Sinter-Hardening Alloy Powder
Table of Contents
Sinter-hardening alloy powders are a cornerstone of modern metallurgy and materials engineering. These materials offer the unique advantage of combining the processes of sintering and hardening into a single step, providing significant improvements in efficiency and performance for various industrial applications. This guide delves deep into the world of sinter-hardening alloy powders, exploring their types, compositions, properties, applications, and more. Whether you’re a seasoned professional or a curious learner, this article will offer valuable insights into this fascinating topic.
Overview of Sinter-Hardening Alloy Powder
Sinter-hardening is a process that involves compacting metal powder into a desired shape and then subjecting it to a high-temperature treatment to induce bonding between the particles, resulting in a solid piece. What sets sinter-hardening alloy powders apart is their ability to undergo both sintering and hardening simultaneously, eliminating the need for a separate heat treatment step. This results in improved mechanical properties and dimensional accuracy, making these materials highly sought after in industries like automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing.
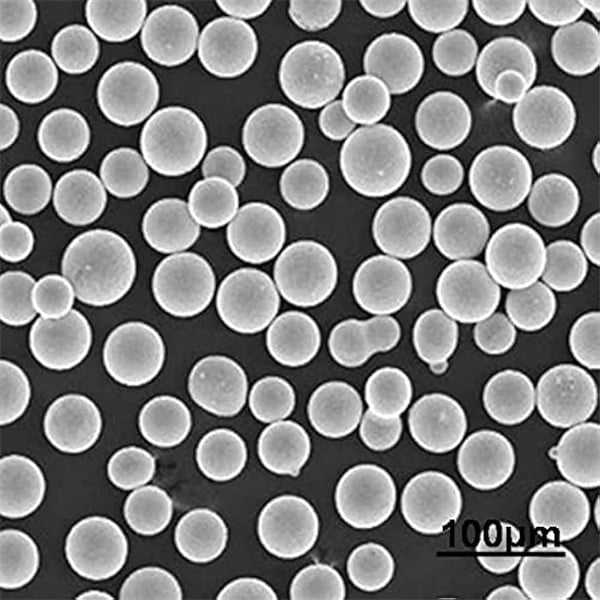
Types, Composition, and Properties of Sinter-Hardening Alloy Powders
Understanding the specific types, compositions, and properties of sinter-hardening alloy powders is crucial for selecting the right material for your application. Below is a detailed table summarizing key models of sinter-hardening alloy powders, their compositions, and properties.
| Type | Composition | Properties | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Model A | Fe-Cu-Ni-Mo | High strength, good wear resistance | Ideal for structural parts |
| Model B | Fe-Mn-Si | Excellent toughness, moderate hardness | Suitable for gears and bearings |
| Model C | Fe-Ni-Mo-Cr | Superior fatigue resistance, high hardness | Used in high-stress applications |
| Model D | Fe-Mo-C | Good machinability, balanced properties | Versatile for various applications |
| Model E | Fe-Cr-Mn | High corrosion resistance, good toughness | Perfect for marine environments |
| Model F | Fe-Ni-Mn | Excellent wear resistance, high hardness | Preferred for cutting tools |
| Model G | Fe-Mo-W | High temperature stability, good wear resistance | Suitable for high-temperature applications |
| Model H | Fe-Co-Ni | Superior magnetic properties, good strength | Used in electrical and magnetic applications |
| Model I | Fe-Cu-Mo-Ni-Cr | Excellent overall performance, high toughness | Ideal for automotive components |
| Model J | Fe-Mn-V | Good ductility, moderate strength | Used in complex-shaped parts |
Detailed Descriptions of Specific Models
Model A: Fe-Cu-Ni-Mo
Model A is a popular sinter-hardening alloy powder known for its high strength and good wear resistance. The combination of iron, copper, nickel, and molybdenum results in a material that is ideal for making structural parts. This alloy is particularly favored in the automotive industry for components such as transmission gears and engine parts due to its excellent
dimensional stability and mechanical performance.
Model B: Fe-Mn-Si
Model B’s composition of iron, manganese, and silicon gives it excellent toughness and moderate hardness, making it a suitable choice for gears and bearings. This alloy powder is often used in applications where shock absorption and impact resistance are critical, such as in heavy machinery and construction equipment.
Model C: Fe-Ni-Mo-Cr
Model C stands out for its superior fatigue resistance and high hardness, owing to its composition of iron, nickel, molybdenum, and chromium. This makes it ideal for high-stress applications such as aerospace components and high-performance automotive parts, where durability and reliability are paramount.
Model D: Fe-Mo-C
Model D features a balanced composition of iron, molybdenum, and carbon, providing good machinability and a balance of mechanical properties. This versatility makes it a popular choice for a wide range of applications, from industrial machinery parts to consumer products.
Model E: Fe-Cr-Mn
Model E is known for its high corrosion resistance and good toughness, thanks to its iron, chromium, and manganese composition. This alloy is particularly suitable for use in marine environments and other settings where exposure to moisture and corrosive elements is a concern.
Model F: Fe-Ni-Mn
With excellent wear resistance and high hardness, Model F, composed of iron, nickel, and manganese, is preferred for cutting tools and other applications where maintaining sharpness and durability is critical. Its properties make it suitable for use in both industrial and consumer cutting applications.
Model G: Fe-Mo-W
Model G combines iron, molybdenum, and tungsten to achieve high temperature stability and good wear resistance. This alloy powder is ideal for high-temperature applications, such as in turbine engines and other components that must withstand extreme heat without degrading.
Model H: Fe-Co-Ni
Model H features superior magnetic properties and good strength, due to its iron, cobalt, and nickel composition. This makes it highly suitable for electrical and magnetic applications, such as in motors, transformers, and magnetic sensors.
Model I: Fe-Cu-Mo-Ni-Cr
Model I boasts excellent overall performance and high toughness, resulting from its complex composition of iron, copper, molybdenum, nickel, and chromium. It is commonly used in automotive components, including drive shafts and differential gears, where a combination of strength, toughness, and wear resistance is required.
Model J: Fe-Mn-V
Model J, with its composition of iron, manganese, and vanadium, offers good ductility and moderate strength. This makes it suitable for manufacturing complex-shaped parts that require a degree of flexibility without sacrificing structural integrity.
Applications of Sinter-Hardening Alloy Powders
The applications of sinter-hardening alloy powders are vast and varied, reflecting the unique properties of these materials. Below is a table outlining the primary applications for different sinter-hardening alloy powders.
| Application | Suitable Alloy Models | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive Parts | Model A, Model I | High strength and wear resistance for gears, engine parts, and drive shafts |
| Aerospace Components | Model C, Model G | Superior fatigue resistance and high temperature stability for high-stress applications |
| Industrial Machinery | Model B, Model D | Good toughness and machinability for gears, bearings, and other machinery parts |
| Marine Environments | Model E | High corrosion resistance for components exposed to moisture and corrosive elements |
| Cutting Tools | Model F | Excellent wear resistance and hardness for maintaining sharpness and durability |
| Electrical and Magnetic Applications | Model H | Superior magnetic properties for motors, transformers, and sensors |
| Consumer Products | Model D, Model J | Versatility and good ductility for a wide range of products, from household appliances to electronics |
Automotive Parts
Sinter-hardening alloy powders like Model A and Model I are extensively used in the automotive industry. Their high strength and wear resistance make them ideal for manufacturing critical components such as gears, engine parts, and drive shafts. These materials ensure that the parts can withstand the demanding conditions of automotive applications, including high loads, friction, and temperature variations.
Aerospace Components
The aerospace industry demands materials with exceptional fatigue resistance and high-temperature stability, qualities found in Model C and Model G. These alloy powders are used to manufacture parts that must endure extreme stresses and temperatures, such as turbine blades, engine components, and structural parts of aircraft.
Industrial Machinery
Industrial machinery applications benefit from the toughness and machinability of Model B and Model D. These materials are used to produce gears, bearings, and other critical parts that must perform reliably under heavy loads and repetitive motion, often in harsh environments.
Marine Environments
Model E’s high corrosion resistance makes it perfect for components used in marine environments. Parts made from this alloy powder, such as propellers, shafts, and structural elements of ships and submarines, can withstand the corrosive effects of seawater and other marine conditions.
Cutting Tools
Cutting tools require materials that maintain sharpness and resist wear, which is where Model F excels. This alloy powder is used to manufacture blades, drill bits, and other cutting implements that must perform consistently and efficiently over time, even under intense usage.
Electrical and Magnetic Applications
Model H’s superior magnetic properties and strength make it ideal for electrical and magnetic applications. Components such as motors, transformers, and magnetic sensors benefit from this alloy powder’s ability to conduct and interact with magnetic fields effectively.
Consumer Products
The versatility and good ductility of Model D and Model J make them suitable for a wide range of consumer products. From household appliances to electronic devices, these materials offer the necessary balance of strength, flexibility, and durability required for everyday use.
Specifications, Sizes, Grades, and Standards
Selecting the right sinter-hardening alloy powder requires understanding the specifications, sizes, grades, and standards associated with these materials. The table below provides a detailed overview of these parameters.
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Sizes | Typically range from 5 µm to 150 µm particle size |
| Grades | Vary by application, including standard industrial grades and high-performance aerospace grades |
| Standards | Adhere to ASTM, ISO, and DIN standards for consistency and quality assurance |
| Specifications | Include chemical composition, mechanical properties, and physical characteristics tailored to specific applications |
Particle Sizes
Sinter-hardening alloy powders are available in a range of particle sizes, typically from 5 micrometers (µm) to 150 µm. The choice of particle size depends on the specific requirements of the application, with finer particles generally providing better surface finish and detail in the final product, while coarser particles may offer improved flowability and packing density.
Grades
These materials are available in various grades to meet the needs of different industries and applications. Standard industrial grades are suitable for general manufacturing purposes, while high-performance aerospace grades are designed to meet the stringent requirements of the aerospace industry, including higher strength and fatigue resistance.
Standards
Sinter-hardening alloy powders must comply with established standards to ensure quality and consistency. Common standards include those set by the ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials), ISO (International Organization for Standardization), and DIN (Deutsches Institut für Normung, the German Institute for Standardization). Adherence to these standards ensures that the materials meet specific chemical composition, mechanical property, and physical characteristic requirements.
Specifications
Specifications for sinter-hardening alloy powders include detailed information about their chemical composition, mechanical properties (such as tensile strength, hardness, and elongation), and physical characteristics (such as density and thermal conductivity). These specifications are tailored to the specific needs of different applications, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.
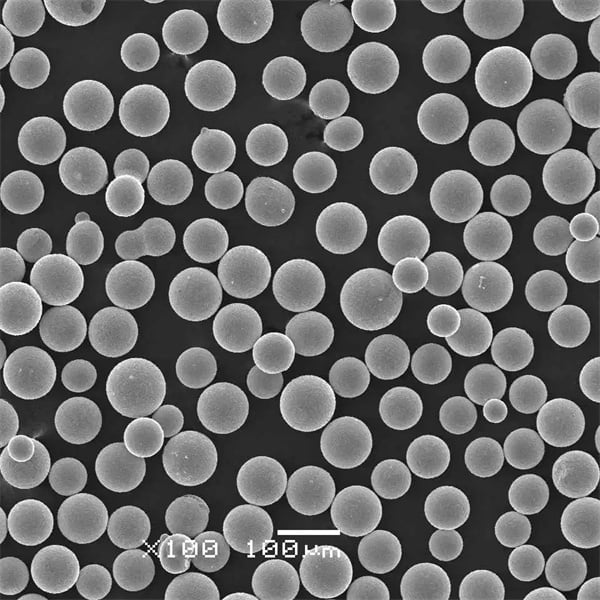
Suppliers and Pricing Details
Choosing the right supplier for sinter-hardening alloy powders is crucial for ensuring quality and consistency. Below is a table listing some prominent suppliers along with their pricing details.
| Supplier | Location | Pricing (per kg) | Specialties |
|---|---|---|---|
| Höganäs AB | Sweden | $50 – $150 | Wide range of alloy powders, excellent quality control |
| GKN Hoeganaes | USA | $45 – $140 | Extensive product range, advanced technology |
| Sandvik | Sweden | $55 – $160 | High-performance powders, strong R&D focus |
| Carpenter Technology | USA | $60 – $170 | Specialty alloys, tailored solutions |
| Rio Tinto Metal Powders | Canada | $48 – $145 | High-purity powders, reliable supply chain |
| Ametek Specialty Metal Products | USA | $52 – $155 | Customizable alloy compositions, high consistency |
| Sumitomo Electric Industries | Japan | $50 – $150 | Innovative materials, advanced production techniques |
| Daido Steel | Japan | $55 – $160 | High-quality alloys, extensive application expertise |
| Mitsubishi Materials | Japan | $50 – $150 | Broad product portfolio, strong customer support |
| Kennametal | USA | $58 – $165 | High-performance materials, global presence |
Supplier Highlights
- Höganäs AB is renowned for its wide range of alloy powders and excellent quality control, making it a preferred choice for many industries.
- GKN Hoeganaes offers an extensive product range and advanced technology, ensuring high performance and reliability.
- Sandvik focuses on high-performance powders and has a strong R&D division, continually innov
ating to meet industry needs.
- Carpenter Technology specializes in tailored solutions with their specialty alloys, catering to specific customer requirements.
- Rio Tinto Metal Powders provides high-purity powders and a reliable supply chain, ensuring consistent product availability.
Comparing Pros and Cons, Advantages and Limitations
To make an informed decision, it’s important to understand the pros and cons of sinter-hardening alloy powders compared to other materials. The table below highlights these aspects.
| Aspect | Sinter-Hardening Alloy Powders | Traditional Alloy Powders |
|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | Sinter and harden in one step, saving time and energy | Requires separate sintering and heat treatment steps |
| Mechanical Properties | Improved strength, hardness, and wear resistance | Good properties but may require additional processing |
| Dimensional Accuracy | High precision due to single-step process | Potential for dimensional changes during multiple processing steps |
| Cost | Higher initial cost but lower overall due to process efficiency | Lower initial cost but higher overall due to additional processing steps |
| Applications | Suitable for high-performance and demanding applications | Suitable for general and some specialized applications |
| Complexity | Requires advanced equipment and control systems | Simpler equipment and processes, but with added steps |
| Customization | Highly customizable compositions and properties | Customization possible but may require more processing |
Advantages of Sinter-Hardening Alloy Powders
- Efficiency: The primary advantage is the ability to sinter and harden in a single step, which saves time and energy compared to traditional methods that require separate sintering and heat treatment processes.
- Mechanical Properties: Sinter-hardening alloy powders typically exhibit superior mechanical properties, including higher strength, hardness, and wear resistance, making them ideal for high-performance applications.
- Dimensional Accuracy: The single-step process minimizes the risk of dimensional changes, resulting in high precision and consistency in the final product.
- Customization: These powders offer highly customizable compositions and properties, allowing for tailored solutions to meet specific application requirements.
Disadvantages of Sinter-Hardening Alloy Powders
- Cost: While the overall cost may be lower due to process efficiency, the initial cost of sinter-hardening alloy powders can be higher compared to traditional powders.
- Complexity: The process requires advanced equipment and control systems, which can add to the complexity and cost of production.
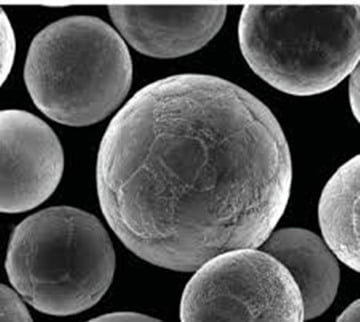
Insights, Examples, and Comparisons
Performance Insights
To illustrate the advantages of sinter-hardening alloy powders, consider an automotive application where a component made from Model A (Fe-Cu-Ni-Mo) is compared to a traditional steel part. The sinter-hardened part not only exhibits higher strength and wear resistance but also maintains dimensional accuracy, reducing the need for post-processing adjustments. This results in a more efficient manufacturing process and a longer-lasting component, providing better value over time.
Real-World Example
In the aerospace industry, the use of Model G (Fe-Mo-W) for turbine blades demonstrates the material’s high-temperature stability and wear resistance. Traditional alloy powders would require additional heat treatment to achieve similar properties, increasing both time and cost. The sinter-hardening process streamlines production, ensuring that the blades can withstand extreme conditions without compromising performance.
Comparative Analysis
When comparing sinter-hardening alloy powders to traditional alloy powders, it’s clear that the former offer significant benefits in terms of efficiency, mechanical properties, and dimensional accuracy. However, they may not be the best choice for every application, particularly where cost and simplicity are primary considerations. For general manufacturing needs, traditional alloy powders might suffice, but for high-performance, demanding applications, sinter-hardening alloys provide unmatched advantages.

FAQ
What is sinter-hardening?
Sinter-hardening is a process that combines sintering and hardening into a single step. Metal powder is compacted into a desired shape and then heated to a high temperature to induce bonding and hardening simultaneously, resulting in a solid piece with enhanced mechanical properties.
Why use sinter-hardening alloy powders?
Sinter-hardening alloy powders offer several advantages, including improved strength, hardness, wear resistance, and dimensional accuracy. They also streamline the manufacturing process by combining sintering and hardening into one step, saving time and energy.
What industries benefit from sinter-hardening alloy powders?
Industries such as automotive, aerospace, industrial machinery, marine, and electrical applications benefit significantly from the use of sinter-hardening alloy powders due to their superior properties and efficiency in production.
How do sinter-hardening alloy powders compare to traditional alloy powders?
Sinter-hardening alloy powders provide better mechanical properties, higher efficiency, and greater dimensional accuracy compared to traditional alloy powders. However, they can be more expensive initially and require advanced equipment for processing.
What are some common compositions of sinter-hardening alloy powders?
Common compositions include combinations of iron with elements such as copper, nickel, molybdenum, manganese, silicon, chromium, and tungsten. Each combination offers unique properties suitable for specific applications.
Can sinter-hardening alloy powders be customized?
Yes, sinter-hardening alloy powders can be highly customized to meet specific application requirements. Adjustments in composition can tailor properties such as strength, hardness, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance.
Where can I buy sinter-hardening alloy powders?
Sinter-hardening alloy powders can be purchased from suppliers like Höganäs AB, GKN Hoeganaes, Sandvik, Carpenter Technology, Rio Tinto Metal Powders, Ametek Specialty Metal Products, Sumitomo Electric Industries, Daido Steel, Mitsubishi Materials, and Kennametal.
What factors should I consider when selecting a sinter-hardening alloy powder?
When selecting a sinter-hardening alloy powder, consider factors such as the specific application, required mechanical properties, dimensional accuracy, cost, and supplier reliability. It’s also important to ensure that the material meets relevant standards and specifications for your industry.
Conclusion
Sinter-hardening alloy powders represent a significant advancement in materials engineering, offering a unique combination of sintering and hardening in a single step. With a variety of compositions tailored to meet the needs of different industries, these materials provide superior mechanical properties, efficiency, and precision. Whether you’re involved in automotive manufacturing, aerospace engineering, or any other high-performance application, understanding and utilizing sinter-hardening alloy powders can lead to improved product quality and manufacturing efficiency.
Share On
MET3DP Technology Co., LTD is a leading provider of additive manufacturing solutions headquartered in Qingdao, China. Our company specializes in 3D printing equipment and high-performance metal powders for industrial applications.
Inquiry to get best price and customized Solution for your business!
Related Articles
About Met3DP
Recent Update
Our Product
CONTACT US
Any questions? Send us message now! We’ll serve your request with a whole team after receiving your message.

Metal Powders for 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing
COMPANY
PRODUCT
cONTACT INFO
- Qingdao City, Shandong, China
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- +86 19116340731

















