Comparing 3D printing technology with traditional technology in Jewelry industry
Table of Contents
Imagine crafting intricate objects, from delicate jewelry to sturdy machine parts, not by carving or welding, but by building them layer by layer with a laser beam and a vat of fine metallic dust. This isn’t science fiction; it’s the reality of 3D printing metal powder, a revolutionary technology transforming manufacturing across industries.
Traditional Jewelry Forming Technology
For centuries, jewelry crafting has relied on meticulous handwork or traditional techniques like casting and forging. These methods, while creating stunning pieces, can be time-consuming, limited in design complexity, and often result in material waste. Imagine a jeweler wanting to create a ring with an intricate, lace-like design. Traditional methods might struggle to achieve such delicate features without compromising the ring’s structure.
3D Printing Technology in Jewelry
Enter 3D printing with metal powder. This technology acts like a high-tech sculptor, meticulously building the desired object using a computer-controlled laser. Here’s the magic: a layer of fine metal powder is spread across a platform. The laser beam, guided by a digital blueprint, selectively melts the powder particles, fusing them together. Layer by layer, the object takes shape, transforming digital dreams into tangible reality.
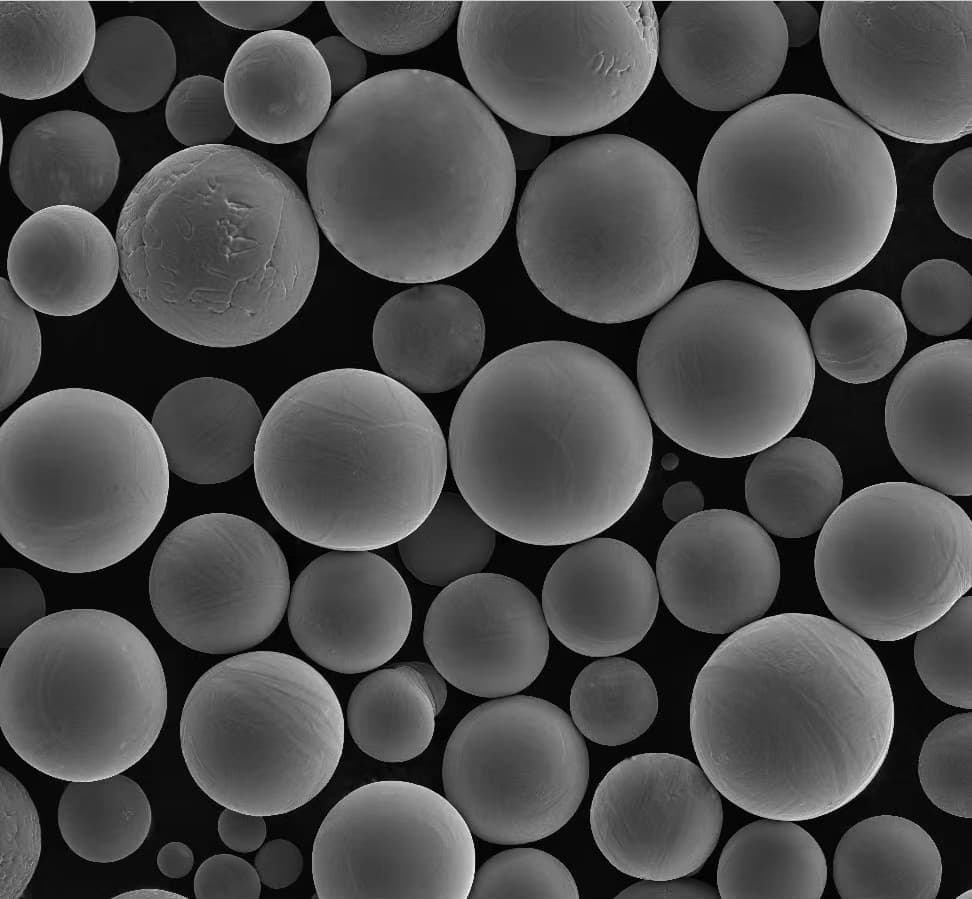
Comparison Between These Two Technologies
Let’s break down the key differences:
| Feature | Traditional Techniques | 3D Printing with Metal Powder |
|---|---|---|
| Design Complexity | Limited by tools and techniques | Highly versatile, can create intricate designs |
| Material Waste | Can be significant, especially with complex shapes | Minimizes waste by building only the required material |
| Production Speed | Time-consuming, often involving handwork | Faster turnaround time, especially for complex designs |
| Customization | Limited to existing molds and tools | Highly customizable, allows for personalized designs |
A Universe of Metal Powders
Not all metal powders are created equal. Different metals and alloys offer unique properties, catering to diverse applications. Here’s a glimpse into the world of 3D printable metal powders:
- Stainless Steel: A popular choice for its durability, corrosion resistance, and aesthetics. It’s commonly used for jewelry, medical implants, and industrial components.
- Titanium: Renowned for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and biocompatibility. It finds applications in aerospace parts, medical implants, and high-performance sporting goods.
- Inconel: A superalloy known for its ability to withstand extreme temperatures and harsh environments. It’s used in jet engine components, rocket parts, and chemical processing equipment.
- Gold and Silver: These precious metals can be used to create stunning jewelry with intricate details and smooth finishes.
The Nuances of Choosing the Right Powder
Picking the perfect metal powder depends on the desired outcome. For a delicate necklace, a fine silver powder might be ideal, while a robust tool for an industrial machine might call for a sturdier stainless steel powder. Understanding the properties of each metal powder, such as its melting point, strength, and corrosion resistance, is crucial for making informed choices.
Applications of 3D Printed Metal Powder
The applications of 3D printed metal powder extend far beyond the realm of jewelry. This technology is revolutionizing various industries:
- Aerospace: Lighter, stronger aircraft components are being created, leading to more fuel-efficient planes.
- Automotive: Customized engine parts and intricate cooling systems are being produced, enhancing performance and efficiency.
- Medical: Personalized prosthetics and implants are being tailored to individual needs, improving patient outcomes.
- Consumer Goods: From customized bike frames to innovative tools, 3D printing with metal powder is shaping the future of product design.
The Advantages and Potential Drawbacks
Like any technology, 3D printing with metal powder has its own set of pros and cons:
Advantages:
- Design Freedom: Unleashes creativity with the ability to produce complex geometries previously impossible with traditional methods.
- Reduced Waste: Minimizes material waste compared to traditional subtractive manufacturing techniques.
- Lightweighting: Enables the creation of strong, lightweight parts, critical for applications like aerospace.
- Customization: Allows for personalized designs and on-demand manufacturing.
Potential Drawbacks:
- Cost: The technology can be expensive, especially for larger or high-resolution prints.
- Material Limitations: Not all metals are readily available in printable powder form.
- Post-Processing: 3D printed metal parts often require additional finishing steps after printing.
The Future of 3D Printed Metal Powder
- Reduced Costs: With advancements in technology and increased adoption, the cost of 3D printing with metal powder is expected to decrease, making it more accessible to a wider range of industries and applications.
- Material Innovation: The development of new and improved metal powders with enhanced properties like increased strength, conductivity, and biocompatibility will further expand the technology’s reach.
- Multi-Material Printing: The ability to combine different metal powders within a single print could pave the way for the creation of objects with unique functional properties in distinct areas. Imagine a tool with a lightweight titanium handle and a wear-resistant steel working tip, all printed in one go.
- Integration with Other Technologies: The merging of 3D printing with metal powder with other technologies like artificial intelligence and robotics has the potential to create intelligent, self-optimizing manufacturing processes.
Beyond the Hype: Addressing Common Concerns
While 3D printing with metal powder offers exciting possibilities, some concerns linger:
- Safety: Laser-based printing processes involve heat and molten metal, necessitating proper safety protocols to protect users from fumes and potential hazards.
- Environmental Impact: The energy consumption of 3D printing and the potential environmental impact of metal powder production need to be addressed through sustainable practices and energy-efficient technologies.
- Standardization: Developing standardized processes and material qualifications will be crucial for ensuring the quality and consistency of 3D printed metal parts.
Addressing these concerns will be essential for the continued growth and adoption of this transformative technology.
Is 3D Printed Metal Powder Right for You?
If you’re looking for a way to create complex, high-strength metal objects with minimal waste and maximum design freedom, then 3D printing with metal powder might be the answer. Here are some factors to consider:
- Complexity of your design: If your design is intricate or has unique features, 3D printing might be the only viable option.
- Material requirements: Consider the specific properties needed for your project. Does it require strength, corrosion resistance, or biocompatibility? Choose the metal powder that best suits your needs.
- Production volume: For high-volume production, traditional manufacturing techniques might still be more cost-effective. However, for low-volume, customized projects, 3D printing can be a great option.
Getting Started with 3D Printed Metal Powder
If you’re ready to explore the world of 3D printed metal powder, here are some initial steps:
- Research: Familiarize yourself with the technology, different metal powders, and their applications.
- Design: Develop a 3D model of your desired object using computer-aided design (CAD) software. Ensure the design is optimized for 3D printing.
- Find a Service Provider: Several companies offer 3D printing services with metal powder. They can handle the printing process and post-processing steps.
Embrace the Future
3D printed metal powder is a groundbreaking technology with the potential to revolutionize how we design, manufacture, and use metal objects. As the technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more exciting possibilities to emerge, shaping the future of various industries and opening doors to a world of limitless creation.
FAQ
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What are the different types of metal powders used in 3D printing? | Common metal powders include stainless steel, titanium, Inconel, gold, and silver. Each offers unique properties for specific applications. |
| Is 3D printed metal powder jewelry as strong as traditionally made jewelry? | Yes, 3D printed metal powder jewelry can be just as strong, or even stronger, than traditionally made jewelry, depending on the chosen metal powder. |
| What are the post-processing steps involved in 3D printed metal powder objects? | Depending on the desired finish, post-processing might involve support removal, heat treatment, and surface finishing techniques like sandblasting or polishing. |
| Is 3D printed metal powder environmentally friendly? | While 3D printing can minimize material waste compared to traditional methods, the energy consumption and environmental impact of metal powder production need to be addressed for true sustainability. |
| How much does it cost to 3D print with metal powder? | The cost can vary depending on the size, complexity, and chosen metal powder. It’s generally more expensive than traditional methods for larger prints, but the cost is expected to decrease as the technology matures. |
Share On
MET3DP Technology Co., LTD is a leading provider of additive manufacturing solutions headquartered in Qingdao, China. Our company specializes in 3D printing equipment and high-performance metal powders for industrial applications.
Inquiry to get best price and customized Solution for your business!
Related Articles
About Met3DP
Recent Update
Our Product
CONTACT US
Any questions? Send us message now! We’ll serve your request with a whole team after receiving your message.

Metal Powders for 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing
COMPANY
PRODUCT
cONTACT INFO
- Qingdao City, Shandong, China
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- +86 19116340731