gas atomization metal powder
Table of Contents
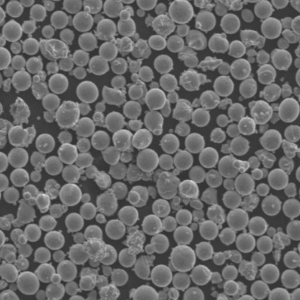
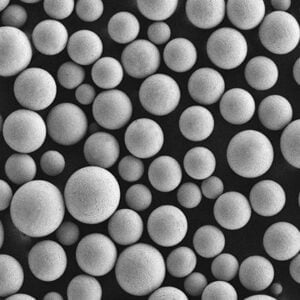
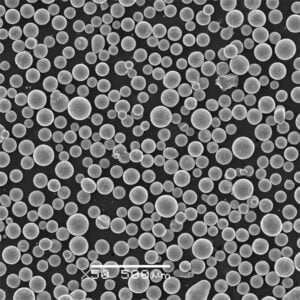
Gas atomization metal powder refers to a material processing method to produce fine spherical metal powders for applications like metal injection molding (MIM), additive manufacturing, pressing and sintering, thermal spray coatings, powder metallurgy, and more.
In gas atomization, molten metal alloys are disintegrated into droplets using high pressure inert gas jets. The droplets rapidly solidify into powder, yielding highly spherical morphologies ideal for powder consolidation processes.
This guide covers gas atomized metal powder compositions, characteristics, applications, specifications, production methods, suppliers, pros vs cons, and FAQs to consider.

Composition of Gas Atomized Metal Powders
Various metals and alloys with tailored chemistries are atomized into powders:
| Material | Composition Overview | Common Alloys |
|---|---|---|
| Stainless steel | Fe-Cr + Ni/Mn/Mo | 304, 316, 410, 420 |
| Tool steel | Fe-Cr-C + W/V/Mo alloys | H13, M2, P20 |
| Aluminum alloy | Al + Cu/Mg/Mn/Si | 2024, 6061, 7075 |
| Titanium alloy | Ti + Al/V alloys | Ti-6Al-4V |
| Nickel alloy | Ni + Cr/Fe/Mo alloys | Inconel 625, 718 |
| Copper alloy | Cu + Sn/Zn/alloys | Brass, bronze |
These metal powders offer specific mechanical, thermal, electrical and other physical properties for manufacturing needs.
Characteristics of gas atomization metal powder
In addition to chemistry, characteristics like particle size, shape, density, and microstructure determine performance:
| Attribute | Description | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size distribution | Range/distribution of diameters | Impacts minimum feature resolution, packing efficiency |
| Particle morphology | Powder shape/surface structure | Rounded, smooth particles provide best flow and handling |
| Apparent density | Weight per volume including interparticle voids | Influences compactability and clustering |
| Tap density | Settled density after mechanical tapping | Relates to ease of powder bed compaction |
| Surface chemistry | Surface oxides, residual gases or moisture | Affects powder stability and consistency |
| Microstructure | Grain size/phase distribution | Determines properties like hardness, ductility after consolidation |
These interconnected aspects are balanced for needs.
Applications of gas atomization metal powder
The consistent material input and net shaping capabilities support diverse applications:
| Industry | Uses | Component Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Additive manufacturing | 3D printing feedstock | Aerospace airfoils, medical implants |
| Metal injection molding | Small intricate metal parts | Nozzles, gears, fasteners |
| Press and sinter | P/M component production | Structural auto parts, military/firearm components |
| Thermal spray | Surface coatings | Anti-wear, anti-corrosive overlays |
| Powder metallurgy | Oilite bearings, self-lubricating bushings | Wear components with porous structures |
Gas atomization provides unique access to tailor microstructures and chemistries suited to end-performance needs.
Specifications
While application-specific, common nominal ranges include:
| Parameter | Typical Range | Test Method |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size distribution | 10 – 250 μm | Laser diffraction, sieve |
| Particle shape | >85% spherical | Microscopy |
| Apparent density | 2 – 5 g/cm3 | Hall flowmeter |
| Tap density | 3 – 8 g/cm3 | Tapping volumeter |
| Residual gases | < 1000 ppm | Inert gas analysis |
| Surface oxide content | < 1000 ppm | Inert gas analysis |
Tighter distribution curves ensure reliable performance in subsequent processes.
Gas Atomization Production Overview
- Charge induction furnace with raw materials like metal ingots, waste scrap
- Melt material; sample chemistry and temperature
- Force molten metal stream into close-coupled gas atomizer nozzle(s)
- Shape smooth liquid metal stream(s)
- High velocity inert gas jets (N2, Ar) disintegrate stream into droplets
- Metal droplets rapidly solidify into powder ~100-800 μm
- Thermally classify coarse fractions via cyclone separators
- Collect fine powders in collection system and bins
- Sieve classify into size fractions as needed
- Package/store material with inert backfill
Precisely controlling all aspects of this process is key to consistency.
gas atomization metal powder Suppliers
Many leading global material producers offer gas atomization manufacturing:
| Supplier | Materials | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Sandvik | Tool steels, stainless steels, superalloys | Broad range of gas atomized alloys |
| Carpenter Technology | Tool steels, stainless steels, specialty alloys | Custom alloys available |
| Höganäs | Tool steels, stainless steels | Global leader in atomization |
| Praxair | Titanium alloys, superalloys | Reliable supplier of precision materials |
| Osprey Metals | Stainless steel, superalloys | Focus on reactive and exotic alloys |
Volume pricing depends on market conditions, lead times, exotic material charges, and other commercial factors.
Tradeoffs When Considering gas atomization metal powder
Pros:
- Consistent spherical morphology
- Narrow particle size distributions
- Known and uniform input chemistry
- Controlled, clean material microstructure
- Ideal flow characteristics for AM deposition
- Allows thin walls/intricate geometries
Cons:
- Requires significant up front capital infrastructure
- Limited alloy availability vs water atomization
- Special handling to prevent contamination
- Costs more than alternate methods at production volumes
- Lower yield than alternate processes
- Limited capacity for ultrafine particle sizes
For critical applications, gas atomized powder provides unique advantages related to consistency and performance.

Frequently Asked Questions
What is the key difference between gas and water atomization?
Gas atomization relies purely on inert gas jets to disintegrate molten metal into powder whereas water atomization uses water sprays interacting with gas jets, yielding faster cooling rates but more irregular powder.
What is the narrowest particle size distribution achievable?
Specialized nozzles, tuning, and classifier stages allow particle size distributions down to D10: 20 μm, D50: 30 μm, D90: 44 μm for gas atomization. Even tighter ranges continue to be developed.
How small can gas atomization nozzles get?
Nozzle bore sizes down to 0.5 mm have been developed to produce batch volumes less than 1 kg per hour. Though free-fall type powder classification remains challenging below 20 μm sizes.
What affects consistency between powder batches?
Control over composition, cleanliness, temperature profiles, gas pressures, atomization conditions, and powder handling/storage all contribute to reproducibility. Tight process control is essential.
What is the typical powder yield relative to initial mass?
For common alloys and size ranges, yield percentages typically span 50-85% depending on desired distribution widths and acceptable fraction outs. Finer distributions have lower yields.
Share On
MET3DP Technology Co., LTD is a leading provider of additive manufacturing solutions headquartered in Qingdao, China. Our company specializes in 3D printing equipment and high-performance metal powders for industrial applications.
Inquiry to get best price and customized Solution for your business!
Related Articles
About Met3DP
Recent Update
Our Product
CONTACT US
Any questions? Send us message now! We’ll serve your request with a whole team after receiving your message.

Metal Powders for 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing
COMPANY
PRODUCT
cONTACT INFO
- Qingdao City, Shandong, China
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- +86 19116340731