Nickel Nanopowder
Table of Contents
Welcome to the fascinating world of nickel nanopowder, a cutting-edge material that is rapidly transforming various industries with its unique properties and versatile applications. Imagine a substance so small and yet so powerful, possessing characteristics that defy conventional boundaries. This is the allure of nickel nanopowder, a realm where the laws of physics and chemistry intersect to create something truly remarkable.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricate details of nickel nanopowder, exploring its composition, properties, applications, and the boundless possibilities it holds for the future. So, fasten your seatbelts and get ready to embark on an extraordinary journey through the world of nanotechnology.
Overview: Unlocking the Power of the Nano-Scale
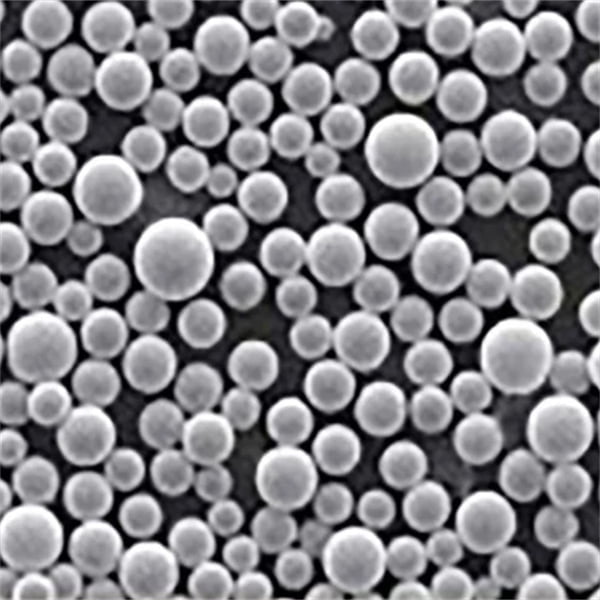
Nickel nanopowder is a highly advanced form of nickel, where the particles are measured in billionths of a meter, or nanometers. At this minuscule scale, the properties of materials can change dramatically, often exhibiting behaviors that are strikingly different from their bulk counterparts. This unique characteristic is what makes nickel nanopowder a game-changer across various industries.
But what exactly is a nanopowder, you might ask? Picture this: if a regular grain of sand were the size of a tennis ball, a nanoparticle would be akin to the size of a tiny speck of dust. This incredible reduction in size results in an exponential increase in surface area, granting nickel nanopowder remarkable chemical reactivity, thermal conductivity, and catalytic properties.

Composition and Properties of Nickel Nanopowder
To fully appreciate the magic of nickel nanopowder, let’s explore its composition and properties in detail:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Composition | Nickel nanopowder is composed primarily of pure elemental nickel, with particle sizes ranging from 1 to 100 nanometers. |
| Surface Area | Due to its incredibly small size, nickel nanopowder boasts an enormous surface area-to-volume ratio, which enhances its chemical reactivity and catalytic properties. |
| Thermal Conductivity | Nanoparticles of nickel exhibit exceptional thermal conductivity, making them ideal for applications that require efficient heat transfer. |
| Magnetic Properties | Nickel nanopowder retains its ferromagnetic properties, opening up possibilities in fields like data storage and electronics. |
| Catalytic Activity | The high surface area and unique electronic structure of nickel nanoparticles endow them with remarkable catalytic capabilities, driving chemical reactions with greater efficiency. |
| Chemical Reactivity | The increased surface area of nickel nanopowder leads to heightened chemical reactivity, enabling its use in various chemical processes. |
As you can see, the unique properties of nickel nanopowder stem from its diminutive size, making it a truly versatile material with a wide range of potential applications.
Industrial Applications of Nickel Nanopowder
The exceptional properties of nickel nanopowder have paved the way for its integration into numerous industrial sectors, revolutionizing processes and enabling groundbreaking technological advancements. Let’s explore some of the key applications:
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Catalysis | Nickel nanopowder’s high surface area and catalytic activity make it an ideal catalyst for various chemical reactions, including hydrogenation, oxidation, and fuel cell reactions. |
| Energy Storage | The high surface area and electrical conductivity of nickel nanopowder make it a promising material for energy storage devices, such as batteries and supercapacitors. |
| Electronics | The magnetic properties of nickel nanopowder have applications in data storage, magnetic sensors, and other electronic devices. |
| Coatings and Composites | Nickel nanopowder can be incorporated into coatings and composites to enhance their mechanical, thermal, and electrical properties. |
| Environmental Remediation | The high reactivity of nickel nanopowder can be harnessed for environmental applications, such as water treatment and air purification. |
| Biomedical Applications | Nickel nanopowder has shown promise in biomedical fields, including drug delivery, cancer treatment, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast agents. |
These applications merely scratch the surface of the vast potential that nickel nanopowder holds. As research and development in nanotechnology continue to advance, we can expect to see even more innovative uses for this remarkable material.
Specifications, Grades, and Standards of Nickel Nanopowder
To ensure consistent quality and performance, nickel nanopowder is available in various grades and specifications, adhering to industry standards. Here’s an overview of some common specifications and standards:
| Specification | Description |
|---|---|
| Particle Size | Nickel nanopowder is available in various particle size ranges, typically from 1 to 100 nanometers, with specific sizes tailored to different applications. |
| Purity | The purity of nickel nanopowder can range from 99% to 99.9%, depending on the application and required level of impurities. |
| Surface Area | The surface area of nickel nanopowder is a critical parameter, with higher surface areas generally desired for catalytic and energy storage applications. |
| Morphology | Nickel nanopowder can exhibit different morphologies, such as spherical, irregular, or porous, which can influence its properties and performance. |
| Standards | Nickel nanopowder production and handling are subject to various industry standards, including ISO, ASTM, and other regulatory bodies, to ensure safety and quality. |
It’s essential to select the appropriate grade and specification of nickel nanopowder based on the specific requirements of your application to achieve optimal performance and results.
Suppliers and Pricing of Nickel Nanopowder
As the demand for nickel nanopowder continues to grow, so does the number of suppliers offering this remarkable material. Here’s an overview of some reputable suppliers and pricing information:
| Supplier | Pricing (USD/gram) |
|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich | $50 – $200 |
| Nanostructured & Amorphous Materials, Inc. | $80 – $250 |
| American Elements | $60 – $180 |
| Nano-Micro Letter | $70 – $220 |
| US Research Nanomaterials, Inc. | $90 – $300 |
Please note that these prices are subject to change and may vary based on the specific grade, purity, and quantity of nickel nanopowder required. It’s always advisable to contact suppliers directly for the most up-to-date pricing information and to discuss your specific requirements.
Pros and Cons of Nickel Nanopowder
Like any material, nickel nanopowder has its advantages and limitations. Let’s weigh the pros and cons to gain a more comprehensive understanding:
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| High surface area-to-volume ratio | Potential health and environmental concerns |
| Enhanced chemical reactivity | Increased risk of agglomeration and oxidation |
| Exceptional catalytic activity | Higher production costs compared to bulk materials |
| Improved thermal conductivity | Handling and storage challenges |
| Unique magnetic properties | Potential for increased toxicity at the nanoscale |
| Diverse range of applications | Limited understanding of long-term effects |
While the advantages of nickel nanopowder are undeniable, it’s crucial to address the potential risks and challenges associated with its production, handling, and disposal. Ongoing research and stringent safety protocols are essential to ensure the responsible and sustainable use of this innovative material.
FAQs
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the primary difference between nickel nanopowder and bulk nickel? | The primary difference lies in the size of the particles. Nickel nanopowder consists of particles with dimensions on the nanometer scale, while bulk nickel has larger particle sizes. This size difference results in unique properties and behaviors in nickel nanopowder. |
| Is nickel nanopowder toxic or hazardous? | Like many nanomaterials, nickel nanopowder may pose potential health and environmental risks due to its small size and increased reactivity. Proper handling, storage, and disposal procedures must be followed to mitigate these risks. |
| Can nickel nanopowder be used in biomedical applications? | Yes, nickel nanopowder has shown promise in various biomedical applications, such as drug delivery, cancer treatment, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast agents. However, further research is needed to ensure its safety and efficacy. |
| What industries currently utilize nickel nanopowder? | Nickel nanopowder is used in various industries, including catalysis, energy storage, electronics, coatings and composites, environmental remediation, and biomedical applications. |
| How stable is nickel nanopowder? | Nickel nanopowder can be prone to agglomeration and oxidation due to its high surface area and reactivity. Proper storage conditions and handling procedures are crucial to maintain its stability and performance. |
| Can nickel nanopowder be recycled or reused? | Recycling and reusing nickel nanopowder can be challenging due to its unique properties and potential contamination issues. However, research is ongoing to develop sustainable practices for the responsible management of nanomaterials. |
Remember, as with any cutting-edge technology, it’s essential to stay informed and follow best practices to ensure the safe and responsible use of nickel nanopowder.
Conclusion
Nickel nanopowder is a true marvel of modern science, a material that has the potential to revolutionize countless industries and shape the future of technology. From its incredible surface area and chemical reactivity to its unique magnetic properties and catalytic activity, this tiny powder packs a powerful punch.
As we continue to explore the vast possibilities of nanotechnology, nickel nanopowder stands as a shining example of what can be achieved when we push the boundaries of innovation. Whether it’s revolutionizing energy storage, catalyzing chemical reactions, or advancing biomedical treatments, the applications of this remarkable material are truly limitless.
Share On
MET3DP Technology Co., LTD is a leading provider of additive manufacturing solutions headquartered in Qingdao, China. Our company specializes in 3D printing equipment and high-performance metal powders for industrial applications.
Inquiry to get best price and customized Solution for your business!
Related Articles
About Met3DP
Recent Update
Our Product
CONTACT US
Any questions? Send us message now! We’ll serve your request with a whole team after receiving your message.

Metal Powders for 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing
COMPANY
PRODUCT
cONTACT INFO
- Qingdao City, Shandong, China
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- +86 19116340731

















