Electrode Induction Melting Inert Gas (EIGA)
Table of Contents
Imagine a world where crafting intricate parts with exotic metals wasn’t limited by contamination or poor quality. Enter Electrode Induction Melting Inert Gas (EIGA), a revolutionary process that’s shaking up the metal powder production scene. This innovative technique offers a gateway to a universe of possibilities for engineers, researchers, and manufacturers alike. But what exactly is EIGA, and how does it work its magic? Buckle up, because we’re about to embark on a journey into the heart of molten metal and cutting-edge technology.
Unveiling the EIGA Process: A Crucible-Free Revolution
EIGA stands for Electrode Induction Melting Inert Gas Atomization. Let’s break down this mouthful term piece by piece. First, we have the “Electrode Induction Melting” part. Picture a constantly rotating metal rod – the electrode – immersed within a specially designed coil. This coil, energized by high-frequency electricity, acts like a magical wand, heating the electrode through a phenomenon called induction. Unlike traditional melting methods that rely on external heat sources, EIGA heats the metal from within, ensuring uniform and precise control over the melting process.
Now, here’s where things get interesting. The entire melting chamber is bathed in an inert gas, typically argon or helium. This gas, devoid of reactive elements like oxygen or nitrogen, acts as a shield, preventing the molten metal from any unwanted interactions that could compromise its purity.
Finally, the grand finale – the atomization. Once the metal reaches its molten state, it drips from the bottom of the electrode. This molten stream encounters a high-pressure stream of the same inert gas, shattering it into tiny droplets that rapidly solidify into fine, spherical metal powders.
The Magic of EIGA: A Crucible-Free Advantage
One of the most significant advantages of EIGA lies in its “crucible-free” design. Traditional melting techniques often involve crucibles made of ceramic materials. While they get the job done, these crucibles can introduce unwanted contaminants into the molten metal, impacting its final properties. EIGA eliminates this risk altogether. Because the melt never touches any container, the resulting powder boasts exceptional purity, making it ideal for applications demanding the highest quality.
A Glimpse into the EIGA Metal Powder Menagerie
The beauty of EIGA lies in its versatility. It can be used to produce a wide range of metal powders, each with unique properties and applications. Here’s a sneak peek into some of the most popular EIGA metal powder varieties:
- Titanium Powders: These lightweight, high-strength powders are perfect for aerospace, biomedical, and sporting goods applications. EIGA-produced titanium powders offer exceptional purity and flowability, making them ideal for additive manufacturing techniques like 3D printing.
- Nickel Powders: Renowned for their corrosion resistance and high-temperature performance, nickel powders find their place in everything from electronics and catalysts to chemical processing equipment. EIGA ensures minimal oxygen content, a crucial factor for optimal nickel powder performance.
- Cobalt Powders: A vital component of lithium-ion batteries, permanent magnets, and superalloys, cobalt powders benefit tremendously from EIGA’s clean processing. The resulting powders exhibit superior magnetic properties and chemical stability.
- Iron Powders: The workhorse of the metalworking industry, iron powders are used in applications ranging from metal injection molding to powder metallurgy. EIGA-processed iron powders offer excellent control over particle size and morphology, leading to enhanced performance in finished parts.
- Copper Powders: Highly conductive and malleable, copper powders are in high demand for electronics, electrical components, and heat sinks. EIGA ensures minimal oxidation, a critical factor for maintaining copper’s exceptional electrical conductivity.
- Aluminum Powders: Lightweight and versatile, aluminum powders find use in everything from aerospace components to pyrotechnics. EIGA processing minimizes the formation of surface oxides, leading to superior powder flowability and reactivity.
- Stainless Steel Powders: Offering a combination of strength, corrosion resistance, and aesthetics, stainless steel powders are a game-changer for various industries. EIGA ensures these powders retain the desirable properties of their bulk counterparts, making them perfect for additive manufacturing.
- Inconel Powders: These high-performance nickel-chromium alloys are renowned for their resistance to extreme temperatures and harsh environments. EIGA processing helps preserve the unique properties of Inconel, making them ideal for jet engine components and other demanding applications.
- Tungsten Powders: Incredibly dense and heat-resistant, tungsten powders are essential for applications like welding electrodes, heat sinks, and armor-piercing projectiles. EIGA ensures minimal decarburization, a critical factor for maintaining tungsten’s high melting point and strength.
- Molybdenum Powders: Another high-temperature hero,
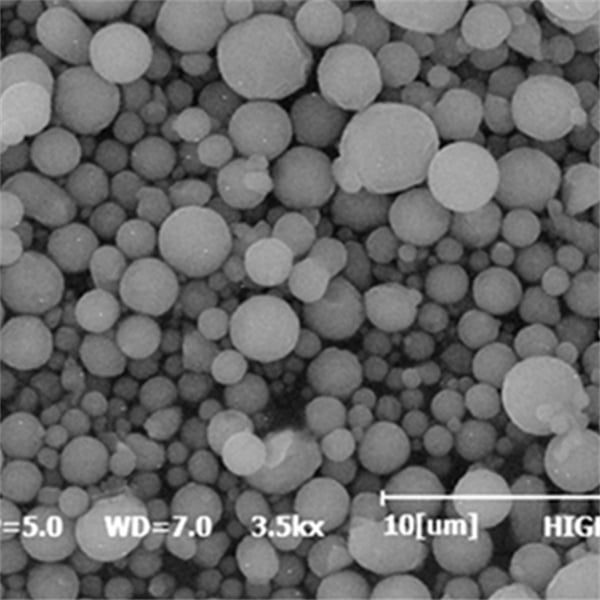
Unveiling the Applications of EIGA Metal Powders
The exceptional purity and controlled properties of EIGA metal powders unlock a treasure trove of applications across various industries. Here’s a glimpse into how these remarkable powders are transforming the manufacturing landscape:
- Additive Manufacturing (AM): EIGA shines brightest in the realm of AM, also known as 3D printing. The spherical morphology and consistent flowability of EIGA powders make them ideal for various AM techniques, like laser melting and electron beam melting. This translates to the creation of complex, high-performance parts with superior mechanical properties. Imagine constructing intricate aerospace components, lightweight medical implants, or even customized prosthetics – all thanks to the magic of EIGA powders.
- Metal Injection Molding (MIM): This technique combines the precision of injection molding with the strength and versatility of metals. EIGA powders, with their fine particle size and excellent packing density, are tailor-made for MIM. This allows for the mass production of intricate and near-net-shape metal parts with complex geometries. From intricate gears and fasteners to intricate medical devices, MIM with EIGA powders opens doors to previously unimaginable design possibilities.
- Thermal Spraying: This process involves depositing molten or semi-molten material onto a substrate to create a protective coating. EIGA powders, with their excellent flowability and high purity, are ideal for thermal spraying applications. They can be used to create wear-resistant coatings for tools and machinery, corrosion-resistant barriers for pipelines and storage tanks, and even biocompatible coatings for medical implants.
- Brazing and Welding: EIGA powders can be used as filler materials in brazing and welding processes. Their controlled melting points and superior wetting characteristics create strong and reliable joints. This opens doors for applications in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and construction.
- Catalysts: Certain EIGA metal powders, like platinum or palladium, find use as catalysts in chemical reactions. Their high surface area and controlled particle size enhance their catalytic efficiency, leading to faster reaction times and improved product yields.
Unveiling Hidden Gems of EIGA Applications
The potential applications of EIGA metal powders extend far beyond the traditional domains. Here are some exciting possibilities on the horizon:
- Biomedical Engineering: The exceptional biocompatibility of certain EIGA powders, like titanium and tantalum, makes them ideal for creating customized implants and prosthetics. Their high purity minimizes the risk of rejection, paving the way for a future of personalized medical care.
- Electronics: EIGA copper and aluminum powders hold immense promise for creating high-performance electronic components with superior conductivity and thermal management properties. This could revolutionize the miniaturization and efficiency of future electronic devices.
- Energy Storage: The unique properties of EIGA powders, like their high surface area and controlled morphology, make them prime candidates for next-generation battery technologies. This could lead to the development of more efficient and longer-lasting batteries, a critical factor in the transition to a sustainable future.
Specifications and Standards
Selecting the right EIGA metal powder for your application requires careful consideration of its specifications and adherence to relevant standards. Here’s a breakdown of some key parameters to keep in mind:
- Particle Size Distribution (PSD): This parameter refers to the variation in size of the individual particles within the powder. EIGA powders can be tailored to have a narrow or broad PSD depending on the desired application. For instance, finer powders may be better suited for AM techniques, while coarser powders might be preferred for thermal spraying.
- Chemical Composition: EIGA powders boast exceptional purity. However, trace elements can still be present, and their exact composition is crucial for specific applications. Manufacturers typically provide detailed chemical analysis reports to ensure users get the precise powder for their needs.
- Flowability: This refers to the ease with which the powder flows. EIGA powders generally exhibit excellent flowability due to their spherical shape and smooth surface. Good flowability is essential for processes like AM and MIM, where consistent powder feeding is critical.
- Surface Area: The surface area of the powder particles plays a significant role in applications like catalysis and brazing. EIGA powders can be engineered to have a high surface area, maximizing their effectiveness in these processes.
- Standards: Several international and national standards govern the quality and specifications of metal powders. Common standards include ASTM International (ASTM) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). Choosing EIGA powders that comply with these standards ensures consistent quality and performance.
Suppliers and Pricing
The EIGA metal powder market is experiencing rapid growth, with several leading suppliers offering a diverse range of powders. Here’s a glimpse into the supplier landscape and pricing considerations:
- Leading Suppliers: Some of the prominent names in the EIGA metal powder market include:
- Carpenter Additive (USA): Renowned for their high-quality titanium and nickel alloy powders, Carpenter Additive offers a range of EIGA powders tailored for additive manufacturing applications.
- ALD Vacuum Technologies (Germany): This established company provides a comprehensive portfolio of EIGA powders, including titanium, aluminum, and reactive metals.
- Höganäs AB (Sweden): A global leader in metal powder production, Höganäs offers EIGA powders for various applications, including AM, MIM, and thermal spraying.
- Hunan Skyline Smart Material & Technology Co., Ltd. (China): This emerging player specializes in EIGA titanium and titanium alloy powders, catering to the growing demand in the Asian market.
- LP Powder (UK): Focused on high-performance metal powders, LP Powder offers EIGA options for a variety of applications, including aerospace and medical devices.
- Pricing Considerations: The cost of EIGA metal powders can vary depending on several factors, including:
- Metal Type: Powders made from precious metals like platinum or palladium will naturally be more expensive than those made from common metals like iron or aluminum.
- Purity Level: Higher purity powders with lower oxygen content typically command a premium price.
- Particle Size Distribution: Powders with a very narrow or precise PSD may be more expensive due to the additional processing involved.
- Order Quantity: Bulk purchases generally benefit from economies of scale, leading to lower per-unit costs.
Weighing the Pros and Cons
While EIGA powders offer a plethora of advantages, it’s essential to consider their limitations before making a purchasing decision. Here’s a balanced perspective on the pros and cons:
Advantages of EIGA Metal Powders:
- Exceptional Purity: EIGA’s crucible-free design minimizes contamination, leading to powders with superior purity levels.
- Consistent Quality: The controlled nature of the EIGA process ensures consistent powder properties across batches.
- Fine Particle Size and Spherical Morphology: The ideal characteristics for optimal flowability and performance in various applications.
- Broad Range of Materials: EIGA can be used to produce a diverse range of metal powders, catering to various industry needs.
- Tailored Properties: EIGA powders can be customized to meet specific application requirements, such as particle size or surface area.
Disadvantages of EIGA Metal Powders:
- Higher Cost: Compared to traditional atomization methods, EIGA powders can be more expensive due to the sophisticated technology involved.
- Limited Production Capacity: The EIGA process might have a lower production capacity compared to some conventional techniques.
- Process Complexity: EIGA setups require a high level of expertise to operate and maintain.
Finding the Right Balance: Choosing the Ideal EIGA Metal Powder
The decision to use EIGA metal powders boils down to a cost-benefit analysis. If your application demands exceptional purity, consistent quality, and tailored properties, then EIGA powders are a compelling option. However, if cost is a primary concern, and high purity isn’t absolutely necessary, traditional atomization methods might be a more suitable choice.
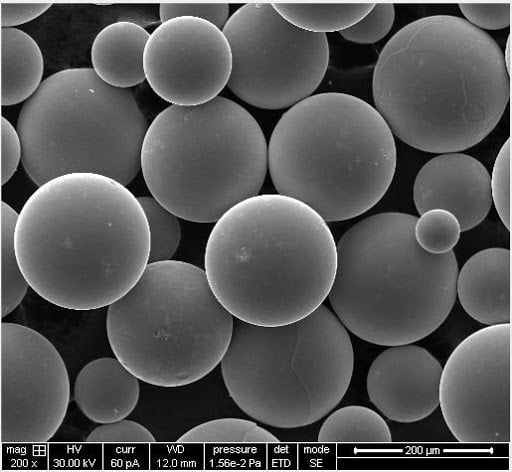
FAQ
Q: What are the typical applications of EIGA metal powders?
A: EIGA metal powders find use in various applications, including additive manufacturing, metal injection molding, thermal spraying, brazing and welding, catalysis, and even biocompatible coatings for medical implants.
Q: What are the advantages of EIGA powders compared to traditionally atomized powders?
A: EIGA powders offer superior purity, consistent quality, finer particle size, and a spherical morphology. These characteristics translate to improved performance in various applications.
Q: Are EIGA metal powders more expensive than traditionally atomized powders?
A: Generally, yes. The EIGA process is more complex, leading to a higher cost per unit of powder compared to some traditional methods.
Q: What factors influence the cost of EIGA metal powders?
A: The metal type, purity level, particle size distribution, and order quantity all play a role in determining the final cost of EIGA metal powders.
Q: How do I choose the right EIGA metal powder for my application?
A: Consider your specific application requirements, including the desired metal type, purity level, particle size, and budget. Consulting with a reputable EIGA metal powder supplier can also be helpful.
Share On
MET3DP Technology Co., LTD is a leading provider of additive manufacturing solutions headquartered in Qingdao, China. Our company specializes in 3D printing equipment and high-performance metal powders for industrial applications.
Inquiry to get best price and customized Solution for your business!
Related Articles
About Met3DP
Recent Update
Our Product
CONTACT US
Any questions? Send us message now! We’ll serve your request with a whole team after receiving your message.

Metal Powders for 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing
COMPANY
PRODUCT
cONTACT INFO
- Qingdao City, Shandong, China
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- +86 19116340731

















