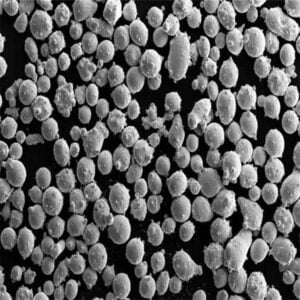
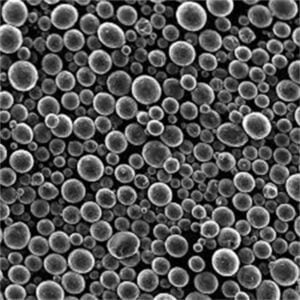
Tungsten Metal Powder Suppliers
Table of Contents
Tungsten powder is a dense powder metal valued for its very high melting point, hardness, wear resistance and high-temperature strength. This article provides an overview of tungsten metal powders, manufacturing methods, grades, applications and leading tungsten metal powder supplier.
Overview of Tungsten Metal Powder
Tungsten metal powder, also known as tungsten carbide or simply tungsten powder, is composed of microfine particles of pure elemental tungsten metal or an alloy containing tungsten. Key properties include:
- Extremely high melting point of 3422°C
- Density almost twice that of steel
- Hardness close to diamond
- Excellent wear and erosion resistance
Tungsten powder is available in various grades based on purity, chemistry, particle size distribution and morphology. Custom alloys contain cobalt, nickel, iron or copper to enhance properties.
Tungsten Powder Types
| Type | Description | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Pure tungsten | Elemental tungsten 99.9% purity | Highest melting point, density, stiffness |
| Tungsten carbide | Tungsten carbide-cobalt cermet | Extreme hardness and wear resistance |
| Heavy alloys | Tungsten alloys with nickel, copper etc. | High-density ballast applications |
Tungsten Powder Properties
| Property | Pure Tungsten | Tungsten Carbide |
|---|---|---|
| Density (g/cc) | 19.3 | 15.63 |
| Melting Point | 3422°C | 2870°C (decomposes) |
| Mohs Hardness | 7.5 | 8.5-9.5 |
| Strength (MPa) | 550 | 700-2000 |
Tungsten Powder Specifications
Tungsten powder is available in different particle sizes, size distributions, shapes and purity levels based on the production process and final application requirements.
| Parameter | Range |
|---|---|
| Particle size | 0.5 – 15 microns |
| Tap density | 3-12 g/cc |
| Apparent density | >50% of true density |
| Purity | 99.9% to 99.995% |
| Oxygen content | <100 – 1000 ppm |
| Carbon content | <100 – 500 ppm |

Production Methods for Tungsten Powder
The extreme high temperature properties of tungsten require specialized powder production techniques under inert atmospheres. The main methods include:
1. Hydrogen Reduction
Tungsten ores are reacted with hydrogen gas to produce tungsten powder. It generates irregular angular powders suitable for pressing or additive manufacturing.
2. Thermal Plasma Spheroidization
Irregular tungsten powder feedstock is injected into a thermal plasma jet to create fully dense, spherical powders ideal for additive manufacturing, thermal spray, MIM etc.
3. Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
Ultrafine tungsten powders with particle sizes below one micron and high purity levels are produced via tungsten hexafluoride in a CVD reactor.
Tungsten Powder Manufacturing Methods
| Method | Particle Shape | Solid Density | Size Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen Reduction | Irregular, angular | Low | 1-10 microns |
| Plasma Spheroidization | Spherical | High | 10-100 microns |
| Chemical Vapor Deposition | Spherical | Medium | 0.05-1 micron |
Applications of Tungsten Metal Powder
| Application | Properties Leveraged | Benefits | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Incandescent Lighting Filaments | High melting point (~3422°C) & excellent thermal conductivity | Enables filaments to withstand intense heat for extended periods, producing bright light | Traditional light bulbs |
| Electrical Contacts & Switches | High melting point, good electrical conductivity, and resistance to arcing | Ensures reliable electrical connections and minimizes contact wear | Spark plugs, high-voltage switches, circuit breakers |
| Heating Elements | High melting point, good electrical conductivity, and resistance to oxidation | Allows efficient conversion of electricity to heat in harsh environments | Furnace heating elements, rocket engine nozzles |
| Electrodes for Welding | High melting point, good electrical conductivity, and dimensional stability | Facilitates precise and reliable welding processes | Gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW) electrodes |
| X-ray & Gamma-ray Shielding | High density | Provides effective protection against ionizing radiation | Medical X-ray shielding, nuclear power plant shielding |
| Armor-Piercing Penetrators | High density and hardness | Penetrates thick armor effectively | Kinetic energy penetrators (KEPs) for tank ammunition |
| Cutting Tools & Wear-Resistant Parts | Can be combined with carbon to form tungsten carbide (WC), known for exceptional hardness and wear resistance | Enables machining of hard materials and extends tool life | Drill bits, milling inserts, dies & punches for metal forming |
| Sporting Goods | High density in a compact form | Improves balance, swing weight, and overall performance | Golf club weights, fishing weights for deep-sea fishing |
| Catalysts in Chemical Processes | Tailorable surface area and specific activity | Enhances reaction rates in various chemical reactions | Ammonia synthesis catalysts, hydrogenation catalysts |
| Vibration Damping | High density | Reduces unwanted vibrations and improves stability | Vibration dampers in machines and instruments |
Global tungsten metal powder supplier
| Feature | Global Tungsten & Powders (GTP) | Kennametal Inc. | Hunan Xiangtan Electric Material Co., Ltd. (HXEMC) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Headquarters Location | Towanda, Pennsylvania, USA | Latrobe, Pennsylvania, USA | Xiangtan, Hunan, China |
| Global Reach | Manufacturing facilities in USA, Finland, Czech Republic, and Luxembourg | Extensive distribution network but primary production in USA | Focus on domestic Chinese market with some export capabilities |
| Product Range | Tungsten metal powders, tungsten carbide powders, tungsten-based thermal spray powders, tungsten heavy alloy (WHA) powders | Primarily tungsten carbide powders and finished products like cutting tools | Tungsten and molybdenum powders, tungsten carbide powders, composite materials |
| Industry Focus | Aerospace, automotive, construction, defense, oil & gas, electronics | Metalworking, mining, construction | Electronics, automotive, machinery, energy |
| Sustainability Efforts | Investment in R&D for eco-friendly production methods | Limited public information on sustainability initiatives | Focus on efficient production processes but details unclear |
| Customer Service | Dedicated sales team and online quote request system | Established customer service network | Information primarily in Mandarin Chinese, limited English support availability |
| Quality Certifications | ISO 9001:2015 certified | IATF 16949:2016 certified for automotive industry standards | ISO 9001 certified |
| Competitive Advantages | Long history (over 75 years) in tungsten industry, diverse production capabilities across multiple countries, focus on finished components for specific sectors (e.g., aerospace) | Expertise in metalworking applications, strong brand recognition within the industry | Competitive pricing, established presence in the Chinese market |
Tungsten Powder Pricing
| Supplier | Product | Particle Size | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| Buffalo Tungsten | Pure tungsten | 1-10 microns | $50/lb |
| HC Starck | Tungsten carbide | 0.5-3 microns | $50/lb |
| Global Tungsten | Pure tungsten | 1 micron | $175/kg |
| XiangLu Tungsten | Tungsten powder | 1-10 microns | $30/kg |
Tungsten and tungsten carbide powders demand premium pricing due to hazardous production methods and specialized applications. Significant volume discounts apply.
Choosing tungsten metal powder supplier
| Factor | Description | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Technical Specifications | This is the foundation of your selection. Tungsten powder properties vary significantly to suit diverse applications. | Purity: Purity levels range from 97% (cost-effective) to 99.995% (ultrafine, high-performance). Consider the trade-off between cost and functionality for your project. Particle Size & Distribution: Particle size and distribution significantly impact the final product’s properties. Finer powders create smoother surfaces but may be trickier to work with. Coarser powders offer better flow characteristics but might result in a rougher finish. Morphology (Shape): Spherical shapes offer excellent flowability and packing density, while irregular shapes can enhance strength. Chemical Composition: Identify any allowable impurities or trace elements based on your application. |
| Supplier Capabilities | A reliable supplier can ensure consistent quality and meet your specific needs. | Production Technology: Investigate the supplier’s technology for achieving your desired purity levels. Different methods can influence powder characteristics. Quality Control & Certifications: Look for ISO 9001 certification, indicating a robust quality management system. Inquire about their testing procedures to ensure consistent adherence to specifications. Customization: If you require specific powder characteristics beyond their standard offerings, assess their ability to customize production processes. |
| Commercial Considerations | Price is just one aspect. Reliable delivery and responsive communication are equally important. | Pricing: Tungsten powder pricing is influenced by purity, particle size, quantity, and market fluctuations. Obtain quotes from multiple suppliers for comparison. Negotiate for bulk purchases if applicable. Delivery & Lead Times: Understand the supplier’s lead times and shipping options to align with your production schedule. Factor in any potential import/export restrictions. Payment Terms: Negotiate favorable payment terms that suit your cash flow. Minimum Order Quantities: Be aware of minimum order requirements, especially if you’re starting with smaller projects. |
| Supplier Reputation & Service | Partnering with a reputable supplier fosters long-term success. | Industry Experience: Look for suppliers with a proven track record in tungsten powder production and experience catering to your specific industry. Customer Service: Responsive and knowledgeable customer support is crucial for addressing questions and resolving issues. Technical Support: If you require assistance with selecting the appropriate powder or troubleshooting application challenges, assess the supplier’s technical support capabilities. Environmental & Social Responsibility: Consider the supplier’s commitment to sustainable practices and ethical sourcing, especially if these factors align with your company values. |
Tungsten vs. Alternative Powder Metals
Tungsten vs. Tantalum
Similar high melting point but tungsten is harder and has higher wear resistance. Tantalum more ductile and expensive due to rarity. Both used in electronics and alloying applications.
Tungsten vs. Lead
Lead cheaper but toxic while tungsten eco-friendly alternative for weighting applications. Higher strength lead alloys approach tungsten in density. Lead melts easily unlike tungsten’s extreme resistance.
Tungsten vs. Gold
Gold extremely expensive precious metal. Tungsten used since WW1 as heavy substitute for gold electroplating in counterfeiting coins. Similar density allows tungsten to mimic the feel of gold.
Tungsten vs. Depleted Uranium
Depleted uranium ~40% denser but low-level radioactivity limits applications. Tungsten suitable non-hazardous alternative for radiation shielding and defense uses. Cheaper, easier to handle.
Tungsten vs. Platinum
Platinum higher melting point than tungsten but costs thousands per ounce. Tungsten an affordable substitute for high-temperature electrical contacts to replace costly platinum group metals.

FAQ
Q: What is the difference between tungsten metal powder and tungsten carbide powder?
A: Pure tungsten metal powder is elemental tungsten whereas cemented tungsten carbide is a composite of tungsten carbide particles bonded together by cobalt. Carbide grades focus on extreme hardness.
Q: What hazards are associated with tungsten powder handling?
A: Tungsten fine powder can combust spontaneously in air forming explosive mixtures. Strict inert atmosphere protocols are mandatory. Water contact produces volatile hydrogen gas. Respirators required to prevent lung tissue damage.
Q: What particle size tungsten powder is best suited for additive manufacturing?
A: For binder jetting processes, fine tungsten powder from 5-50 microns with spherical morphology and high powder flow is ideal. For laser-based printers, 10-100+ micron powder is commonly used.
Q: What postprocessing is used on additively manufactured tungsten parts?
A: Sintering followed by hot isostatic pressing (HIP) helps achieve maximum density and uniform fine-grained microstructure. Additional heat treatments, machining and finishing may be used per application requirements.
Q: How are tungsten and its alloys joined to other components?
A: Brazing is commonly used to join tungsten parts using silver-based and copper-based alloys. Diffusion bonding and adhesive bonding are alternate methods. Welding requires specialized techniques due to contamination concerns.
Share On
MET3DP Technology Co., LTD is a leading provider of additive manufacturing solutions headquartered in Qingdao, China. Our company specializes in 3D printing equipment and high-performance metal powders for industrial applications.
Inquiry to get best price and customized Solution for your business!
Related Articles
About Met3DP
Recent Update
Our Product
CONTACT US
Any questions? Send us message now! We’ll serve your request with a whole team after receiving your message.

Metal Powders for 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing
COMPANY
PRODUCT
cONTACT INFO
- Qingdao City, Shandong, China
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- +86 19116340731