High-Temperature Alloy K477: An In-Depth Analysis
Table of Contents
Overview of High-Temperature Alloy K477
High-temperature alloy K477 is a specialized superalloy designed for extreme conditions, particularly those involving high temperatures and corrosive environments. It is widely used in industries such as aerospace, power generation, and chemical processing, where materials are exposed to extreme heat and stress. The alloy is known for its excellent mechanical strength, oxidation resistance, and thermal stability, making it a go-to choice for critical components.
In this article, we’ll dive into the various aspects of High-Temperature Alloy K477, including its composition, characteristics, applications, and much more. We’ll also compare different metal powder models, highlight the pros and cons, and provide detailed information about suppliers and pricing.
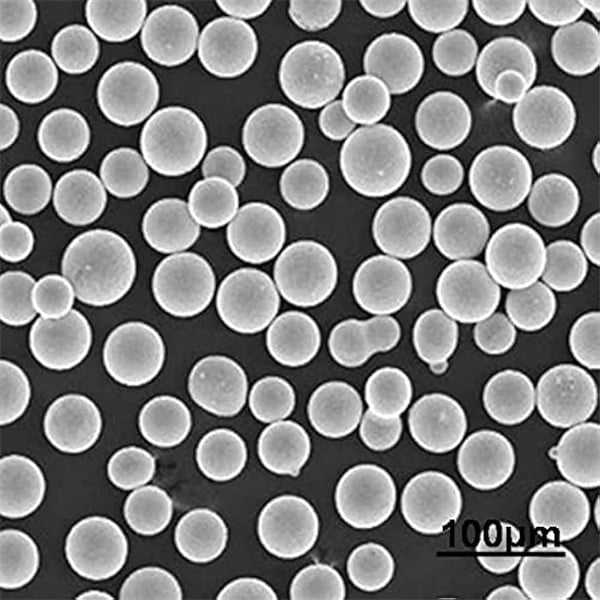
Composition of High-Temperature Alloy K477
The composition of High-Temperature Alloy K477 plays a crucial role in its performance. This alloy typically consists of a combination of nickel, chromium, and other elements that provide it with unique properties.
| Element | Composition (%) | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Nickel (Ni) | 60-70 | Provides high-temperature strength and corrosion resistance |
| Chromium (Cr) | 10-20 | Enhances oxidation resistance and high-temperature stability |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | 2-5 | Increases creep resistance and mechanical strength at high temperatures |
| Cobalt (Co) | 5-10 | Adds to the alloy’s strength and corrosion resistance |
| Tungsten (W) | 1-3 | Improves strength and hardness at elevated temperatures |
| Carbon (C) | 0.05-0.15 | Aids in carbide formation, which enhances strength |
| Iron (Fe) | Balance | Provides additional mechanical strength and toughness |
| Aluminum (Al) | 0.5-2.0 | Contributes to oxidation resistance and formation of a protective oxide layer |
| Titanium (Ti) | 0.5-2.0 | Helps in precipitation hardening and improving strength |
Characteristics of High-Temperature Alloy K477
Understanding the characteristics of High-Temperature Alloy K477 is essential to appreciate its applications and performance in various industries.
- High-Temperature Strength: K477 alloy retains its mechanical properties even at temperatures exceeding 1,000°C, making it ideal for turbine blades, exhaust systems, and other high-stress components.
- Oxidation Resistance: The chromium content provides excellent oxidation resistance, allowing the alloy to withstand harsh environments without significant degradation.
- Corrosion Resistance: This alloy is resistant to various forms of corrosion, including pitting, crevice corrosion, and stress corrosion cracking, which is vital for its longevity in aggressive environments.
- Creep Resistance: The alloy’s microstructure is designed to resist deformation under long-term stress at high temperatures, ensuring stability and reliability in critical applications.
- Thermal Stability: K477 maintains its properties across a wide temperature range, ensuring consistent performance under fluctuating conditions.
Specific Metal Powder Models of High-Temperature Alloy K477
Here, we’ll explore specific metal powder models derived from the K477 alloy, which are used in various advanced manufacturing processes, such as additive manufacturing (3D printing) and powder metallurgy.
| Metal Powder Model | Description |
|---|---|
| K477-1 | Fine-grained powder ideal for precision casting and additive manufacturing, offering excellent flow characteristics and minimal porosity in finished components. |
| K477-2 | High-purity powder with enhanced corrosion resistance, suitable for aerospace components exposed to harsh environments. |
| K477-3 | This model offers improved creep resistance and is often used in the production of turbine blades and high-performance engine parts. |
| K477-4 | Optimized for additive manufacturing, this powder has a uniform particle size distribution, ensuring consistent layer-by-layer deposition in 3D printing processes. |
| K477-5 | Features increased aluminum content for superior oxidation resistance, commonly used in high-temperature exhaust systems and industrial gas turbines. |
| K477-6 | Designed for powder metallurgy, this model offers enhanced ductility and toughness, making it suitable for high-stress mechanical components. |
| K477-7 | This variant is engineered for use in aggressive chemical environments, offering both high corrosion resistance and thermal stability. |
| K477-8 | A low-carbon version of K477, this powder is used where minimized carbide precipitation is critical, such as in welding and repair applications. |
| K477-9 | Enhanced with titanium, this model provides superior strength and is often used in structural components subjected to extreme loads. |
| K477-10 | A specialized powder for the oil and gas industry, offering resistance to sulfidation and other forms of chemical attack at high temperatures. |
Applications of High-Temperature Alloy K477
High-Temperature Alloy K477 is used in various industries where performance under extreme conditions is paramount. Let’s explore some of its most common applications.
| Industry | Application |
|---|---|
| Aerospace | Used in the manufacture of turbine blades, combustion chambers, and exhaust systems. |
| Power Generation | Essential for components in gas turbines, steam turbines, and other high-temperature energy systems. |
| Chemical Processing | Applied in reactors, heat exchangers, and piping systems that handle corrosive and high-temperature fluids. |
| Oil and Gas | Used in downhole tools, drilling equipment, and components exposed to harsh, high-temperature environments. |
| Automotive | Applied in turbochargers, exhaust manifolds, and other high-performance engine components. |
| Marine | Used in marine gas turbines, exhaust systems, and other components exposed to salty, corrosive environments. |
| Nuclear Energy | Essential for fuel rods, control rods, and structural components in nuclear reactors. |
| Industrial Gas Turbines | Used in large-scale power generation turbines and other heavy-duty industrial applications. |
| 3D Printing | Powder forms of K477 are used in additive manufacturing for producing complex, high-performance parts. |
| Welding and Repair | Utilized for welding and repairing high-temperature components, thanks to its excellent weldability and stability. |
Specifications and Standards of High-Temperature Alloy K477
When dealing with high-temperature alloys like K477, it’s important to adhere to specific standards and specifications to ensure optimal performance.
| Specification/Standard | Description |
|---|---|
| ASTM B637 | Covers precipitation-hardening, nickel-based alloy rods, bars, forgings, and forging stock. |
| AMS 5599 | Standard specification for nickel alloy sheets and plates, applicable to high-temperature environments. |
| ISO 15156-3 | Specifies the use of materials resistant to sulfide stress cracking in oil and gas production. |
| UNS N07718 | Unified Numbering System designation for nickel-chromium alloy. |
| DIN 17744 | German standard for high-temperature alloys, focusing on the chemical composition and mechanical properties. |
| EN 10269 | European standard for hot-rolled and cold-drawn bars and wire rods in nickel alloys. |
| JIS G4902 | Japanese industrial standard for nickel-based alloys used in high-temperature applications. |
| BS 3076 | British standard for nickel-based superalloys in the form of bars, rods, and sections. |
| ASME SB 637 | American Society of Mechanical Engineers standard for nickel alloys used in high-temperature service. |
| NACE MR0175 | Specifies the material requirements for resistance to sulfide stress cracking in sour oilfield environments. |
Suppliers and Pricing of High-Temperature Alloy K477
Finding reliable suppliers for High-Temperature Alloy K477 is crucial for industries that rely on this material. Here’s a look at some of the leading suppliers and an overview of pricing.
| Supplier | Location | Product Offerings | Approximate Pricing |
|---|---|---|---|
| ATI Metals | United States | Offers a range of nickel-based alloys, including K477, in various forms such as bars, sheets, and powder. | $30 – $50 per kg, depending on the form and quantity. |
| Carpenter Technology | United States | Specializes in high-performance alloys for aerospace, energy, and industrial applications, including K477 powder for additive manufacturing. | $35 – $55 per kg for powder forms. |
| Haynes International | United States | Provides nickel and cobalt-based alloys, including K477, for extreme temperature and corrosive environments. | $28 – $48 per kg, available in different grades. |
| VDM Metals | Germany | Offers a variety of high-temperature alloys, including K477, in forms such as wire, rod, and sheet. | €25 – €45 per kg, depending on size and specification. |
| Special Metals | United Kingdom | Supplies nickel alloys, including K477, for use in aerospace, oil & gas, and power generation industries. | £24 – £44 per kg, based on the specific alloy form. |
| Outokumpu | Finland | Produces high-temperature alloys and stainless steels, including K477, for industrial and manufacturing applications. | €30 – €50 per kg, with discounts for bulk orders. |
| KGHM Ecoren | Poland | Provides specialized metal powders, including K477, for additive manufacturing and powder metallurgy applications. | €35 – €55 per kg, depending on the purity and particle size. |
| Hitachi Metals | Japan | Produces high-performance alloys, including K477, for a variety of industries, offering both standard and custom compositions. | ¥3,000 – ¥5,000 per kg, based on the alloy form and quantity. |
| Mitsubishi Materials | Japan | Supplies high-temperature alloys, including K477, with a focus on precision casting and manufacturing. | ¥3,200 – ¥5,200 per kg, varies by grade and specification. |
| Metallurgical Plant “Electrostal” | Russia | A major producer of high-temperature alloys, including K477, offering a wide range of sizes and forms. | ₽2,500 – ₽4,500 per kg, depending on the alloy form and size. |
Advantages and Disadvantages of High-Temperature Alloy K477
While High-Temperature Alloy K477 offers numerous benefits, it also has some limitations. Let’s explore the pros and cons.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| High-Temperature Strength: Retains mechanical properties at extreme temperatures. | Cost: K477 is more expensive than other alloys due to its specialized composition and manufacturing process. |
| Oxidation and Corrosion Resistance: Withstands harsh environments without significant degradation. | Machinability: Difficult to machine compared to lower-grade alloys, requiring specialized equipment and techniques. |
| Creep Resistance: Maintains structural integrity under prolonged stress. | Availability: Not as widely available as more common alloys, leading to potential supply chain challenges. |
| Thermal Stability: Performs consistently across a wide temperature range. | Density: The alloy is relatively dense, which may be a disadvantage in weight-sensitive applications. |
| Versatility: Can be used in various forms, including powder, sheet, and bar, making it adaptable to different processes. | Weldability: Requires advanced welding techniques to avoid cracking and other issues. |
Comparing High-Temperature Alloy K477 with Other Alloys
When selecting materials for high-temperature applications, it’s important to compare K477 with other available options to determine the best fit.
| Alloy | Temperature Resistance | Oxidation Resistance | Cost | Machinability | Corrosion Resistance | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inconel 718 | Up to 700°C | Excellent | Moderate | Challenging | Excellent | Aerospace, nuclear reactors, gas turbines |
| Haynes 230 | Up to 980°C | Superior | High | Moderate | Very Good | Industrial gas turbines, chemical processing |
| Waspaloy | Up to 870°C | Excellent | High | Difficult | Good | Gas turbine blades, rocket engines |
| Hastelloy X | Up to 1,090°C | Very Good | High | Moderate | Excellent | Gas turbines, industrial furnaces |
| Alloy 625 | Up to 815°C | Very Good | High | Challenging | Excellent | Marine applications, chemical processing |
| Stellite 6B | Up to 650°C | Good | Moderate | Moderate | Excellent | Wear-resistant coatings, valves, and bearings |
| K477 | Up to 1,000°C | Superior | High | Difficult | Excellent | Turbine blades, chemical processing, 3D printing |
FAQs
Here are some frequently asked questions about High-Temperature Alloy K477.
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What industries commonly use K477 alloy? | K477 is widely used in aerospace, power generation, chemical processing, and oil & gas industries. |
| Can K477 be used in 3D printing? | Yes, K477 powder is specifically designed for additive manufacturing, making it ideal for 3D printing high-performance parts. |
| How does K477 compare to Inconel 718? | While both alloys offer excellent high-temperature performance, K477 is superior in oxidation resistance and creep strength at temperatures above 900°C. |
| Is K477 difficult to machine? | Yes, K477 requires specialized equipment and techniques due to its hardness and high-temperature stability. |
| What are the main benefits of using K477 in turbine blades? | K477 offers excellent creep resistance, oxidation resistance, and thermal stability, making it ideal for high-stress, high-temperature environments. |
| Is K477 suitable for marine applications? | Yes, its corrosion resistance makes it suitable for marine environments, particularly in high-temperature applications. |
| What are the main disadvantages of K477? | The main disadvantages are its cost, machinability, and relative density, which may limit its use in certain applications. |
Conclusion
High-Temperature Alloy K477 is a high-performance material designed for the most demanding applications. Its unique combination of strength, oxidation resistance, and thermal stability makes it a preferred choice in industries where reliability under extreme conditions is non-negotiable. While it does come with some challenges, such as cost and machinability, the benefits it offers far outweigh these drawbacks in critical applications.
For industries like aerospace, power generation, and chemical processing, K477 is more than just an alloy; it’s a crucial component in ensuring the safety, efficiency, and longevity of their operations.
Share On
MET3DP Technology Co., LTD is a leading provider of additive manufacturing solutions headquartered in Qingdao, China. Our company specializes in 3D printing equipment and high-performance metal powders for industrial applications.
Inquiry to get best price and customized Solution for your business!
Related Articles
About Met3DP
Recent Update
Our Product
CONTACT US
Any questions? Send us message now! We’ll serve your request with a whole team after receiving your message.

Metal Powders for 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing
COMPANY
PRODUCT
cONTACT INFO
- Qingdao City, Shandong, China
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- +86 19116340731

















