Electrode Induction Melting Inert Gas Atomisation
Table of Contents
Overview
Electrode Induction Melting Inert Gas Atomisation (EIGA) is a cutting-edge process used to produce high-quality metal powders. This technique, known for its precision and efficiency, involves melting metal electrodes through induction heating in an inert gas atmosphere, followed by atomisation to form fine metal powders. EIGA is widely employed in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and medical for its ability to produce powders with uniform particle sizes and exceptional purity.
In this article, we’ll dive deep into the EIGA process, explore various metal powder models, and discuss their specific applications, properties, and benefits. We’ll also compare EIGA with other powder production methods, examine its advantages and limitations, and provide practical insights into its industrial applications.
Understanding Electrode Induction Melting Inert Gas Atomisation
What is EIGA?
EIGA is a process designed to produce fine, high-purity metal powders by melting metal electrodes using induction heating in an inert gas environment, usually argon or nitrogen. This method ensures minimal contamination and oxidation of the metals, resulting in superior quality powders.
How Does EIGA Work?
The EIGA process involves several key steps:
- Induction Melting: Metal electrodes are melted using high-frequency induction heating.
- Inert Gas Atmosphere: The melting occurs in an inert gas environment to prevent oxidation.
- Atomisation: The molten metal is then atomised using a high-pressure inert gas stream, breaking it into fine droplets.
- Solidification: These droplets solidify into fine metal powders upon cooling.
Benefits of EIGA
- High Purity: The inert gas environment minimizes contamination and oxidation.
- Uniform Particle Size: The process allows for precise control over particle size distribution.
- Versatility: Suitable for a wide range of metals and alloys.
- Efficiency: High production rates with minimal waste.
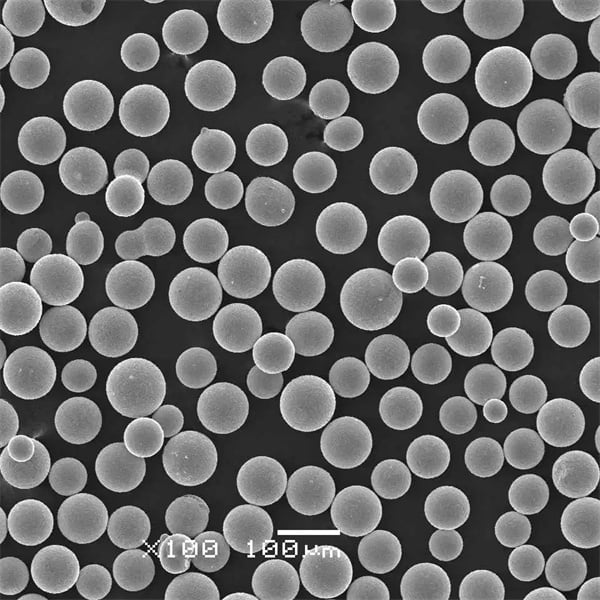
Types of Metal Powders Produced by EIGA
Specific Metal Powder Models
Here are ten specific metal powders produced using the EIGA process, along with their unique characteristics and applications:
| Metal Powder | Composition | Properties | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Titanium (Ti) | Pure Titanium | High strength, low density, excellent corrosion resistance | Aerospace components, medical implants |
| Nickel (Ni) | Pure Nickel | High melting point, good corrosion resistance | Turbine blades, aerospace engines |
| Aluminum (Al) | Pure Aluminum | Lightweight, good conductivity | Automotive parts, electrical components |
| Stainless Steel (SS) | Fe-Cr-Ni Alloy | Corrosion resistance, high strength | Medical instruments, kitchenware |
| Cobalt-Chrome (CoCr) | Co-Cr Alloy | High wear resistance, biocompatibility | Dental implants, orthopedic devices |
| Copper (Cu) | Pure Copper | Excellent electrical and thermal conductivity | Electrical components, heat exchangers |
| Inconel (Ni-Cr) | Ni-Cr Alloy | High temperature strength, oxidation resistance | Aerospace, chemical processing |
| Tool Steel (TS) | Fe-C alloy | High hardness, wear resistance | Cutting tools, molds |
| Magnesium (Mg) | Pure Magnesium | Lightweight, high strength-to-weight ratio | Aerospace, automotive |
| Bronze (Cu-Sn) | Cu-Sn Alloy | Good wear resistance, high strength | Bearings, bushings |
Properties and Characteristics of EIGA Metal Powders
Key Characteristics
EIGA-produced metal powders exhibit several notable characteristics that make them suitable for various high-performance applications:
- Particle Size Distribution: EIGA allows for precise control over the size of the metal powder particles, ensuring uniformity and consistency.
- High Purity: The use of an inert gas atmosphere significantly reduces the risk of contamination, resulting in high-purity metal powders.
- Spherical Shape: The atomisation process produces powders with a spherical shape, enhancing flowability and packing density.
- Minimal Oxidation: The inert gas environment prevents oxidation, preserving the integrity of the metal powders.
Table: Properties of EIGA Metal Powders
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Particle Size Range | Typically 10-100 microns |
| Purity Level | Up to 99.99% depending on the metal |
| Shape | Spherical |
| Flowability | Excellent due to spherical shape |
| Density | Consistent and high packing density |
| Oxidation Resistance | Minimal due to inert gas environment |
Applications of EIGA Metal Powders
Industries and Uses
EIGA metal powders are used across various industries due to their superior properties and versatility. Here are some common applications:
| Industry | Application | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Turbine blades, structural components | High strength, lightweight, corrosion resistance |
| Automotive | Engine parts, lightweight components | Reduced weight, improved fuel efficiency |
| Medical | Implants, surgical instruments | Biocompatibility, high strength |
| Electronics | Conductive components, heat sinks | Excellent conductivity, thermal management |
| Energy | Wind turbine parts, nuclear reactor components | High temperature resistance, durability |
| Manufacturing | 3D printing, additive manufacturing | Precision, customization, rapid prototyping |
| Jewelry | High-quality, intricate designs | High purity, aesthetic appeal |
| Tooling | Cutting tools, molds | High hardness, wear resistance |
Table: Applications of EIGA Metal Powders
| Application | Metal Powder | Reason for Use |
|---|---|---|
| Turbine Blades | Nickel, Inconel | High temperature strength, oxidation resistance |
| Medical Implants | Titanium, CoCr | Biocompatibility, high strength |
| Engine Components | Aluminum, Magnesium | Lightweight, high strength-to-weight ratio |
| 3D Printing | Stainless Steel, Tool Steel | Precision, customization |
| Electrical Components | Copper, Aluminum | Excellent conductivity |
| Cutting Tools | Tool Steel, Inconel | High hardness, wear resistance |
| Heat Exchangers | Copper, Aluminum | Thermal conductivity |
| Orthopedic Devices | Titanium, CoCr | High strength, corrosion resistance |
| Automotive Parts | Aluminum, Magnesium | Lightweight, improved fuel efficiency |
| Jewelry | Bronze, Stainless Steel | Aesthetic appeal, high quality |
Specifications, Sizes, Grades, and Standards
Specifications of EIGA Metal Powders
Each type of metal powder produced via EIGA comes with specific specifications and standards to meet industry requirements.
| Metal Powder | Standard | Specification |
|---|---|---|
| Titanium (Ti) | ASTM B348 | Particle size: 15-45 microns, purity: 99.5% |
| Nickel (Ni) | ASTM B330 | Particle size: 20-50 microns, purity: 99.8% |
| Aluminum (Al) | ASTM B214 | Particle size: 10-45 microns, purity: 99.7% |
| Stainless Steel (SS) | ASTM B213 | Particle size: 15-50 microns, various grades |
| Cobalt-Chrome (CoCr) | ASTM F75 | Particle size: 20-60 microns, biocompatible |
| Copper (Cu) | ASTM B216 | Particle size: 10-45 microns, purity: 99.9% |
| Inconel (Ni-Cr) | ASTM B638 | Particle size: 20-50 microns, oxidation resistant |
| Tool Steel (TS) | ASTM B214 | Particle size: 15-50 microns, high hardness |
| Magnesium (Mg) | ASTM B557 | Particle size: 10-45 microns, purity: 99.5% |
| Bronze (Cu-Sn) | ASTM B427 | Particle size: 15-50 microns, good wear resistance |
Table: Specifications and Standards for EIGA Metal Powders
| Metal Powder | Grade | Specification |
|---|---|---|
| Titanium (Ti) | Grade 5 | 15-45 microns, ASTM B348 |
| Nickel (Ni) | Nickel 200 | 20-50 microns, ASTM B330 |
| Aluminum (Al) | 6061-T6 | 10-45 microns, ASTM B214 |
| Stainless Steel (SS) | 316L | 15-50 microns, ASTM B213 |
| Cobalt-Chrome (CoCr) | CoCr-Mo | 20-60 microns, ASTM F75 |
| Copper (Cu) | OFHC Copper | 10-45 microns, ASTM B216 |
| Inconel (Ni-Cr) | Inconel 625 | 20-50 microns, ASTM B638 |
| Tool Steel (TS) | A2 | 15-50 microns, ASTM B214 |
| Magnesium (Mg) | AZ31B | 10-45 microns, ASTM B557 |
| Bronze (Cu-Sn) | C93200 | 15-50 microns, ASTM B427 |
Suppliers and Pricing Details
Finding the Right Supplier
When sourcing EIGA metal powders, it’s crucial to consider the supplier’s reputation, quality control measures, and pricing. Here are some top suppliers and their pricing details:
| Supplier | Metal Powders | Pricing (per kg) | Quality Certifications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Advanced Powders | Ti, Ni, Al, SS, CoCr | $100 – $200 | ISO 9001, AS9100 |
| Precision Metals | Cu, Inconel, TS, Mg, Bronze | $150 – $250 | ISO 13485, ASTM |
| Metal Powders Inc. | Al, SS, Ti, CoCr | $120 – $220 | ISO 9001, NADCAP |
| PowderTech | Ni, Mg, Cu, Inconel | $130 – $240 | ISO 9001, ISO 14001 |
| Atomised Metals | Ti, Al, SS, TS, Bronze | $110 – $230 | AS9100, ASTM |
Table: Suppliers and Pricing for EIGA Metal Powders
| Supplier | Metal Powders Available | Pricing Range (per kg) | Certifications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Advanced Powders | Ti, Ni, Al, SS, CoCr | $100 – $200 | ISO 9001, AS9100 |
| Precision Metals | Cu, Inconel, TS, Mg, Bronze | $150 – $250 | ISO 13485, ASTM |
| Metal Powders Inc. | Al, SS, Ti, CoCr | $120 – $220 | ISO 9001, NADCAP |
| PowderTech | Ni, Mg, Cu, Inconel | $130 – $240 | ISO 9001, ISO 14001 |
| Atomised Metals | Ti, Al, SS, TS, Bronze | $110 – $230 | AS9100, ASTM |
Comparing EIGA with Other Metal Powder Production Methods
EIGA vs. Gas Atomisation
Gas atomisation is another popular method for producing metal powders. Let’s compare the two:
| Feature | EIGA | Gas Atomisation |
|---|---|---|
| Purity | Higher, due to inert gas environment | Moderate, potential for oxidation |
| Particle Size Control | Excellent | Good |
| Production Rate | High | High |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Lower |
| Applications | High-performance, aerospace, medical | General industrial, additive manufacturing |
EIGA vs. Plasma Atomisation
Plasma atomisation uses a plasma torch to melt the metal. Here’s how it stacks up against EIGA:
| Feature | EIGA | Plasma Atomisation |
|---|---|---|
| Purity | Higher | Very high, almost no contamination |
| Particle Size Control | Excellent | Excellent |
| Production Rate | High | Lower |
| Cost | Moderate to high | High |
| Applications | Aerospace, medical, automotive | High-end applications, titanium powders |
EIGA vs. Water Atomisation
Water atomisation uses high-pressure water jets. Let’s see the differences:
| Feature | EIGA | Water Atomisation |
|---|---|---|
| Purity | Higher | Lower, risk of contamination |
| Particle Size Control | Excellent | Moderate |
| Production Rate | High | Very high |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Low |
| Applications | Aerospace, medical, high-performance | General industrial, low-cost applications |
Table: Comparison of EIGA with Other Production Methods
| Feature | EIGA | Gas Atomisation | Plasma Atomisation | Water Atomisation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Purity | Higher | Moderate | Very high | Lower |
| Particle Size Control | Excellent | Good | Excellent | Moderate |
| Production Rate | High | High | Lower | Very high |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Lower | High | Low |
| Applications | High-performance, aerospace, medical | General industrial | High-end applications | Low-cost applications |
Advantages and Disadvantages of EIGA
Advantages of EIGA
- High Purity: The inert gas atmosphere ensures minimal contamination.
- Uniform Particle Size: Precise control over particle size distribution.
- Spherical Particles: Enhanced flowability and packing density.
- Versatile: Suitable for a wide range of metals and alloys.
- Efficient: High production rates with minimal waste.
Disadvantages of EIGA
- Cost: Higher production costs compared to some other methods.
- Complexity: Requires sophisticated equipment and controls.
- Limited Metal Types: Not all metals are suitable for EIGA.
Table: Advantages and Disadvantages of EIGA
| Aspect | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Purity | High due to inert gas environment | – |
| Particle Size Control | Excellent, uniform distribution | – |
| Production Rate | High | – |
| Cost | – | Higher compared to some methods |
| Complexity | – | Requires sophisticated equipment |
| Versatility | Suitable for many metals and alloys | Limited metal types |
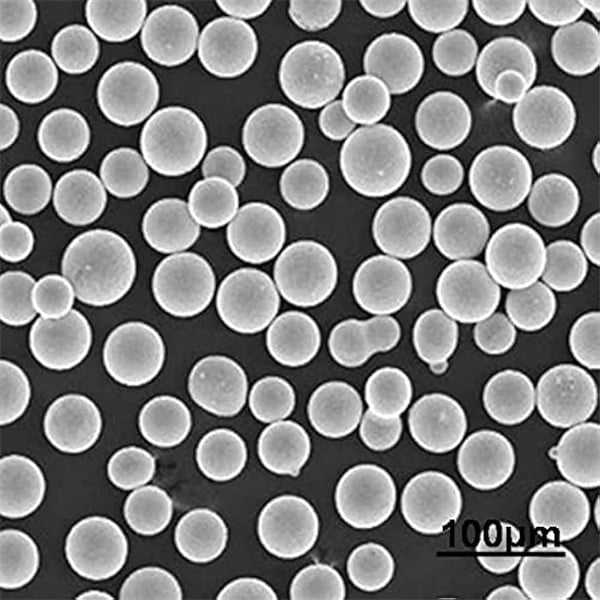
FAQs
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is EIGA? | A process to produce high-purity metal powders using induction melting in an inert gas atmosphere. |
| What metals can be processed with EIGA? | Metals like Titanium, Nickel, Aluminum, Stainless Steel, and more. |
| Why is EIGA preferred for high-performance applications? | It produces powders with high purity and uniform particle size. |
| How does EIGA compare to Gas Atomisation? | EIGA offers higher purity and better particle size control but at a higher cost. |
| What are the main applications of EIGA metal powders? | Aerospace, medical implants, automotive components, and 3D printing. |
| Are EIGA metal powders more expensive? | Generally, yes, due to the sophisticated process and equipment required. |
| Can EIGA be used for all metals? | No, it’s best suited for specific metals and alloys. |
| What are the benefits of spherical particles in EIGA powders? | Better flowability and packing density, important for applications like 3D printing. |
| Is EIGA environmentally friendly? | Yes, it produces minimal waste and uses inert gases that don’t react with the environment. |
| Who are the leading suppliers of EIGA metal powders? | Companies like Advanced Powders, Precision Metals, and Metal Powders Inc. |
Share On
MET3DP Technology Co., LTD is a leading provider of additive manufacturing solutions headquartered in Qingdao, China. Our company specializes in 3D printing equipment and high-performance metal powders for industrial applications.
Inquiry to get best price and customized Solution for your business!
Related Articles
About Met3DP
Recent Update
Our Product
CONTACT US
Any questions? Send us message now! We’ll serve your request with a whole team after receiving your message.

Metal Powders for 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing
COMPANY
PRODUCT
cONTACT INFO
- Qingdao City, Shandong, China
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- +86 19116340731

















