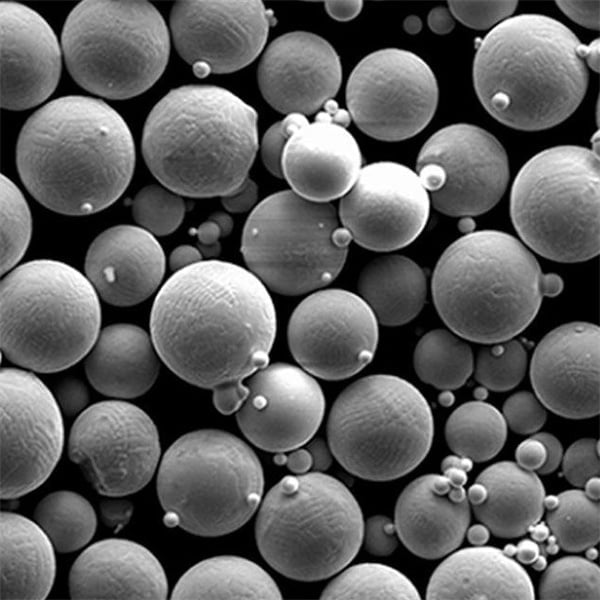
Advantages and Disadvantages of Bonded Powder
Advantages of Bonded Powder
- Enhanced Properties: Bonded powders can achieve superior mechanical and physical properties compared to single-material powders.
- Versatility: They can be used in a wide range of industries and applications, from aerospace to medical devices.
- Customization: The composition of bonded powders can be tailored to meet specific requirements of different applications.
- Improved Performance: Increased wear resistance, thermal stability, and corrosion resistance make them ideal for demanding environments.
Disadvantages of Bonded Powder
- Cost: The production and processing of bonded powders can be more expensive than traditional materials.
- Complexity: The manufacturing processes involved in creating bonded powders are often more complex and require specialized equipment.
- Processing Challenges: Achieving uniform bonding and consistency can be challenging, potentially affecting the quality and performance of the final product.

FAQ
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is bonded powder? | Bonded powder refers to composite materials made by combining different types of powders to enhance their properties. |
| What are the advantages of using bonded powders? | They offer enhanced mechanical and physical properties, versatility, and customization for specific applications. |
| Where are bonded powders commonly used? | They are used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, electronics, medical devices, and industrial coatings. |
| What are some common types of bonded powders? | Metal-ceramic powders, thermal spray powders, sintered powders, composite powders, and additive manufacturing powders. |
| How are bonded powders manufactured? | Methods include mechanical alloying, thermal spray, and sintering. |
| What are some challenges associated with bonded powders? | Higher costs, complex manufacturing processes, and consistency issues during production. |
Conclusion
Bonded powders represent a fascinating and highly versatile class of materials with a wide array of applications across multiple industries. By understanding the types, properties, applications, and specific models of bonded powders, manufacturers and engineers can make informed decisions to optimize their processes and products. Despite the challenges associated with their production and cost, the advantages of bonded powders in terms of enhanced properties and performance make them a valuable choice for advanced technological applications.
Feel free to explore the specific metal powder models discussed here, each offering unique benefits suited to various industrial needs. Whether you’re in aerospace, automotive, or any other sector, bonded powders could be the key to unlocking new levels of performance and innovation in your projects.
Share On
MET3DP Technology Co., LTD is a leading provider of additive manufacturing solutions headquartered in Qingdao, China. Our company specializes in 3D printing equipment and high-performance metal powders for industrial applications.
Inquiry to get best price and customized Solution for your business!
Related Articles
About Met3DP
Recent Update
Our Product
CONTACT US
Any questions? Send us message now! We’ll serve your request with a whole team after receiving your message.

Metal Powders for 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing
COMPANY
PRODUCT
cONTACT INFO
- Qingdao City, Shandong, China
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- +86 19116340731

















