Nickel Powder: Suppliers,Types and Properties
Table of Contents
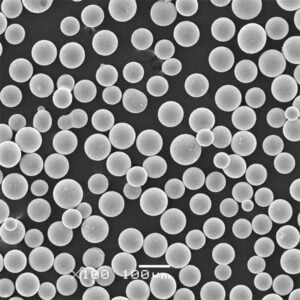
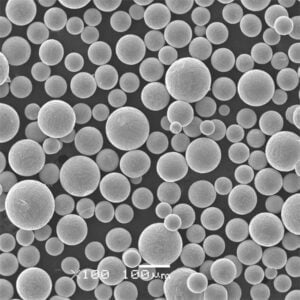
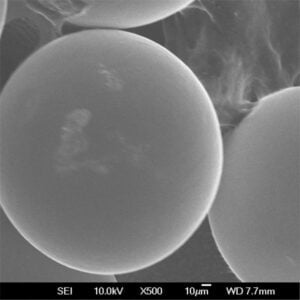
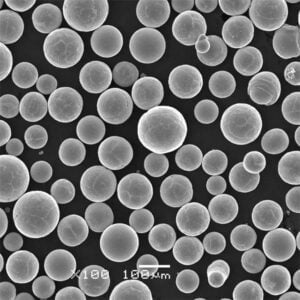
Nickel powder is a finely divided, particulate form of the metallic element nickel. This silvery-white material has captured the attention of various industries due to its exceptional properties and versatility. In this article, we’ll delve into the world of nickel powder, exploring its composition, characteristics, applications, and everything you need to know about this remarkable material.
Overview of Nickel Powder
Nickel powder is a fundamental component in numerous industrial processes and products. It’s renowned for its corrosion resistance, high-temperature strength, and excellent electrical and magnetic properties. From electronics to chemical processing, aerospace to automotive, nickel powder plays a crucial role in various sectors.
Composition and Types of Nickel Powder
| Type | Composition | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
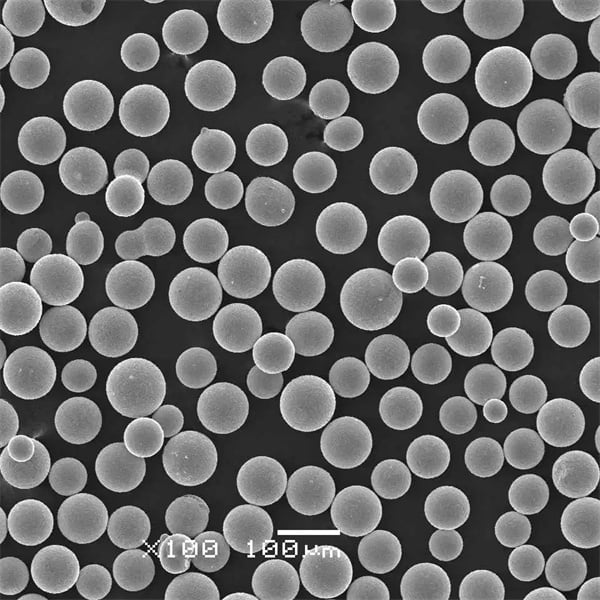
| Carbonyl Nickel Powder | Pure nickel obtained via nickel carbonyl process | High purity, spherical particles, excellent flow |
| Electrolytic Nickel Powder | Pure nickel produced by electrolytic deposition | Irregularly shaped particles, high surface area |
| Inert Gas Atomized Nickel Powder | Nickel alloys atomized in inert gas | Spherical particles, controlled size distribution |
| Water Atomized Nickel Powder | Nickel alloys atomized in water | Irregular particle shape, suitable for sintering |

Properties of Nickel Powder
| Property | Characteristic |
|---|---|
| Color | Silvery-gray |
| Density | 8.9 g/cm³ |
| Melting Point | 1455°C (2651°F) |
| Thermal Conductivity | 90.7 W/(m·K) |
| Electrical Resistivity | 6.99 × 10^-8 Ω·m |
| Magnetic Properties | Ferromagnetic |
Applications of Nickel Powder
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Electronics and Batteries | Used in nickel-cadmium and nickel-metal hydride batteries, conductive coatings, and electronic components |
| Catalysts | Employed as a catalyst in various chemical processes, such as hydrogenation and steam reforming |
| Electroplating | Nickel electroplating provides corrosion resistance and decorative finishes |
| Powder Metallurgy | Nickel powder is used in the production of high-strength, wear-resistant components |
| Welding and Brazing | Nickel powder is a key ingredient in welding and brazing alloys |
| Magnetic Materials | Utilized in the production of permanent magnets and magnetic recording media |
Specifications and Grades of Nickel Powder
| Grade | Particle Size | Purity | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| ASTM B438 Type I | 3-7 μm | 99.8% min | Batteries, catalysts, electronics |
| ASTM B438 Type II | 3-7 μm | 99.5% min | Powder metallurgy, coatings |
| ASTM B438 Type III | 7-15 μm | 99.5% min | Powder metallurgy, coatings |
| ASTM B438 Type IV | >15 μm | 99.5% min | Powder metallurgy, coatings |
Suppliers and Pricing of Nickel Powder
| Supplier | Price Range (USD/kg) | Grades Available |
|---|---|---|
| Norilsk Nickel | $20 – $30 | Carbonyl, Electrolytic |
| Vale | $18 – $25 | Carbonyl, Inert Gas Atomized |
| Sumitomo Metal Mining | $22 – $28 | Carbonyl, Water Atomized |
| Glencore | $19 – $27 | Carbonyl, Electrolytic |
| BHP Billiton | $21 – $29 | Carbonyl, Inert Gas Atomized |
Pros and Cons of Nickel Powder
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Excellent corrosion resistance | Potential health and environmental concerns |
| High-temperature strength | Relatively expensive compared to some alternatives |
| Versatile applications | Sensitivity to certain chemical environments |
| Magnetic properties | – |
| Electrical conductivity | – |
When it comes to nickel powder, the pros often outweigh the cons, making it a highly sought-after material in various industries. However, it’s essential to handle and dispose of nickel powder responsibly, adhering to safety and environmental regulations.
FAQs
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the difference between carbonyl and electrolytic nickel powder? | Carbonyl nickel powder is produced via a chemical process and has a spherical particle shape, while electrolytic nickel powder is obtained through electrolytic deposition and has an irregular particle shape. Carbonyl powder typically has higher purity and better flow characteristics. |
| How is nickel powder used in batteries? | Nickel powder is a key component in nickel-cadmium (Ni-Cd) and nickel-metal hydride (Ni-MH) rechargeable batteries, where it serves as the positive electrode material. |
| What are the advantages of using nickel powder in powder metallurgy? | Nickel powder offers excellent mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, and wear resistance to sintered components. It is often used in combination with other metallic powders to produce high-performance parts. |
| Are there any health concerns associated with nickel powder? | Yes, nickel compounds can cause skin irritation and respiratory issues in some individuals. Proper handling and safety measures should be taken when working with nickel powder. |
| How does the particle size of nickel powder affect its applications? | Smaller particle sizes typically result in higher surface area and reactivity, making them suitable for applications like catalysis and electrochemical processes. Larger particle sizes are preferred for powder metallurgy and coatings. |
In conclusion, nickel powder is a remarkable material that finds applications in a wide range of industries. From electronics and batteries to catalysts and powder metallurgy, this versatile material continues to shape the world around us. As technology advances, the demand for nickel powder is likely to grow, driving further innovation and exploration of its potential.
Share On
MET3DP Technology Co., LTD is a leading provider of additive manufacturing solutions headquartered in Qingdao, China. Our company specializes in 3D printing equipment and high-performance metal powders for industrial applications.
Inquiry to get best price and customized Solution for your business!
Related Articles
About Met3DP
Recent Update
Our Product
CONTACT US
Any questions? Send us message now! We’ll serve your request with a whole team after receiving your message.

Metal Powders for 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing
COMPANY
PRODUCT
cONTACT INFO
- Qingdao City, Shandong, China
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- +86 19116340731