Metal Powder for Electronics
Table of Contents
When you think about electronics, the tiny, intricate components that power our devices come to mind. But did you know that many of these components are made from metal powders? Metal powders play a crucial role in the manufacturing of electronic devices, providing essential properties that improve performance, durability, and efficiency. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll dive deep into the world of metal powders for electronics, covering everything from specific models to their applications, properties, advantages, and disadvantages. So, grab a cup of coffee, and let’s explore this fascinating topic together!
Overview of Metal Powders in Electronics
Metal powders are finely divided metals used in various applications, including electronics. They are produced through different methods such as atomization, chemical reduction, and electrolysis. These powders are then used to manufacture electronic components like capacitors, resistors, inductors, and even in the field of additive manufacturing for creating intricate parts.
Metal powders offer unique properties such as high electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and magnetic properties, making them ideal for electronic applications. Different types of metals and their alloys are used, each providing distinct advantages depending on the application.
Why Metal Powders?
Ever wondered why metal powders are so integral to electronics? It’s simple. They offer a unique combination of properties that bulk metals cannot match. For instance, metal powders can be compacted and sintered to create complex shapes that are impossible with traditional metalworking methods. Additionally, the fine particles allow for precise control over the composition and properties of the final product, ensuring optimal performance in electronic devices.
Common Metals Used
Here’s a quick rundown of some common metals used in electronic powders:
- Silver: Known for its excellent electrical conductivity.
- Copper: Offers a good balance between cost and conductivity.
- Nickel: Provides magnetic properties and corrosion resistance.
- Gold: Exceptional conductivity and corrosion resistance, albeit expensive.
- Aluminum: Lightweight with good conductivity.
- Iron: Magnetic properties, often used in inductors and transformers.
Now, let’s delve into specific metal powder models used in electronics.
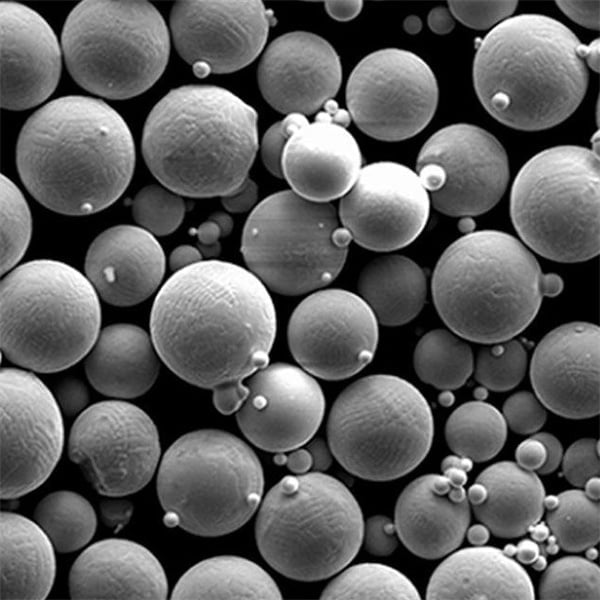
Specific Metal Powder Models for Electronics
In the electronics industry, specific metal powder models are developed to meet the stringent requirements of different applications. Below, we’ve listed ten notable models, along with detailed descriptions of their properties and uses.
1. Silver Powder (Ag-1)
Description: Silver powder, particularly the Ag-1 model, is known for its unparalleled electrical conductivity. It’s commonly used in conductive adhesives, inks, and pastes for printed electronics.
Properties:
- High electrical conductivity
- Excellent thermal conductivity
- Anti-bacterial properties
Applications: Conductive adhesives, printed circuits, RFID tags.
2. Copper Powder (Cu-2)
Description: The Cu-2 copper powder model is widely used due to its excellent balance of conductivity and cost. It is often used in thick-film pastes and electronic coatings.
Properties:
- Good electrical conductivity
- Cost-effective
- Good thermal conductivity
Applications: Thick-film pastes, electronic coatings, EMI shielding.
3. Nickel Powder (Ni-3)
Description: Ni-3 nickel powder is prized for its magnetic properties and corrosion resistance. It’s extensively used in inductors and transformers.
Properties:
- Magnetic properties
- Corrosion-resistant
- Good electrical conductivity
Applications: Inductors, transformers, magnetic sensors.
4. Gold Powder (Au-4)
Description: The Au-4 gold powder is exceptionally conductive and resistant to corrosion, making it ideal for high-reliability applications like aerospace and medical electronics.
Properties:
- Exceptional electrical conductivity
- High corrosion resistance
- Biocompatible
Applications: Aerospace electronics, medical devices, high-reliability connectors.
5. Aluminum Powder (Al-5)
Description: Al-5 aluminum powder is lightweight and provides good conductivity. It’s commonly used in thermal management applications.
Properties:
- Lightweight
- Good electrical conductivity
- Excellent thermal conductivity
Applications: Heat sinks, thermal interface materials, lightweight electronic components.
6. Iron Powder (Fe-6)
Description: Fe-6 iron powder is used for its magnetic properties, particularly in the manufacturing of cores for inductors and transformers.
Properties:
- Magnetic properties
- Good mechanical strength
- Cost-effective
Applications: Inductor cores, transformer cores, magnetic shielding.
7. Titanium Powder (Ti-7)
Description: Ti-7 titanium powder is known for its strength, lightweight, and resistance to corrosion. It’s used in specialized electronic components.
Properties:
- High strength-to-weight ratio
- Corrosion-resistant
- Biocompatible
Applications: Biomedical electronics, aerospace electronics, high-strength connectors.
8. Zinc Powder (Zn-8)
Description: Zn-8 zinc powder is often used in batteries and protective coatings due to its excellent electrochemical properties.
Properties:
- Good electrochemical properties
- Corrosion-resistant
- Cost-effective
Applications: Batteries, protective coatings, anodes.
9. Tin Powder (Sn-9)
Description: Sn-9 tin powder is widely used in soldering applications due to its low melting point and good wettability.
Properties:
- Low melting point
- Good wettability
- Corrosion-resistant
Applications: Soldering, conductive coatings, electronic packaging.
10. Tungsten Powder (W-10)
Description: W-10 tungsten powder is valued for its high melting point and density, making it suitable for specialized applications requiring high thermal stability.
Properties:
- High melting point
- High density
- Good thermal conductivity
Applications: High-temperature electronics, radiation shielding, specialized thermal management.
Composition, Properties, and Characteristics
Understanding the composition, properties, and characteristics of these metal powders is essential for selecting the right material for a specific application. Here’s a detailed table summarizing these aspects for each metal powder model discussed above:
| Metal Powder | Model | Composition | Electrical Conductivity | Thermal Conductivity | Magnetic Properties | Corrosion Resistance | Melting Point |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silver | Ag-1 | 99.9% Ag | Excellent | Excellent | None | High | 961.8°C |
| Copper | Cu-2 | 99.9% Cu | Good | Good | None | Moderate | 1085°C |
| Nickel | Ni-3 | 99.9% Ni | Moderate | Moderate | High | High | 1455°C |
| Gold | Au-4 | 99.9% Au | Exceptional | Good | None | Very High | 1064°C |
| Aluminum | Al-5 | 99.9% Al | Good | Excellent | None | Moderate | 660.3°C |
| Iron | Fe-6 | 99.9% Fe | Moderate | Moderate | High | Low | 1538°C |
| Titanium | Ti-7 | 99.9% Ti | Moderate | Moderate | None | High | 1668°C |
| Zinc | Zn-8 | 99.9% Zn | Low | Low | None | Moderate | 419.5°C |
| Tin | Sn-9 | 99.9% Sn | Low | Low | None | High | 232°C |
| Tungsten | W-10 | 99.9% W | Low | High | None | High | 3422°C |
Applications of Metal Powder for Electronics
Metal powders are used across various applications in the electronics industry. Each metal powder offers unique benefits that make it suitable for specific uses. Here’s a detailed table showing common applications of each metal powder model:
| Metal Powder | Model | Applications | Specific Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Silver | Ag-1 | Conductive adhesives, printed circuits, RFID tags | Conductive pastes, sensor electrodes |
| Copper | Cu-2 | Thick-film pastes, electronic coatings, EMI shielding | Circuit board coatings, conductive inks |
| Nickel | Ni-3 | Inductors, transformers, magnetic sensors | Magnetic cores, shielding, inductive components |
| Gold | Au-4 | Aerospace electronics, medical devices, high-reliability connectors | Bonding wires, high-precision components |
| Aluminum | Al-5 | Heat sinks, thermal interface materials, lightweight components | Power electronics, cooling systems |
| Iron | Fe-6 | Inductor cores, transformer cores, magnetic shielding | Chokes, magnetic assemblies |
| Titanium | Ti-7 | Biomedical electronics, aerospace electronics, high-strength connectors | Implantable devices, aerospace connectors |
| Zinc | Zn-8 | Batteries, protective coatings, anodes | Battery anodes, galvanic protection |
| Tin | Sn-9 | Soldering, conductive coatings, electronic packaging | Solder pastes, plated finishes |
| Tungsten | W-10 | High-temperature electronics, radiation shielding, thermal management | X-ray shielding, high-power electronics |
Specifications, Sizes, Grades, and Standards
Metal powders come in various specifications, sizes, grades, and standards to meet the diverse needs of electronic applications. Here’s a detailed table showcasing these aspects:
| Metal Powder | Model | Particle Size | Purity | Grade | Standards |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silver | Ag-1 | 1-5 µm | 99.9% | Electronic Grade | ASTM B832 |
| Copper | Cu-2 | 1-10 µm | 99.9% | Electronic Grade | ASTM B212 |
| Nickel | Ni-3 | 1-10 µm | 99.9% | Electronic Grade | ASTM B330 |
| Gold | Au-4 | 1-5 µm | 99.9% | High Purity | ASTM B562 |
| Aluminum | Al-5 | 1-15 µm | 99.9% | Electronic Grade | ASTM B214 |
| Iron | Fe-6 | 1-20 µm | 99.9% | Soft Magnetic | ASTM A595 |
| Titanium | Ti-7 | 1-10 µm | 99.9% | Medical Grade | ASTM F67 |
| Zinc | Zn-8 | 1-15 µm | 99.9% | Battery Grade | ASTM B330 |
| Tin | Sn-9 | 1-10 µm | 99.9% | Solder Grade | ASTM B339 |
| Tungsten | W-10 | 1-10 µm | 99.9% | High Purity | ASTM B777 |
Suppliers and Pricing Details
Finding the right supplier is critical for ensuring the quality and consistency of metal powders. Here’s a table of some well-known suppliers and their pricing details:
| Metal Powder | Model | Supplier | Price (per kg) | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silver | Ag-1 | American Elements | $1500 | USA |
| Copper | Cu-2 | Sigma-Aldrich | $200 | Global |
| Nickel | Ni-3 | Alfa Aesar | $300 | Global |
| Gold | Au-4 | Metalor Technologies | $50000 | Switzerland |
| Aluminum | Al-5 | Valimet Inc. | $50 | USA |
| Iron | Fe-6 | Höganäs AB | $20 | Sweden |
| Titanium | Ti-7 | AP&C | $800 | Canada |
| Zinc | Zn-8 | EverZinc | $10 | Belgium |
| Tin | Sn-9 | William Rowland | $100 | UK |
| Tungsten | W-10 | Global Tungsten & Powders | $600 | USA |
Comparing Pros and Cons
Every material has its strengths and weaknesses. Let’s compare the pros and cons of these metal powders:
| Metal Powder | Model | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Silver | Ag-1 | Best conductivity, thermal properties | High cost |
| Copper | Cu-2 | Good balance of cost and conductivity | Prone to oxidation |
| Nickel | Ni-3 | Magnetic properties, corrosion resistance | Moderate conductivity |
| Gold | Au-4 | Excellent conductivity, corrosion resistance | Very high cost |
| Aluminum | Al-5 | Lightweight, good conductivity | Lower strength compared to other metals |
| Iron | Fe-6 | Magnetic properties, cost-effective | Prone to rust |
| Titanium | Ti-7 | High strength-to-weight ratio, biocompatible | High cost |
| Zinc | Zn-8 | Good electrochemical properties, low cost | Lower conductivity |
| Tin | Sn-9 | Low melting point, good wettability | Lower conductivity |
| Tungsten | W-10 | High melting point, density | Very high cost, difficult to process |
FAQ
Here are some frequently asked questions about metal powders for electronics, along with their answers.
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What are metal powders used for in electronics? | Metal powders are used in manufacturing components like capacitors, resistors, inductors, and in additive manufacturing. |
| Why is silver powder preferred for conductive applications? | Silver powder offers the highest electrical and thermal conductivity, making it ideal for conductive adhesives and inks. |
| How is copper powder beneficial in electronics? | Copper powder provides a good balance between cost and conductivity, suitable for thick-film pastes and coatings. |
| What makes nickel powder suitable for magnetic components? | Nickel powder has excellent magnetic properties and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for inductors and transformers. |
| Why is gold powder so expensive? | Gold powder is expensive due to its exceptional conductivity and resistance to corrosion, often used in high-reliability applications. |
| Can aluminum powder be used for thermal management? | Yes, aluminum powder has excellent thermal conductivity, making it suitable for heat sinks and thermal interface materials. |
| What are the typical applications of zinc powder? | Zinc powder is commonly used in batteries, protective coatings, and anodes due to its good electrochemical properties. |
| Why is tin powder used in soldering? | Tin powder has a low melting point and good wettability, which is crucial for creating strong, reliable solder joints. |
| What properties make tungsten powder unique? | Tungsten powder has a high melting point and density, making it suitable for high-temperature electronics and radiation shielding. |
| Are there any environmental concerns with using metal powders? | Yes, certain metal powders can pose environmental and health risks if not handled properly, necessitating safe handling and disposal practices. |
Conclusion
Metal powders play a pivotal role in the electronics industry, offering unique properties that enhance the performance and reliability of electronic components. From the unmatched conductivity of silver to the high-temperature stability of tungsten, each metal powder brings its own set of advantages to the table. Understanding the specific models, their properties, applications, and the pros and cons can help in making informed decisions for various electronic applications. So, whether you’re a manufacturer, engineer, or just a tech enthusiast, knowing about metal powders can give you a deeper appreciation of the intricate world of electronics.
If you have any more questions or need further information, feel free to reach out. Happy reading and exploring the world of metal powders for electronics!
Share On
MET3DP Technology Co., LTD is a leading provider of additive manufacturing solutions headquartered in Qingdao, China. Our company specializes in 3D printing equipment and high-performance metal powders for industrial applications.
Inquiry to get best price and customized Solution for your business!
Related Articles
About Met3DP
Recent Update
Our Product
CONTACT US
Any questions? Send us message now! We’ll serve your request with a whole team after receiving your message.

Metal Powders for 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing
COMPANY
PRODUCT
cONTACT INFO
- Qingdao City, Shandong, China
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- +86 19116340731