A Guide to Powder-Making Equipment
Table of Contents
Imagine a world where complex metal parts are built not through subtractive manufacturing (cutting away material), but by meticulously crafting and shaping tiny metal particles. This fantastical scenario is the very foundation of metal additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing. But before these metal marvels can take form, they need a crucial starting point: metal powder.
This guide delves into the fascinating realm of powder-making equipment, the unsung heroes that transform raw materials into the building blocks of 3D-printed innovation. We’ll explore the different types of equipment, understand their inner workings, and unveil the specific models that reign supreme in the industry. Buckle up and get ready to dive into the world of metal powder magic!
the Allure of Metal Powders
Metal powders aren’t just your average dust bunnies. These fine, granular materials boast unique properties that make them ideal for 3D printing applications. Here’s a breakdown of some key characteristics:
- Flowability: Imagine pouring sand through an hourglass. That’s the essence of flowability – the powder’s ability to move freely, ensuring smooth and consistent layering during the 3D printing process.
- Particle Size and Distribution: The size and distribution of the metal particles significantly impact the final product’s properties. Finer powders generate smoother surfaces, while coarser powders offer better strength.
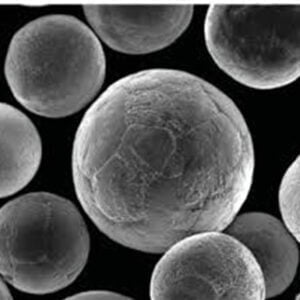
- Sphericity: Ideally, metal powder particles should be spherical, resembling tiny metal marbles. This shape optimizes packing density, leading to stronger and more uniform 3D-printed parts.
- Chemical Composition: The specific metal or alloy composition directly influences the final product’s properties like strength, corrosion resistance, and thermal conductivity.
Metal Powder Composition
The world of metal powders is brimming with variety, each type offering distinct advantages:
| Metal/Alloy Powder | Composition | Key Properties | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel Powders (316L, 17-4PH) | Iron, chromium, nickel, molybdenum (316L) | Excellent corrosion resistance, high strength | Aerospace components, medical implants, dental applications |
| Titanium Powders (Grade 2, CP) | Titanium | High strength-to-weight ratio, biocompatible | Aerospace parts, medical implants, sporting goods |
| Aluminum Powders (AlSi10Mg, AlSi7Mg0.3) | Aluminum, silicon, magnesium | Lightweight, good heat conductivity | Automotive components, heat exchangers, electronic enclosures |
| Nickel Powders | Nickel | High strength, good ductility | Electrical components, electrodes, chemical processing equipment |
| Cobalt Chrome Powders | Cobalt, chromium | Excellent wear resistance, biocompatible | Medical implants, tooling components, cutting tools |
| Inconel Powders (IN625, 718) | Nickel, chromium, iron, molybdenum | High-temperature resistance, good corrosion resistance | Gas turbine components, heat exchangers, rocket engines |
| Copper Powders | Copper | Excellent electrical conductivity, good thermal conductivity | Electrical components, heat sinks, electromagnetic shielding |
Metal Powder Applications
The applications of metal powders are as diverse as they are innovative. Here are some prominent examples:
| Industry | Applications | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Lightweight aircraft components, rocket engine parts | Reduced weight for improved fuel efficiency and performance |
| Medical | Biocompatible implants, dental prosthetics | Customized designs for improved patient outcomes |
| Automotive | Complex engine parts, lightweight body components | Enhanced performance and fuel efficiency |
| Consumer Electronics | Heat sinks, intricate housings | Increased design freedom and miniaturization |
| Tooling | Conformal cooling channels in molds and dies | Improved cooling efficiency and productivity |
Types of Powder-Making Equipment
Now, let’s delve into the heart of the matter – the equipment responsible for crafting these magical metal powders. Here are the main types:
- Gas Atomization: This method involves injecting molten metal into a high-pressure gas stream, breaking it into fine droplets that solidify into spherical powder particles.
- Water Atomization: Similar to gas atomization, but uses a high-pressure water jet to atomize the molten metal. This method is typically used for less reactive metals like aluminum.
- Plasma Atomization: This high-energy process utilizes an ionized gas (plasma) to melt and atomize the metal feedstock. It’s ideal for producing high-performance powders like
Top Powder-Making Equipment Models
With an understanding of the different powder-making equipment types, let’s get granular (pun intended) and explore some of the industry’s leading models:
Gas Atomization Powerhouses:
- Höganäs Höger Atomizer: Renowned for its exceptional powder quality and spherical particle morphology, the Höger Atomizer series from Höganäs is a popular choice for demanding applications. These robust systems boast precise control over particle size and distribution, making them ideal for producing high-performance powders for aerospace, medical, and automotive industries.
- GE Additive Arcam A1: This industrial-grade atomizer from GE Additive (formerly Arcam) is designed for high-volume powder production. The A1 system offers a scalable platform for various metal powders, including titanium, nickel alloys, and stainless steel. Its integrated automation features ensure consistent and reliable powder quality for large-scale 3D printing operations.
- SLM Solutions AtomaxX: Known for its speed and efficiency, the AtomaxX series from SLM Solutions caters to high-throughput powder production. This innovative system utilizes a two-stage atomization process for exceptional control over particle size and morphology. Additionally, the AtomaxX boasts a user-friendly interface and advanced safety features, making it a compelling option for industrial powder manufacturers.
Water Atomization Warriors:
- Waterland SAS – WA Series: A global leader in water atomization technology, Waterland SAS offers the WA Series for cost-effective production of aluminum powders. These versatile systems are well-suited for various aluminum alloys, making them ideal for the automotive and consumer electronics industries. The WA Series is known for its energy efficiency and low operating costs, contributing to sustainable powder production.
- Bühler Group – SHS Series: Bühler Group’s SHS Series represents a reliable and proven solution for water atomization of aluminum powders. These robust systems are designed for continuous operation, ensuring consistent powder quality for high-volume production lines. The SHS Series offers flexibility for a wide range of aluminum alloy feedstocks, catering to diverse application needs.
Plasma Atomization Powerhouses:
- AMPO – Poet Atomizer: Engineered for the production of high-performance powders for demanding applications, AMPO’s Poet Atomizer utilizes inductively coupled plasma technology. This innovative approach delivers exceptional control over powder chemistry, microstructure, and particle morphology. The Poet Atomizer is particularly well-suited for producing powders for aerospace, medical, and tool-and-die industries, where superior material properties are critical.
- Plasma Powders – Plasma Atomization Systems: Specializing in plasma atomization technology, Plasma Powders offers a range of customizable systems for producing high-quality metal powders. Their systems cater to various metal feedstocks, including titanium alloys, nickel superalloys, and refractory metals. Plasma Powders’ atomizers are known for their versatility and ability to produce powders with tailored properties for specific applications.
Choosing Your Powder-Making Partner
Selecting the right powder-making equipment hinges on several crucial factors:
- Desired Powder Type and Properties: The type of metal powder you aim to produce (e.g., stainless steel, titanium) and its required properties (e.g., particle size, sphericity) will significantly influence your equipment choice.
- Production Volume Requirements: Consider the scale of your operation – are you targeting high-volume production for industrial applications, or a smaller-scale setup for research and development?
- Budget Constraints: Powder-making equipment can range from mid-range to high-investment options. Clearly define your budget and choose a system that offers the desired capabilities within your financial limitations.
- Operational Expertise: The complexity of the equipment varies. Assess your team’s expertise in operating and maintaining the chosen system. Reliable after-sales support from the equipment manufacturer is also crucial.
Additional Considerations for Successful Powder Production
While equipment plays a central role, successful powder production encompasses more than just the machinery. Here are some additional factors to consider:
- Feedstock Quality: The quality of the raw metal feedstock significantly impacts the final powder properties. Ensure you source high-purity metal feedstock to achieve consistent and reliable powder production.
- Process Control: Precise control over process parameters like gas flow rates, atomization pressure, and cooling rates is essential for producing powders with consistent characteristics.
- Powder Handling and Storage: Proper handling and storage procedures are crucial to prevent contamination and maintain the powder’s flowability and other critical properties.
The Future of Powder-Making Equipment
The realm of powder-making equipment is constantly evolving. Here are some exciting trends to watch:
Increased Automation: Automation is on the rise, with manufacturers integrating advanced automation features into their systems to streamline production processes and ensure consistent powder quality. This includes features like automatic powder handling, real-time process monitoring, and data acquisition for continuous improvement.
Focus on Sustainability: As environmental concerns mount, the focus on sustainable powder production practices is intensifying. Manufacturers are developing equipment with improved energy efficiency and exploring ways to minimize waste generation during the atomization process. Additionally, research is underway to explore the use of recycled metal feedstocks for powder production, promoting a more circular economy.
Material Innovation: The quest for novel materials with unique properties is pushing the boundaries of powder-making technology. Manufacturers are developing systems capable of handling reactive metals and exotic alloys, paving the way for the creation of advanced materials for next-generation applications in aerospace, energy, and bioprinting.
Additive Manufacturing Integration: As 3D printing technology matures, tighter integration between powder-making equipment and additive manufacturing systems is becoming increasingly important. This trend involves developing closed-loop systems where powder production and 3D printing are seamlessly connected, minimizing powder handling and optimizing the entire manufacturing workflow.
FAQ
Q: What are the main advantages of using gas atomization over water atomization?
A: Gas atomization generally produces finer and more spherical powder particles compared to water atomization. This translates to improved flowability for 3D printing and potentially better mechanical properties in the final printed part. However, gas atomization tends to be a more energy-intensive process.
Q: Is plasma atomization suitable for all types of metal powders?
A: Plasma atomization excels at producing high-performance powders for demanding applications. It’s particularly well-suited for reactive metals like titanium and tantalum, which can be challenging to process using other methods. However, plasma atomization systems are typically more expensive compared to gas or water atomization equipment.
Q: How important is the quality of the metal feedstock in powder production?
A: The quality of the feedstock directly influences the final powder properties. Impurities in the feedstock can translate to inconsistencies in the powder’s chemistry and microstructure, potentially leading to issues with printability and the performance of the final 3D-printed part.
Q: What are some essential safety considerations when operating powder-making equipment?
A: Powder-making processes can involve high temperatures, pressure, and potentially hazardous materials. Following proper safety protocols, including wearing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and adhering to established operating procedures, is crucial to minimize risks and ensure operator safety.
Q: Where can I find more information about specific powder-making equipment models?
A: Most reputable powder-making equipment manufacturers maintain detailed websites showcasing their product lines. Additionally, industry publications and trade shows often feature the latest advancements in powder-making technology.
Share On
MET3DP Technology Co., LTD is a leading provider of additive manufacturing solutions headquartered in Qingdao, China. Our company specializes in 3D printing equipment and high-performance metal powders for industrial applications.
Inquiry to get best price and customized Solution for your business!
Related Articles
About Met3DP
Recent Update
Our Product
CONTACT US
Any questions? Send us message now! We’ll serve your request with a whole team after receiving your message.

Metal Powders for 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing
COMPANY
PRODUCT
cONTACT INFO
- Qingdao City, Shandong, China
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- +86 19116340731