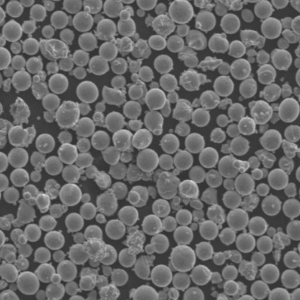
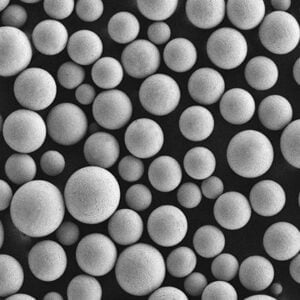
Plasma-Rotating Electrode Process
Table of Contents
Imagine a ballet where a metal rod pirouettes at lightning speed, meeting a scorching hot plasma arc in a dazzling display. The molten metal, flung outwards by centrifugal force, cools and solidifies into tiny, near-perfect spheres. This captivating dance is the essence of the Plasma-Rotating Electrode Process (PREP), a revolutionary technology for creating high-performance metal powders.
Process Principle of Plasma-Rotating Electrode Process
PREP operates like a well-orchestrated symphony. Here’s a breakdown of the key movements:
- The Stage: A sealed chamber filled with an inert gas, like argon or helium, ensures minimal contamination.
- The Star: A rod of the desired metal, the electrode, takes center stage.
- The Spotlight: A plasma torch ignites, generating an intensely hot, ionized gas jet.
- The Grand Jeté: The electrode is mounted on a high-speed spindle, whirling at thousands of rotations per minute. This creates a powerful centrifugal force.
- The Molten Embrace: The plasma arc melts the tip of the rotating electrode.
- The Grand Leap: Centrifugal force flings the molten metal outwards in tiny droplets.
- The Cooling Cotillion: The rapidly flying droplets rapidly cool in the inert gas atmosphere.
- The Curtain Call: The solidified metal spheres, now perfect metal powders, are collected for further processing.
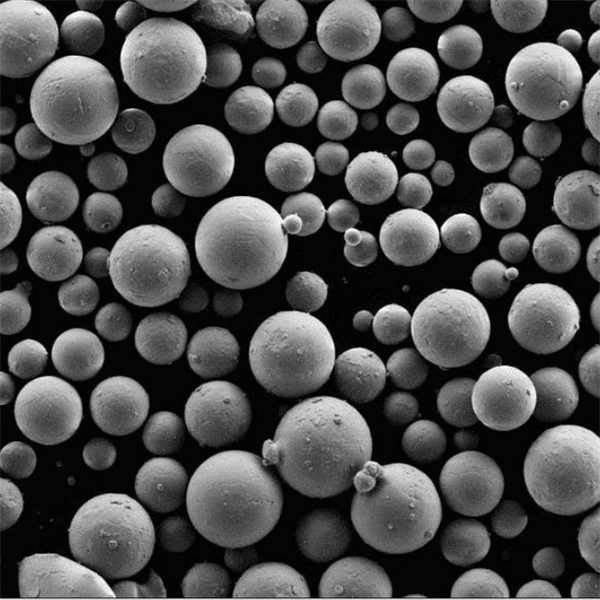

Process Characteristics of Plasma-Rotating Electrode Process
| Process Characteristics | Description | Advantages | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spherical Powder Morphology | PREP excels in producing near-perfect spheres due to the interplay between centrifugal force and rapid solidification. As the molten metal droplets are flung outwards from the rotating electrode, surface tension pulls them into tight spheres. This rapid cooling further locks in the spherical shape, preventing the formation of irregular shapes or satellites (smaller particles attached to larger ones). | * Exceptional Flowability: Spherical powders flow freely, minimizing friction and blockages during AM processes like 3D printing. This smooth flow ensures consistent material deposition and high-quality final products. * High Packing Density: Spherical particles pack together efficiently, maximizing the amount of powder that can be loaded into a build chamber. This translates to increased material utilization and potentially reduced printing times. * Improved Laser Absorption: In laser-based AM techniques, the spherical shape promotes uniform laser absorption across the powder particle. This leads to consistent melting behavior and minimizes the risk of unmelted areas or defects within the printed part. | While other atomization methods can achieve some degree of sphericity, PREP consistently delivers a higher proportion of perfectly spherical particles. This superior morphology is particularly crucial for demanding AM applications where precise control and consistent material properties are essential. |
| Minimal Impurities | The controlled environment of PREP minimizes contamination of the metal powders. The use of an inert gas like argon or helium during the process prevents oxidation and reduces the interaction between the molten metal and the surrounding atmosphere. Additionally, the high temperatures involved in the plasma arc can help to vaporize any volatile impurities present in the feedstock material. | * Enhanced Mechanical Properties: Pure metal powders translate to improved mechanical properties in the final product. Reduced levels of oxides and other contaminants ensure the strength, ductility, and fatigue resistance of the material are not compromised. * Superior Corrosion Resistance: Minimized impurities often lead to better corrosion resistance in the final product. This is particularly important for applications where the metal parts will be exposed to harsh environments. | Strict control over the inert gas atmosphere and plasma torch maintenance are crucial for maintaining the purity of the produced powders. Any leaks or contamination within the chamber can introduce unwanted elements and potentially impact the final product’s properties. |
| Material Versatility | PREP boasts a remarkable ability to handle a wide range of metals, from common elements like titanium and aluminum to reactive metals like tantalum and zirconium. This versatility stems from the carefully controlled plasma environment, which can be adjusted to accommodate the specific melting characteristics of different metals. | * Broad Application Potential: The ability to produce high-quality powders from diverse materials opens doors for innovative applications across various industries. From aerospace components requiring lightweight and high-strength alloys to biomedical implants demanding biocompatible materials like CoCr, PREP caters to a vast spectrum of needs. * Exploration of Advanced Materials: PREP’s capability to handle reactive metals paves the way for exploring novel materials with unique properties. These materials can potentially revolutionize fields like aerospace and energy, where high-temperature performance and corrosion resistance are paramount. | Not all metals exhibit the same behavior under the intense heat and centrifugal forces of PREP. Some materials might require specialized process parameters or even pre-treatment to ensure successful powder formation. |
| Fine Control over Powder Properties | A distinct advantage of PREP lies in its ability to precisely control the size and morphology of the produced powders. By manipulating parameters like rotation speed, plasma arc power, and cooling conditions, manufacturers can tailor the powder characteristics to suit specific application requirements. For instance, finer powders might be preferred for intricate 3D printing jobs, while larger powders could be ideal for applications like thermal spraying. | * Tailored Powders for Specific Needs: The ability to fine-tune powder properties allows manufacturers to optimize the material for the intended application. This level of control ensures the final product possesses the desired mechanical properties, surface finish, and overall functionality. * Reduced Post-Processing Needs: Precise control over powder size distribution can minimize the need for extensive post-processing steps like sieving or classification. This translates to increased production efficiency and potentially lower overall costs. | Achieving the desired level of control requires a deep understanding of the interplay between process parameters and resulting powder characteristics. Expertise and ongoing process optimization are crucial for consistently producing powders that meet exact specifications. |
Metal Powders Produced by Plasma-Rotating Electrode Process
PREP unlocks a treasure trove of high-performance metal powders, each with its unique properties and applications. Here’s a glimpse into ten remarkable examples:
1. Titanium Powder (CP Ti): The workhorse of the AM industry, CP Ti powders are prized for their high strength-to-weight ratio, excellent corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility. They are used in aerospace components, medical implants, and sporting goods.
2. Titanium Alloy Powders (Ti6Al4V): Offering even greater strength and fatigue resistance than CP Ti, Ti6Al4V powders are ideal for demanding applications like jet engine components, prosthetics, and dental implants.
3. Aluminum Powder (AA2024): A popular choice for lightweight and strong applications, AA2024 powders find use in aerospace components, automotive parts, and sporting goods.
4. Aluminum Alloy Powders (AlSi10Mg): Combining the benefits of aluminum with improved castability, AlSi10Mg powders are well-suited for automotive pistons, cylinder heads, and electronic enclosures.
5. Nickel Powder: Renowned for its high-temperature strength and corrosion resistance, nickel powders are used in gas turbine components, chemical processing equipment, and electronics.
6. Nickel Alloy Powders (Inconel 625): An exceptional performer in harsh environments, Inconel 625 powders are employed in jet engine components, heat exchangers, and nuclear reactors.
7. Cobalt-Chrome Powder (CoCr): Biocompatible and wear-resistant, CoCr powders are the go-to material for hip and knee replacements, dental implants, and surgical instruments.
8. Stainless Steel Powders (316L): Offering a winning combination of corrosion resistance and strength, 316L powders are used in medical devices, chemical processing equipment, and marine applications.
9. Copper Powder: A highly conductive and thermally conductive metal, copper powders are used in electrical components, heat sinks, and electromagnetic applications.
10. Tungsten Powder: With its exceptional high-temperature strength and density, tungsten powders are vital for rocket engine nozzles, armor plating, and welding electrodes.
Applications of Plasma-Rotating Electrode Process Powders
| Applications | Description | Key Advantages of PREP Powders | Potential Limitations to Consider |
|---|---|---|---|
| Additive Manufacturing (AM) Techniques | PREP powders shine in the world of AM, particularly in 3D printing processes like laser melting and electron beam melting. Their near-perfect spherical morphology, excellent flowability, and minimal impurities make them ideal for building high-quality, complex metal parts. | * Smooth Printing Processes: The spherical shape and free-flowing nature of PREP powders minimize friction and ensure consistent material deposition during printing. This translates to smooth operation, reduced risk of blockages, and high-precision printing of intricate geometries. * Superior Mechanical Properties: The high purity of PREP powders leads to excellent mechanical properties in the final printed part. The minimal impurities ensure the strength, ductility, and fatigue resistance of the material are not compromised. * Broad Material Compatibility: PREP’s ability to handle a wide range of metals allows for the creation of 3D printed parts from diverse materials. This opens doors for applications demanding specific properties, like lightweight and high-strength titanium alloys for aerospace components or biocompatible CoCr for medical implants. | While PREP powders offer significant advantages, the technology itself might not be readily accessible to all AM users. The initial investment in specialized equipment and expertise can be a barrier for smaller-scale operations. |
| Aerospace Industry | The relentless pursuit of lightweight and high-strength materials in the aerospace industry makes PREP powders a natural fit. Titanium and aluminum alloys produced by PREP are extensively used in aircraft structures, engine components, and spacecraft parts. | * Weight Reduction and Efficiency: The high strength-to-weight ratio of PREP-made alloys like Ti6Al4V allows for significant weight reduction in aircraft components. This translates to improved fuel efficiency and increased payload capacity. * Exceptional Performance: PREP powders enable the creation of aerospace components with excellent mechanical properties, capable of withstanding demanding operating conditions. Their high-temperature performance and resistance to fatigue ensure reliable and safe operation of aircraft. | The cost of PREP powders can be a factor compared to some other metal powder production methods. However, the weight reduction benefits and superior performance often outweigh the initial cost in the long run. |
| Biomedical Industry | Biocompatibility and corrosion resistance are paramount for successful medical implants. PREP-produced powders like CoCr and titanium offer the perfect balance of these properties, making them ideal for hip and knee replacements, dental implants, and surgical instruments. Additionally, the ability to control powder morphology allows for the creation of porous structures that promote bone ingrowth, leading to better implant fixation. | * Enhanced Biocompatibility: The minimal impurities in PREP powders minimize the risk of adverse tissue reactions, making them suitable for implantation within the human body. * Improved Osseointegration: The controlled porosity of some PREP powders encourages bone growth into the implant surface, leading to stronger fixation and longer implant lifespans. * Corrosion Resistance for Long-Term Performance: PREP powders often result in implants with excellent corrosion resistance, ensuring their functionality and integrity over an extended period. | Strict regulatory requirements in the medical device industry necessitate rigorous quality control measures throughout the entire production process, including the metal powders themselves. Manufacturers using PREP powders need to ensure they meet all relevant medical grade standards. |
| Electronics Industry | The miniaturization and high-performance demands of modern electronics are met head-on by PREP powders. Copper and nickel powders, renowned for their excellent conductivity, are used in electrical components, heat sinks, and electronic packaging. The high purity and controlled size distribution of these powders ensure consistent performance and reliable device operation. | * Exceptional Conductivity: The near-perfect spherical shape and minimal impurities in PREP-made copper and nickel powders minimize electrical resistance, leading to efficient current flow in electronic components. * Precise Control for Miniaturization: The ability to control powder size and morphology allows for the creation of highly conductive features on a microscopic level, crucial for miniaturized electronic devices. * Reliable Performance: The high purity and consistent quality of PREP powders ensure the predictable and reliable performance of electronic components. | While PREP powders offer superior performance, alternative methods like electrodeposition might be more cost-effective for some high-volume electronics applications. However, for high-end devices demanding the best possible conductivity and reliability, PREP powders remain a top choice. |
Comparison of Plasma-Rotating Electrode Process with Other Metal Powder Production Methods
PREP isn’t the only player in the metal powder production game. Here’s a breakdown of how it compares to other popular methods:
| Feature | Plasma-Rotating Electrode Process (PREP) | Gas Atomization (GA) | Water Atomization (WA) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Powder Morphology | Spheres | Irregular shapes, satellites | Irregular shapes |
| Flowability | Excellent | Good | Poor |
| Packing Density | High | Good | Moderate |
| Purity | High (inert gas environment) | High | Lower (potential for oxidation) |
| Material Versatility | Wide range of metals | Wide range of metals | Limited to some metals |
| Process Control | High | Moderate | Moderate |
| Cost | Higher | Moderate | Lower |
Advantages and Limitations of Plasma-Rotating Electrode Process
| Advantages and Limitations | Description | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Powder Morphology | PREP excels at producing near-perfect spherical metal powders. This is due to the combined effects of centrifugal force and rapid solidification. Molten metal droplets are flung outwards from the rotating electrode, and surface tension pulls them into tight spheres. The rapid cooling process further locks in this spherical shape, minimizing the formation of irregular particles or satellites (smaller particles attached to larger ones). | * Exceptional Flowability: Spherical powders flow freely with minimal friction, reducing the risk of blockages during Additive Manufacturing (AM) processes like 3D printing. This smooth flow ensures consistent material deposition and contributes to high-quality final products. * High Packing Density: Spherical particles pack together efficiently, maximizing the amount of powder that can be loaded into a build chamber. This translates to increased material utilization and potentially reduced printing times. * Improved Laser Absorption in AM: For laser-based AM techniques, the spherical shape promotes uniform laser absorption across the powder particle. This leads to consistent melting behavior and minimizes the risk of unmelted areas or defects within the printed part. | While other atomization methods can achieve some degree of sphericity, PREP consistently delivers a higher proportion of perfectly spherical particles. This superior morphology is particularly crucial for demanding AM applications where precise control and consistent material properties are essential. |
| Purity | The controlled environment of PREP minimizes contamination of the metal powders. The process utilizes an inert gas like argon or helium to prevent oxidation and reduce interaction between the molten metal and the surrounding atmosphere. Additionally, the high temperatures involved in the plasma arc can help vaporize any volatile impurities present in the feedstock material. | * Enhanced Mechanical Properties: Pure metal powders translate to improved mechanical properties in the final product. Reduced levels of oxides and other contaminants ensure the strength, ductility, and fatigue resistance of the material are not compromised. * Superior Corrosion Resistance: Minimized impurities often lead to better corrosion resistance in the final product. This is particularly important for applications where the metal parts will be exposed to harsh environments. | Strict control over the inert gas atmosphere and plasma torch maintenance are crucial for maintaining the purity of the produced powders. Any leaks or contamination within the chamber can introduce unwanted elements and potentially impact the final product’s properties. |
| Material Versatility | PREP boasts a remarkable ability to handle a wide range of metals, from common elements like titanium and aluminum to reactive metals like tantalum and zirconium. This versatility stems from the carefully controlled plasma environment, which can be adjusted to accommodate the specific melting characteristics of different metals. | * Broad Application Potential: The ability to produce high-quality powders from diverse materials opens doors for innovative applications across various industries. From aerospace components requiring lightweight and high-strength alloys to biomedical implants demanding biocompatible materials like CoCr, PREP caters to a vast spectrum of needs. * Exploration of Advanced Materials: PREP’s capability to handle reactive metals paves the way for exploring novel materials with unique properties. These materials can potentially revolutionize fields like aerospace and energy, where high-temperature performance and corrosion resistance are paramount. | Not all metals exhibit the same behavior under the intense heat and centrifugal forces of PREP. Some materials might require specialized process parameters or even pre-treatment to ensure successful powder formation. |
| Process Control | A distinct advantage of PREP lies in its ability to precisely control the size and morphology of the produced powders. By manipulating parameters like rotation speed, plasma arc power, and cooling conditions, manufacturers can tailor the powder characteristics to suit specific application requirements. For instance, finer powders might be preferred for intricate 3D printing jobs, while larger powders could be ideal for applications like thermal spraying. | * Tailored Powders for Specific Needs: The ability to fine-tune powder properties allows manufacturers to optimize the material for the intended application. This level of control ensures the final product possesses the desired mechanical properties, surface finish, and overall functionality. * Reduced Post-Processing Needs: Precise control over powder size distribution can minimize the need for extensive post-processing steps like sieving or classification. This translates to increased production efficiency and potentially lower overall costs. | Achieving the desired level of control requires a deep understanding of the interplay between process parameters and resulting powder characteristics. Expertise and ongoing process optimization are crucial for consistently producing powders that meet exact specifications. |
| Cost | PREP can be a more expensive metal powder production method compared to some alternatives like water atomization. The technology requires specialized equipment and expertise, making it less accessible to smaller manufacturers. | * High-Performance Powders for Demanding Applications: While the initial cost might be higher, PREP powders offer superior quality and performance, often leading to better outcomes in the final product. This can justify the higher cost, especially for critical applications. | The cost factor can be a significant hurdle for some users, particularly in industries |
Choosing the Right Metal Powder Production Method
| Choosing the Right Metal Powder Production Method | Considerations | Plasma-Rotating Electrode Process (PREP) | Gas Atomization (GA) | Water Atomization (WA) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Application Requirements | The intended use of the metal powder plays a crucial role in selecting the most suitable production method. Faktoren (German for factors) like the desired final product properties, dimensional tolerances, and surface finish should be carefully considered. | * Superior Powder Morphology: PREP excels at producing near-perfect spheres, ideal for AM processes requiring smooth flowability and consistent material deposition. * High Purity: The controlled environment of PREP minimizes contamination, leading to powders with superior mechanical properties and corrosion resistance. * Material Versatility: PREP handles a wide range of metals, suitable for applications demanding specific materials like biocompatible CoCr for implants or high-strength titanium alloys for aerospace components. | * Good Powder Morphology: GA produces powders with a generally spherical shape, suitable for various AM and other applications. * Broad Material Compatibility: GA handles a wide range of metals, similar to PREP. * Moderate Purity: Inert gas environment minimizes oxidation, but some oxygen pick-up might occur compared to PREP. | * Limited Powder Morphology: WA produces irregularly shaped powders with satellites, potentially impacting flowability and final product quality in some applications. * Limited Material Compatibility: WA works best with certain metals, particularly those with lower melting points. * Lower Cost: WA is often the most cost-effective method among the three. |
| Cost Considerations | Budgetary constraints can influence the choice of production method. PREP’s high-performance powders come at a premium, while other methods might offer a more economical option. | * Higher Cost: PREP requires specialized equipment and expertise, making it the most expensive option. * High-Value Applications: The superior quality of PREP powders justifies the cost for critical applications demanding exceptional performance. | * Moderate Cost: GA strikes a balance between cost and powder quality, making it a popular choice for various applications. | * Lower Cost: WA is the most budget-friendly option, but the trade-off lies in the powder morphology and potentially lower suitability for certain applications. |
| Production Volume | The scale of metal powder production required should be factored in. PREP might not be the most suitable choice for high-volume applications due to its slower production rates. | * Lower Production Rates: PREP involves a single electrode and may have slower powder production compared to other methods. | * Moderate Production Rates: GA offers a balance between production speed and powder quality. | * High Production Rates: WA is well-suited for high-volume powder production due to its faster processing capabilities. |
| Level of Expertise | The technical expertise available can influence the choice of method. PREP requires specialized knowledge and experience for successful operation. | * Requires Expertise: PREP demands a high level of technical expertise for operating the equipment and maintaining optimal process parameters. | * Moderate Expertise: GA requires a good understanding of the process and proper equipment operation. | * Lower Expertise: WA has a lower barrier to entry in terms of technical expertise compared to PREP and GA. |
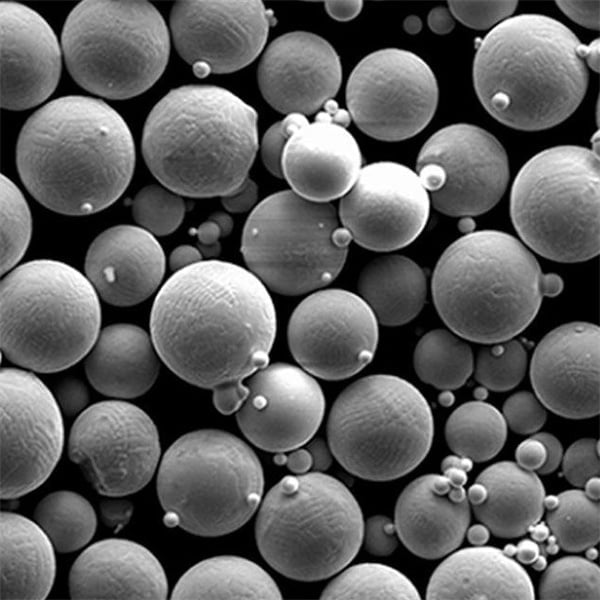
FAQs
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What are the benefits of using PREP powders in 3D printing? | PREP powders offer excellent flowability, leading to smooth printing processes. Their spherical shape minimizes voids and ensures consistent material properties in the final product. Additionally, the high purity of PREP powders reduces the risk of defects and improves the mechanical properties of the printed parts. |
| How does PREP compare to other atomization methods for reactive metals? | PREP’s inert gas environment is particularly advantageous for reactive metals like titanium and tantalum, minimizing oxidation and contamination during |
| What are some of the safety considerations for PREP? | PREP involves high temperatures, molten metal, and plasma torches. Proper safety protocols like wearing personal protective equipment (PPE) and adhering to operating procedures are crucial to ensure operator safety. Additionally, the sealed chamber needs to be well-maintained to prevent gas leaks and potential hazards. |
| What is the future outlook for PREP technology? | As AM and other advanced manufacturing techniques gain traction, the demand for high-performance metal powders is expected to rise. PREP is well-positioned to play a key role in this growth, with ongoing research focusing on improving production rates, expanding material compatibility, and reducing costs. Advancements in automation and process control are also anticipated to further streamline PREP operations. |
| Where can I learn more about PREP? | Several resources offer in-depth information on PREP technology. Reputable scientific journals, industry publications, and websites of leading manufacturers provide detailed technical descriptions, application case studies, and the latest research developments. Additionally, professional organizations and conferences dedicated to AM and metal powder production serve as valuable sources of knowledge. |
Share On
MET3DP Technology Co., LTD is a leading provider of additive manufacturing solutions headquartered in Qingdao, China. Our company specializes in 3D printing equipment and high-performance metal powders for industrial applications.
Inquiry to get best price and customized Solution for your business!
Related Articles
About Met3DP
Recent Update
Our Product
CONTACT US
Any questions? Send us message now! We’ll serve your request with a whole team after receiving your message.

Metal Powders for 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing
COMPANY
PRODUCT
cONTACT INFO
- Qingdao City, Shandong, China
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- +86 19116340731