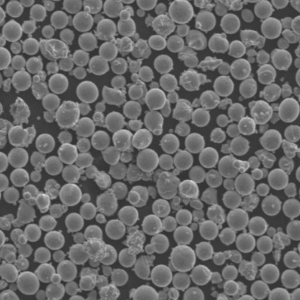
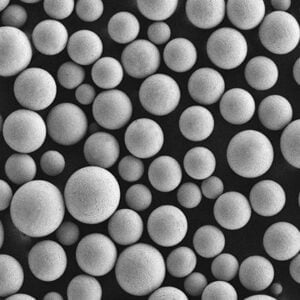
Plasma Atomisation
Table of Contents
Plasma atomisation is a fascinating and highly technical process that transforms metal into fine powder using plasma torches. This article delves deep into the science and applications of plasma atomisation, providing a detailed and SEO-optimized overview of this advanced technology. From its benefits and drawbacks to specific metal powder models, we cover everything you need to know.
Overview of Plasma Atomisation
Plasma atomisation is a cutting-edge technique used to produce fine, spherical metal powders with superior properties. This process involves melting a metal feedstock using a high-temperature plasma torch and then dispersing the molten metal into tiny droplets that solidify into fine powder particles. These powders are essential for various applications, including additive manufacturing, thermal spraying, and high-performance coatings.
How Plasma Atomisation Works
The plasma atomisation process involves several key steps:
- Feeding: The metal feedstock, often in the form of wire or rod, is fed into the plasma torch.
- Melting: The plasma torch generates extremely high temperatures, melting the metal feedstock.
- Atomisation: The molten metal is dispersed into fine droplets by a high-velocity gas stream.
- Solidification: The droplets rapidly cool and solidify into fine, spherical powder particles.
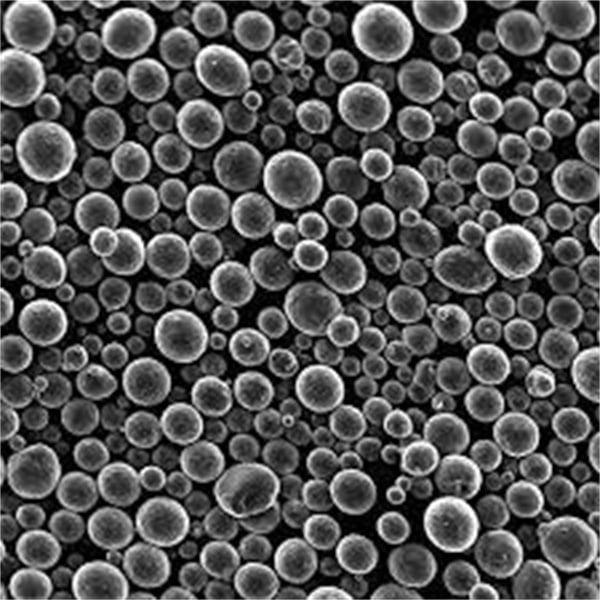
Types and Characteristics of Metal Powders
Plasma atomisation can produce a variety of metal powders, each with unique characteristics tailored to specific applications. Here are some notable models:
Specific Metal Powder Models
- Titanium Alloy (Ti-6Al-4V)
- Composition: Titanium (90%), Aluminum (6%), Vanadium (4%)
- Properties: High strength-to-weight ratio, excellent corrosion resistance
- Applications: Aerospace components, medical implants
- Nickel Alloy (Inconel 625)
- Composition: Nickel (58%), Chromium (21%), Molybdenum (9%), Niobium (3.6%)
- Properties: High temperature and corrosion resistance
- Applications: Turbine blades, marine equipment
- Stainless Steel (316L)
- Composition: Iron (65%), Chromium (18%), Nickel (14%), Molybdenum (3%)
- Properties: Excellent corrosion resistance, good mechanical properties
- Applications: Medical devices, chemical processing equipment
- Aluminum Alloy (AlSi10Mg)
- Composition: Aluminum (88.7%), Silicon (10%), Magnesium (1%)
- Properties: Lightweight, good thermal conductivity
- Applications: Automotive parts, lightweight structures
- Cobalt-Chrome (CoCrMo)
- Composition: Cobalt (60%), Chromium (27%), Molybdenum (5%)
- Properties: High wear resistance, biocompatibility
- Applications: Dental implants, orthopedic devices
- Copper (Cu)
- Composition: Pure Copper
- Properties: Excellent electrical and thermal conductivity
- Applications: Electrical components, heat exchangers
- Tungsten Carbide (WC-Co)
- Composition: Tungsten Carbide (94%), Cobalt (6%)
- Properties: Extremely hard, wear-resistant
- Applications: Cutting tools, wear-resistant coatings
- Bronze (CuSn10)
- Composition: Copper (90%), Tin (10%)
- Properties: Good corrosion resistance, machinability
- Applications: Bearings, bushings
- Hastelloy (C-276)
- Composition: Nickel (57%), Molybdenum (16%), Chromium (15%), Iron (5%)
- Properties: Excellent corrosion resistance, high temperature stability
- Applications: Chemical processing, pollution control
- Maraging Steel (18Ni300)
- Composition: Iron (75%), Nickel (18%), Cobalt (9%), Molybdenum (5%)
- Properties: Ultra-high strength, toughness
- Applications: Aerospace tooling, high-performance gears
Advantages of Plasma Atomisation
Plasma atomisation offers numerous benefits compared to other powder production methods:
- High Purity: The process minimizes contamination, resulting in high-purity powders.
- Uniform Particle Size: Produces spherical particles with consistent size distribution.
- Superior Flowability: The spherical shape enhances flowability, crucial for additive manufacturing.
- Versatility: Capable of processing a wide range of metals and alloys.
- Efficient Production: High yield and efficient use of feedstock material.
Disadvantages of Plasma Atomisation
Despite its advantages, plasma atomisation has some limitations:
- High Cost: Equipment and operational costs are significant.
- Complexity: Requires sophisticated control systems and expertise.
- Energy Intensive: High energy consumption due to plasma torch operation.
- Feedstock Limitations: Not all metals and alloys are suitable for plasma atomisation.
Applications of Plasma Atomisation
Plasma atomisation is utilized in various industries, each benefiting from the unique properties of the powders produced. Here are some key applications:
Applications of Plasma Atomisation
| Application | Description | Example Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Additive Manufacturing | Producing components with complex geometries and fine details | Aerospace parts, medical implants |
| Thermal Spraying | Coating surfaces to enhance wear and corrosion resistance | Gas turbine blades, automotive parts |
| Metal Injection Molding | Creating high-precision, small, complex metal parts | Dental tools, electronics components |
| Powder Metallurgy | Forming metal parts by compacting and sintering metal powders | Gears, bearings, structural components |
| Catalysts | Providing high surface area and active sites for chemical reactions | Industrial catalysts, fuel cells |
| High-Performance Coatings | Applying coatings to improve surface properties such as hardness and durability | Cutting tools, molds, dies |
Specifications and Standards
When selecting metal powders for specific applications, it’s crucial to consider various specifications and standards. Here are some examples:
Specifications of Metal Powders
| Metal Powder | Particle Size (µm) | Purity (%) | Density (g/cm³) | Standards |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti-6Al-4V | 15-45 | 99.5 | 4.43 | ASTM F2924 |
| Inconel 625 | 10-53 | 99.0 | 8.44 | AMS 5666 |
| 316L Stainless Steel | 10-45 | 99.9 | 7.98 | ASTM A276 |
| AlSi10Mg | 20-63 | 99.7 | 2.68 | EN 1706 |
| CoCrMo | 15-45 | 99.9 | 8.29 | ASTM F75 |
| Copper | 10-45 | 99.99 | 8.96 | ASTM B170 |
| WC-Co | 15-45 | 99.5 | 14.95 | ISO 4499-2 |
| CuSn10 | 20-60 | 99.8 | 8.80 | DIN 1705 |
| Hastelloy C-276 | 15-45 | 99.0 | 8.89 | ASTM B575 |
| 18Ni300 Maraging Steel | 10-53 | 99.9 | 8.0 | AMS 6514 |
Suppliers and Pricing Details
Finding the right supplier and understanding the pricing details is crucial for budgeting and procurement. Here are some notable suppliers and their pricing details:
Suppliers and Pricing
| Supplier | Metal Powder | Price (USD/kg) | Availability | Contact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Advanced Powders | Ti-6Al-4V | $300 | In Stock | [email protected] |
| Global Metals | Inconel 625 | $450 | Lead Time 2 Weeks | [email protected] |
| Precision Alloys | 316L Stainless Steel | $150 | In Stock | [email protected] |
| AluTech | AlSi10Mg | $200 | In Stock | [email protected] |
| Cobalt Specialists | CoCrMo | $400 | Lead Time 1 Week | [email protected] |
| Copper Corp | Copper | $100 | In Stock | [email protected] |
| Tungsten Technologies | WC-Co | $500 | Lead Time 3 Weeks | [email protected] |
| Bronze Base | CuSn10 | $180 | In Stock | [email protected] |
| Hastelloy Haven | Hastelloy C-276 | $600 | Lead Time 4 Weeks | [email protected] |
| Maraging Metals | 18Ni300 | $350 | In Stock | [email protected] |
Advantages and Limitations of Plasma Atomisation
Understanding the pros and cons of plasma atomisation is essential for making informed decisions. Here’s a detailed comparison:
Advantages vs. Limitations
| Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|
| High purity and minimal contamination | High equipment and operational costs |
| Consistent particle size and shape | Requires sophisticated control systems |
| Superior flowability of powders | High energy consumption |
| Versatility in processing various metals | Not suitable for all metal types |
| High yield and efficient material use | Complex process with expertise required |
FAQs
To address common questions and provide additional insights, here’s a FAQ section:
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is plasma atomisation used for? | Plasma atomisation is primarily used for producing high-quality metal powders for additive manufacturing, thermal spraying, and high-performance coatings. |
| How does plasma atomisation compare to gas atomisation? | Plasma atomisation generally produces higher purity and more uniform particle size powders, but it is also more expensive and energy-intensive. |
| Can all metals be processed using plasma atomisation? | No, not all metals are suitable for plasma atomisation. The process is best suited for metals and alloys that can be effectively melted and atomised. |
| What are the main advantages of using plasma atomised powders? | The main advantages include high purity, uniform particle size, superior flowability, and versatility in processing different metals and alloys. |
| What are the typical particle sizes produced by plasma atomisation? | Particle sizes typically range from 10 to 100 micrometers, depending on the specific metal and process parameters used. |
| Is plasma atomisation cost-effective? | While plasma atomisation offers high-quality powders, it is generally more expensive due to the high equipment, operational, and energy costs involved. |
| How do you ensure the quality of plasma atomised powders? | Quality is ensured through stringent process control, regular testing, and adherence to industry standards and specifications. |
| What industries benefit most from plasma atomisation? | Industries such as aerospace, medical, automotive, and industrial manufacturing benefit significantly from the high-quality powders produced by plasma atomisation. |
Conclusion
Plasma atomisation stands out as a highly effective method for producing superior metal powders with a range of applications across various industries. Despite its high cost and complexity, the benefits of high purity, consistent particle size, and excellent flowability make it a preferred choice for critical applications. Whether you’re in aerospace, medical, or industrial manufacturing, plasma atomised powders can significantly enhance the quality and performance of your products.
For more information on plasma atomisation and to find the best suppliers, contact the experts in the field and explore the numerous possibilities this advanced technology offers.
Share On
MET3DP Technology Co., LTD is a leading provider of additive manufacturing solutions headquartered in Qingdao, China. Our company specializes in 3D printing equipment and high-performance metal powders for industrial applications.
Inquiry to get best price and customized Solution for your business!
Related Articles
About Met3DP
Recent Update
Our Product
CONTACT US
Any questions? Send us message now! We’ll serve your request with a whole team after receiving your message.

Metal Powders for 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing
COMPANY
PRODUCT
cONTACT INFO
- Qingdao City, Shandong, China
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- +86 19116340731