Molybdenum: The Marvel of Metals
Table of Contents
When we think about the elements that make our modern world possible, iron, aluminum, and copper often come to mind. But there’s another unsung hero in the world of materials science: molybdenum. This versatile metal is crucial in various industries due to its unique properties and wide range of applications. Let’s dive deep into the world of molybdenum and explore its wonders.
Overview of Molybdenum
Molybdenum (Mo) is a silvery-white metal known for its strength, high melting point, and resistance to corrosion. It’s the 54th most abundant element in the Earth’s crust and is primarily obtained from the mineral molybdenite (MoS2). Its remarkable characteristics make it indispensable in many fields, from aerospace and military to electronics and medicine.
Key Properties of Molybdenum
- High Melting Point: Molybdenum has a melting point of 2,623°C (4,753°F), making it one of the highest melting points among the elements.
- Strength and Hardness: It retains its strength at high temperatures and has excellent hardness.
- Corrosion Resistance: Molybdenum is highly resistant to corrosion, especially from acids.
- Thermal and Electrical Conductivity: It has good thermal and electrical conductivity.
- Alloying Capability: Molybdenum is commonly used to enhance the properties of steel and other alloys.
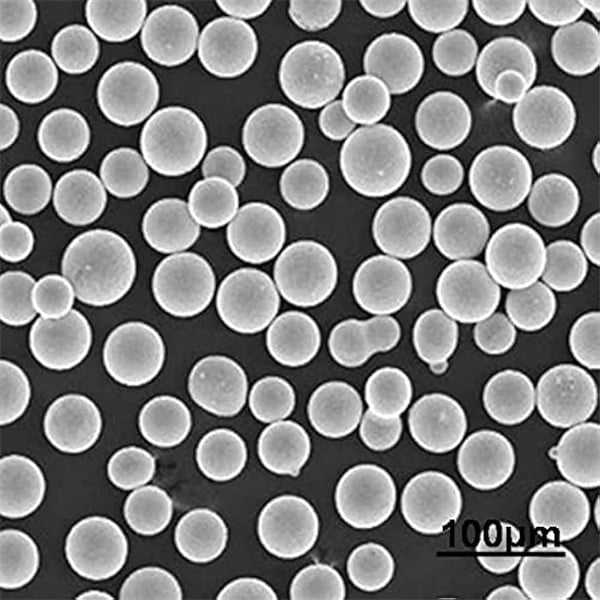
Types and Properties of Molybdenum Powders
When it comes to molybdenum in its powdered form, there are several types, each with its unique properties and applications. Let’s take a closer look at some of the most popular molybdenum powder models available in the market.
| Powder Model | Composition | Properties | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mo-100 | 99.9% Molybdenum | High purity, excellent thermal conductivity, and corrosion resistance | Electronics, aerospace, and coatings |
| Mo-200 | 99.5% Molybdenum | Good balance of strength and ductility, high melting point | Industrial applications, alloying |
| Mo-300 | Molybdenum-Tungsten Alloy | Enhanced strength and hardness, improved wear resistance | Cutting tools, high-temperature parts |
| Mo-400 | Molybdenum-Rhenium Alloy | Superior mechanical properties, excellent resistance to thermal shock | Rocket nozzles, thermocouples |
| Mo-500 | Molybdenum-Lanthanum Alloy | High recrystallization temperature, improved creep resistance | Furnace components, structural parts |
| Mo-600 | Molybdenum-Copper Alloy | Excellent thermal and electrical conductivity, good machinability | Heat sinks, electronic packaging |
| Mo-700 | Molybdenum-Nickel Alloy | Improved corrosion resistance, good mechanical properties | Chemical processing, marine environments |
| Mo-800 | Molybdenum-Titanium Alloy | High strength-to-weight ratio, good corrosion resistance | Aerospace, automotive |
| Mo-900 | Molybdenum-Silicon Alloy | High oxidation resistance, excellent thermal stability | High-temperature applications |
| Mo-1000 | Ultra-Fine Molybdenum Powder | Extremely fine particle size, high surface area, and reactivity | Catalysts, additive manufacturing |
Applications of Molybdenum
Molybdenum’s unique properties make it suitable for a wide range of applications. Here’s a detailed look at where this metal finds its use.
| Industry | Applications |
|---|---|
| Aerospace | Jet engines, missile parts, high-temperature structural components |
| Electronics | Semiconductors, circuit boards, thin-film transistors |
| Energy | Nuclear reactors, power generation, oil and gas drilling equipment |
| Medical | X-ray tubes, radiation shielding, surgical instruments |
| Automotive | Engine components, exhaust systems, turbochargers |
| Construction | Structural steel, pipelines, bridge components |
| Chemical | Catalysts, chemical processing equipment, corrosion-resistant vessels |
| Defense | Armor plating, projectile casings, military vehicles |
| Manufacturing | Cutting tools, molds, dies, furnace components |
| Telecommunications | Waveguides, microwave devices, satellite communications |
Specifications and Standards for Molybdenum
When selecting molybdenum products for specific applications, it’s essential to understand their specifications and standards. Here’s a table summarizing the typical sizes, grades, and standards for molybdenum products.
| Product | Sizes | Grades | Standards |
|---|---|---|---|
| Molybdenum Rods | 1mm to 150mm diameter | Mo-1, Mo-2, TZM, Mo-La | ASTM B387, ASTM F289, ISO 3878 |
| Molybdenum Sheets | 0.1mm to 50mm thickness | Mo-1, Mo-2, TZM, Mo-Re | ASTM B386, ASTM F289, ISO 7452 |
| Molybdenum Wires | 0.05mm to 3mm diameter | Mo-1, Mo-2, TZM | ASTM F289, ISO 8951 |
| Molybdenum Tubes | 1mm to 100mm diameter | Mo-1, Mo-2, TZM, Mo-La | ASTM B387, ASTM F289, ISO 3778 |
| Molybdenum Discs | 10mm to 500mm diameter | Mo-1, Mo-2, TZM, Mo-Re | ASTM B386, ASTM F289, ISO 7452 |
| Molybdenum Foils | 0.01mm to 0.1mm thickness | Mo-1, Mo-2, TZM | ASTM B386, ASTM F289, ISO 7452 |
| Molybdenum Targets | Custom sizes | Mo-1, Mo-2, TZM, Mo-Re | ASTM F289, ISO 7452 |
| Molybdenum Alloys | Various | Mo-W, Mo-Re, Mo-La, TZM | ASTM B386, ASTM F289, ISO 7452 |
| Molybdenum Powder | Varies by application | Pure Mo, Mo-W, Mo-Re | ASTM B387, ASTM F289, ISO 3778 |
Suppliers and Pricing of Molybdenum
Finding reliable suppliers and understanding the pricing structure is crucial for industries relying on molybdenum. Here’s an overview of some top suppliers and the average pricing for different molybdenum products.
| Supplier | Products | Pricing (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Plansee | Rods, sheets, wires, foils, powders | $50 – $300 per kg |
| H.C. Starck | Rods, sheets, powders, alloys | $60 – $320 per kg |
| Molymet | Powders, rods, sheets, alloys | $55 – $310 per kg |
| Midwest Tungsten | Rods, sheets, wires, powders | $45 – $280 per kg |
| Elmet Technologies | Rods, sheets, wires, foils, alloys | $52 – $290 per kg |
| Global Tungsten & Powders Corp. | Powders, rods, sheets, wires | $50 – $300 per kg |
| Advanced Materials | Powders, rods, sheets, foils | $48 – $305 per kg |
| MolyWorks Materials | Powders, rods, sheets | $53 – $295 per kg |
| EdgeTech Industries | Rods, sheets, wires, powders | $47 – $275 per kg |
| Kurt J. Lesker Company | Rods, sheets, foils, alloys | $49 – $285 per kg |
Advantages and Disadvantages of Molybdenum
Every material has its pros and cons, and molybdenum is no exception. Here’s a comparative look at the advantages and disadvantages of using molybdenum.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| High melting point: Suitable for high-temperature applications | Cost: Molybdenum can be more expensive than some alternatives |
| Corrosion resistance: Excellent for harsh environments | Brittleness: Can be brittle at lower temperatures |
| Strength and hardness: Ideal for structural components | Machinability: More challenging to machine compared to softer metals |
| Thermal and electrical conductivity: Useful in electronics | Availability: Less abundant than more common metals like steel or aluminum, molybdenum’s unique properties set it apart in specific applications where its characteristics are essential. |
Comparative Analysis of Molybdenum Products
To better understand how molybdenum stacks up against other materials, let’s compare it with steel and aluminum across key parameters.
Strength and Durability
Molybdenum exhibits exceptional strength and durability, especially at high temperatures, making it suitable for critical applications in aerospace and defense. In contrast, while steel is renowned for its strength, it may not perform as well under extreme heat conditions compared to molybdenum. Aluminum, on the other hand, offers lightweight properties but lacks the strength and high-temperature performance of molybdenum.
Corrosion Resistance
Molybdenum’s superior corrosion resistance makes it invaluable in environments where exposure to acids and harsh chemicals is prevalent. Steel requires additional coatings or treatments to achieve similar corrosion resistance, adding to its overall cost and complexity. Aluminum offers moderate corrosion resistance but may not suffice in highly corrosive environments without protective measures.
Thermal and Electrical Conductivity
While molybdenum demonstrates good thermal and electrical conductivity, it falls short of the high conductivity levels seen in aluminum. However, molybdenum’s conductivity is often sufficient for many applications, especially those requiring higher strength and durability. Steel, known for its poor electrical conductivity, is primarily chosen for its mechanical properties rather than its conductivity.
Cost and Availability
Molybdenum is generally more expensive than both steel and aluminum due to its specialized properties and limited availability compared to more widely used metals. This cost factor often dictates its use in high-value applications where its unique characteristics justify the investment. Steel and aluminum, being more abundant and versatile, are typically more cost-effective for general-purpose applications.
FAQs
What are the main uses of molybdenum?
Molybdenum finds extensive use in aerospace for its high-temperature strength, in electronics for its conductivity, and in chemical processing for its corrosion resistance. It’s also crucial in medical devices, automotive parts, and construction materials.
Is molybdenum environmentally friendly?
Molybdenum itself is inert and does not pose significant environmental risks. However, like all metals, its extraction and processing can have environmental impacts, which are managed through responsible mining practices and recycling initiatives.
How does molybdenum compare to tungsten in terms of applications?
Both molybdenum and tungsten are refractory metals with high melting points and excellent strength. Molybdenum is more commonly used in electronics and high-temperature applications due to its lower density and better machinability, whereas tungsten is preferred in applications requiring the highest melting points and hardness.
What are the challenges of machining molybdenum?
Molybdenum’s high hardness and tendency to work-harden during machining present challenges, requiring specialized tools and techniques for optimal results. Proper cooling and lubrication are crucial to avoid overheating and tool wear.
Conclusion
In conclusion, molybdenum stands as a testament to the ingenuity of material science, offering a blend of strength, durability, and versatility that few metals can match. From enhancing the performance of steel alloys to enabling advancements in electronics and aerospace, its impact spans across multiple industries. While its cost and machining challenges may pose considerations, the benefits of using molybdenum in critical applications far outweigh these concerns.
Whether you’re exploring its uses in aerospace innovations, seeking corrosion-resistant solutions for chemical processing, or pushing the boundaries of electronic conductivity, molybdenum continues to prove its worth as a metal of choice for the future.
Remember, when choosing molybdenum, consider the specific requirements of your application and leverage its unique properties to achieve optimal performance and longevity.
Share On
MET3DP Technology Co., LTD is a leading provider of additive manufacturing solutions headquartered in Qingdao, China. Our company specializes in 3D printing equipment and high-performance metal powders for industrial applications.
Inquiry to get best price and customized Solution for your business!
Related Articles
About Met3DP
Recent Update
Our Product
CONTACT US
Any questions? Send us message now! We’ll serve your request with a whole team after receiving your message.

Metal Powders for 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing
COMPANY
PRODUCT
cONTACT INFO
- Qingdao City, Shandong, China
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- +86 19116340731

















