Stopowanie in situ: Rewolucja w nauce o materiałach
Spis treści
Witamy w fascynującym świecie stopowania in-situ! Jeśli zastanawiasz się, czym jest stopowanie in-situ, nie martw się — mam dla Ciebie rozwiązanie. W tym obszernym przewodniku zagłębiamy się we wszystko, co musisz wiedzieć o tym przełomowym procesie. Pod koniec będziesz wielbicielem stopowania in-situ!
Przegląd Stopowanie in situ
Stopowanie in-situ to skomplikowany proces produkcyjny, w którym dwa lub więcej różnych proszków metalowych jest mieszanych i stapianych w trakcie samego procesu produkcyjnego, zamiast łączenia wstępnie stopionych proszków. Ta metoda umożliwia tworzenie niestandardowych stopów o unikalnych właściwościach dostosowanych do konkretnych zastosowań. Można to sobie wyobrazić jako pieczenie ciasta od podstaw zamiast używania gotowej mieszanki — można kontrolować każdy składnik i dopracować przepis do perfekcji.
Dlaczego stopowanie in-situ?
Dlaczego in-situ alloying zyskało tak dużą popularność w ostatnich latach? Odpowiedź leży w jego licznych zaletach, w tym w możliwości produkcji wysoce dostosowanych materiałów o doskonałych właściwościach. Niezależnie od tego, czy chodzi o tworzenie lekkich, ale wytrzymałych komponentów do zastosowań lotniczych, czy produkcję odpornych na korozję części do zastosowań morskich, in-situ alloying oferuje niezrównaną elastyczność i precyzję.
Główne zalety stopowania in-situ
- Personalizacja: Dostosuj kompozycję do konkretnych potrzeb.
- Wydajność: Połącz wiele kroków w jeden usprawniony proces.
- Jakość: Uzyskaj lepsze właściwości materiału w porównaniu z tradycyjnymi metodami.
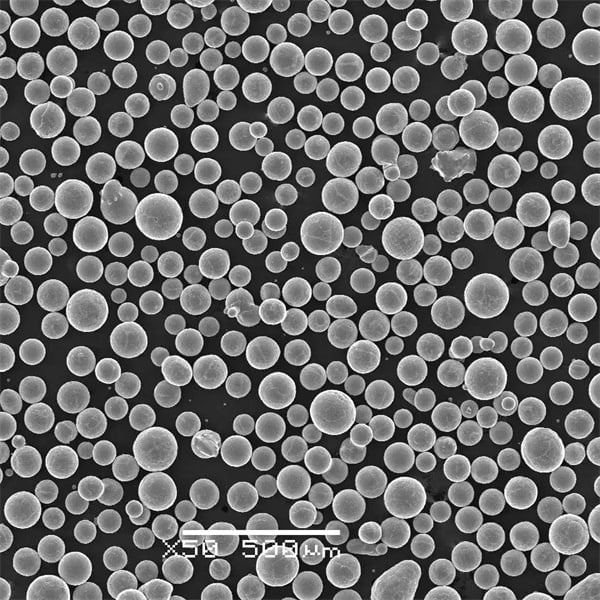
Konkretne modele proszków metalowych w Stopowanie in situ
Teraz przejdźmy do szczegółów proszków metalowych stosowanych w stopowaniu in-situ. Oto przegląd niektórych konkretnych modeli proszków metalowych i ich unikalnych cech.
1. Proszek aluminiowy (Al)
- Opis: Lekkie, odporne na korozję i dobrze przewodzące prąd.
- Zastosowania: Lotnictwo, motoryzacja i elektronika.
- Właściwości: Wysoki stosunek wytrzymałości do masy, doskonała przewodność cieplna i elektryczna.
2. Proszek tytanu (Ti)
- Opis: Znany ze swojej wytrzymałości, lekkości i biokompatybilności.
- Zastosowania: Implanty medyczne, komponenty lotnicze.
- Właściwości: Wysoka wytrzymałość na rozciąganie, odporność na korozję, biokompatybilność.
3. Proszek niklu (Ni)
- Opis: Doskonała odporność na korozję i wysokie temperatury.
- Zastosowania: Łopatki turbin, reaktory jądrowe.
- Właściwości: Wysoka temperatura topnienia, odporność na korozję, dobre właściwości mechaniczne.
4. Proszek miedzi (Cu)
- Opis: Dobrze przewodzący i plastyczny.
- Zastosowania: Komponenty elektryczne, wymienniki ciepła.
- Właściwości: Wysoka przewodność elektryczna i cieplna, dobra ciągliwość.
5. Proszek żelaza (Fe)
- Opis: Wszechstronne i szeroko stosowane w różnych gałęziach przemysłu.
- Zastosowania: Motoryzacja, budownictwo, maszyny.
- Właściwości: Dobre właściwości magnetyczne, wytrzymałość i ciągliwość.
6. Proszek ze stali nierdzewnej (SS)
- Opis: Odporne na korozję i wytrzymałe.
- Zastosowania: Urządzenia medyczne, sprzęt do przetwarzania żywności.
- Właściwości: Wysoka odporność na korozję, dobra wytrzymałość i trwałość.
7. Proszek kobaltu (Co)
- Opis: Doskonała odporność na zużycie i stabilność w wysokich temperaturach.
- Zastosowania: Narzędzia tnące, silniki lotnicze.
- Właściwości: Wysoka twardość, odporność na zużycie, stabilność termiczna.
8. Proszek magnezowy (Mg)
- Opis: Niezwykle lekkie i wytrzymałe.
- Zastosowania: Motoryzacja, lotnictwo i elektronika.
- Właściwości: Wysoki stosunek wytrzymałości do masy, dobra obrabialność.
9. Proszek wolframu (W)
- Opis: Niezwykle gęsty i odporny na ciepło.
- Zastosowania: Osłony przed promieniowaniem, styki elektryczne.
- Właściwości: Duża gęstość, wysoka temperatura topnienia, dobre przewodnictwo cieplne.
10. Proszek molibdenu (Mo)
- Opis: Doskonała wytrzymałość i stabilność w wysokich temperaturach.
- Zastosowania: Elementy pieców, części lotnicze.
- Właściwości: Wysoka temperatura topnienia, dobra przewodność cieplna i elektryczna.
Nauka za tym stoi Stopowanie in situ
Zrozumienie nauki stojącej za stopowaniem in-situ wymaga dogłębnego zanurzenia się w materiałoznawstwo i inżynierię. Gdy różne proszki metali są łączone i poddawane działaniu wysokich temperatur i ciśnień, tworzą stały roztwór lub nową fazę o odrębnych właściwościach. Proces ten można precyzyjnie dostroić, aby uzyskać pożądaną mikrostrukturę i właściwości końcowego stopu.
Właściwości i charakterystyka stopów in-situ
Właściwości stopów in-situ zależą od konkretnych proszków metalowych i warunków przetwarzania. Oto przydatna tabela podsumowująca właściwości niektórych typowych stopów in-situ:
| Metalowy proszek | Skład | Właściwości | Charakterystyka |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminium (Al) | Czysty Al lub stopy Al | Wysoki stosunek wytrzymałości do masy, przewodność | Lekki, odporny na korozję |
| Tytan (Ti) | Czysty Ti lub stopy Ti | Wysoka wytrzymałość na rozciąganie, biokompatybilność | Mocny, lekki, odporny na korozję |
| Nikiel (Ni) | Czysty Ni lub stopy Ni | Wysoka temperatura topnienia, odporność na korozję | Trwała, wysoka stabilność temperaturowa |
| Miedź (Cu) | Czysta Cu lub stopy Cu | Wysoka przewodność elektryczna i cieplna | Ciągliwy, przewodzący prąd |
| Żelazo (Fe) | Czyste żelazo lub stopy żelaza | Dobre właściwości magnetyczne, wytrzymałość | Wszechstronny, mocny |
| Stal nierdzewna (SS) | Różne klasy SS | Odporność na korozję, trwałość | Mocny, odporny na korozję |
| Kobalt (Co) | Czysty Co lub stopy Co | Wysoka twardość, stabilność termiczna | Odporny na zużycie, odporny na ciepło |
| Magnez (Mg) | Czysty Mg lub stopy Mg | Wysoki stosunek wytrzymałości do masy, obrabialność | Lekki, wytrzymały |
| Wolfram (W) | Czysty W lub stopy W | Wysoka gęstość, przewodność cieplna | Gęsty, odporny na ciepło |
| Molibden (Mo) | Czysty Mo lub stopy Mo | Wysoka temperatura topnienia, przewodność | Odporny na ciepło, przewodzący |
Zastosowania stopowania in-situ
Stopowanie in-situ jest stosowane w różnych branżach, od lotnictwa po urządzenia medyczne. Oto niektóre z kluczowych zastosowań:
| Zastosowanie | Opis | Przykłady |
|---|---|---|
| Lotnictwo i kosmonautyka | Lekkie, wytrzymałe komponenty | Łopatki turbin, części konstrukcyjne |
| Motoryzacja | Materiały o wysokiej wytrzymałości i lekkości | Części silnika, elementy podwozia |
| Urządzenia medyczne | Materiały biokompatybilne, odporne na korozję | Implanty, narzędzia chirurgiczne |
| Elektronika | Materiały przewodzące, odporne na ciepło | Płytki drukowane, złącza |
| Budowa | Trwałe, mocne materiały | Elementy konstrukcyjne, narzędzia |
| Energia | Materiały odporne na ciepło i przewodzące | Elementy turbin, reaktory |
| Oprzyrządowanie | Materiały twarde, odporne na zużycie | Narzędzia tnące, formy |
| Marine | Materiały odporne na korozję i trwałe | Elementy statków, konstrukcje offshore |
Specyfikacje, rozmiary, gatunki, normy
Jeśli chodzi o specyfikacje, rozmiary, gatunki i standardy, materiały do stopowania in-situ są bardzo zróżnicowane. Oto tabela szczegółowo opisująca niektóre z tych aspektów dla kilku powszechnych stopów:
| Metalowy proszek | Specyfikacje | Rozmiary | Stopnie | Standardy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminium (Al) | ASTM B221, ASTM B483 | Różne średnice | 1100, 2024, 6061 | ASTM, ISO, SAE |
| Tytan (Ti) | ASTM B348, ASTM F67 | Pręty, arkusze, druty | Klasy 1-5, 23 | ASTM, ISO, AMS |
| Nikiel (Ni) | ASTM B160, ASTM B161 | Różne średnice | 200, 201, 400 | ASTM, SAE, AMS |
| Miedź (Cu) | ASTM B187, ASTM B152 | Arkusze, pręty, druty | C10100, C11000, C12200 | ASTM, SAE, EN |
| Żelazo (Fe) | ASTM A36, ASTM A123 | Różne formy | Różne gatunki stali | ASTM, ISO, SAE |
| Stal nierdzewna (SS) | ASTM A276, ASTM A240 | Pręty, blachy, rury | 304, 316, 410 | ASTM, SAE, ISO |
| Kobalt (Co) | ASTM F75, ASTM F1537 | Proszek, pręty | F75, F799, F1537 | ASTM, ISO |
| Magnez (Mg) | ASTM B107, ASTM B91 | Arkusze, pręty, rury | AZ31B, AZ91D, WE43 | ASTM, SAE, ISO |
| Wolfram (W) | ASTM B760, ASTM B777 | Pręty, arkusze | W1, W2, WHA | ASTM, MIL |
| Molibden (Mo) | ASTM B386, ASTM B387 | Pręty, arkusze, druty | Mo1, Mo2 | ASTM, ISO |
Dostawcy i szczegóły dotyczące cen
Znalezienie odpowiedniego dostawcy materiałów do stopowania in-situ może mieć kluczowe znaczenie dla powodzenia Twojego projektu. Oto lista kilku renomowanych dostawców wraz z przybliżonym wyobrażeniem o cenach:
| Dostawca | Dostarczane materiały | Zakres cen (za kg) | Dane kontaktowe |
|---|---|---|---|
| Firma produkująca proszki metalowe | Stal nierdzewna, miedź, żelazo | $30 – $150 | www.metalpowdercompany.com |
| Innowacje stopowe | Tytan, nikiel, kobalt | $80 – $300 | www.alloyinnovations.com |
| Precision Alloys Inc. | Aluminium, Magnez, Wolfram | $50 – $250 | www.precisionalloysinc.com |
| Korporacja Tech Metals | Nikiel, Miedź, Stal nierdzewna | $40 – $200 | www.techmetalscorp.com |
| Global Alloy Solutions | Kobalt, Tytan, Molibden | $100 – $400 | www.globalalloysolutions.com |
Porównanie zalet i wad stopowania in-situ
Rozważmy zalety i ograniczenia stopowania in-situ, aby dać Ci jasny obraz:
| Zalety | Ograniczenia |
|---|---|
| Wysoce konfigurowalne stopy | Wymaga precyzyjnej kontroli nad warunkami przetwarzania |
| Ulepszone właściwości materiału | Koszty początkowej konfiguracji mogą być wyższe |
| Usprawniony proces produkcyjny | Złożoność projektowania stopów |
| Zmniejszona ilość odpadów materiałowych | Ograniczone do pewnych kompozycji |
| Ekonomiczne rozwiązanie do produkcji małych partii | Potencjał faz międzymetalicznych |
Najczęściej zadawane pytania
Poniżej znajdziesz zwięzłe odpowiedzi na najczęściej zadawane pytania, które pomogą Ci lepiej zrozumieć zjawisko stopowania in-situ:
| Pytanie | Odpowiedź |
|---|---|
| Czym jest stopowanie in-situ? | Stopowanie in-situ to proces produkcyjny, w którym w trakcie produkcji mieszane są różne proszki metali w celu wytworzenia stopów. |
| Jakie są zalety stopowania in-situ? | Pozwala na stosowanie niestandardowych stopów, lepsze właściwości materiałów i redukcję odpadów. |
| Gdzie stosuje się stopowanie in-situ? | Jest stosowany w przemyśle lotniczym, motoryzacyjnym, medycznym i innych gałęziach przemysłu wymagających specjalistycznych materiałów. |
| Jak stopowanie in-situ wypada w porównaniu z metodami tradycyjnymi? | W porównaniu do materiałów stopowych zapewnia większą elastyczność i precyzyjną kontrolę składu stopu. |
| Jakie są wyzwania związane ze stopowaniem in-situ? | Wymaga specjalistycznej wiedzy w zakresie kontroli składu stopu i może wiązać się z wyższymi kosztami początkowymi. |
Wnioski
Podsumowując, stopowanie in-situ to przełom w nauce o materiałach, oferujący niezrównaną elastyczność i precyzję w tworzeniu niestandardowych stopów o doskonałych właściwościach. Niezależnie od tego, czy działasz w przemyśle lotniczym, motoryzacyjnym czy medycznym, zrozumienie niuansów stopowania in-situ może prowadzić do innowacyjnych postępów i opłacalnych rozwiązań. Przy odpowiedniej wiedzy i materiałach możliwości są nieograniczone!
Teraz, gdy poznałeś świat stopowania in-situ, możesz zagłębić się w konkretne zastosowania lub skontaktować się z dostawcami, aby rozpocząć swój kolejny projekt. Pamiętaj, że kluczem jest wykorzystanie mocy metali do przekształcania pomysłów w rzeczywistość.
Udostępnij
MET3DP Technology Co., LTD jest wiodącym dostawcą rozwiązań w zakresie produkcji addytywnej z siedzibą w Qingdao w Chinach. Nasza firma specjalizuje się w sprzęcie do druku 3D i wysokowydajnych proszkach metali do zastosowań przemysłowych.
Zapytaj o najlepszą cenę i spersonalizowane rozwiązanie dla Twojej firmy!
Powiązane artykuły

Wysokowydajne segmenty łopatek dysz: Rewolucja w wydajności turbin dzięki drukowi 3D w metalu
Czytaj więcej "
Drukowane w 3D mocowania dla samochodowych czujników radarowych: Precyzja i wydajność
Czytaj więcej "Informacje o Met3DP
Ostatnia aktualizacja
Nasz produkt
KONTAKT
Masz pytania? Wyślij nam wiadomość teraz! Po otrzymaniu wiadomości obsłużymy Twoją prośbę całym zespołem.

Proszki metali do druku 3D i produkcji addytywnej
PRODUKT
cONTACT INFO
- Miasto Qingdao, Shandong, Chiny
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- +86 19116340731