Powder-Making Equipment
Table of Contents
Powders are all around us, playing vital roles in countless industries. From the life-saving medications we ingest to the makeup that enhances our appearance, these fine particles are the invisible building blocks of our modern world. But how exactly do these materials come to be? Enter the fascinating realm of powder-making equipment, the unsung heroes that transform raw materials into the microscopic marvels that shape our lives.
Different Types Of Powder-Making Equipment
The world of powder-making equipment is surprisingly diverse, with each machine meticulously designed to handle specific materials and achieve desired particle size and properties. Here’s a glimpse into some of the most common types:
- Grinders: Imagine a high-powered blender on steroids. Grinders utilize spinning blades or discs to pulverize materials by sheer force. Think coffee grounds or spices – grinders are the workhorses for these everyday powders.
- Crushers: For tougher materials that require a more heavy-handed approach, crushers come into play. These machines employ powerful jaws or hammers to break down chunky feedstock into smaller pieces. Picture hefty rock crushers or even mortar and pestles – they all belong to the crusher family.
- Mills: Mills take grinding to a whole new level, achieving ultra-fine particle sizes. Ball mills, for instance, use a rotating drum filled with grinding media (like balls or pebbles) that tumble and smash the material into a fine powder. Think of the talcum powder that keeps us cool – ball mills are likely the secret weapon behind its silky texture.
- Micronizers: As the name suggests, micronizers are the ultimate finesse artists of the powder-making world. These machines utilize techniques like fluidized bed jet milling or air jet milling to achieve incredibly fine and uniform particle sizes. Imagine the pigments used in your favorite paints – micronizers ensure their consistent color and smooth application.
- Air Classifiers: Not all heroes wear capes – some come in the form of air classifiers. These clever machines work in conjunction with grinders or mills, separating particles based on their size using precisely controlled airflows. Picture a chef sifting flour – air classifiers perform a similar function, but with much greater precision and automation.
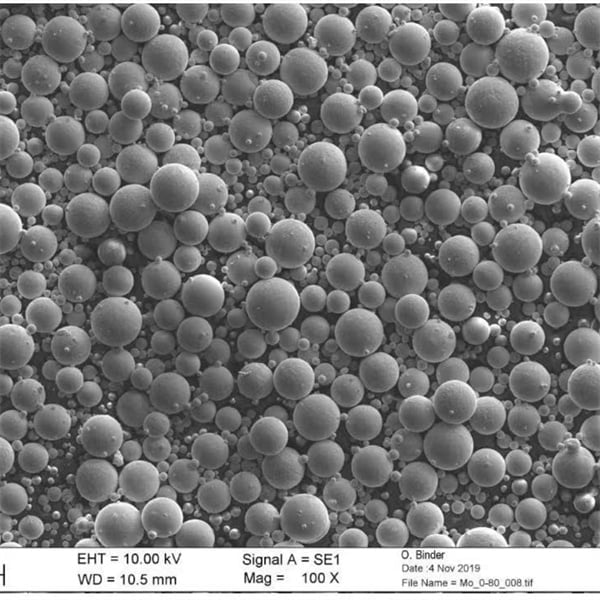

Composition, Properties, And Characteristics Of Powders Made By Different Equipment
| Type of Equipment | Compositional Impact | Property Impact | Characteristic Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grinders | Limited impact | Particle size distribution can be broad | Powders may have a wider range of particle shapes and sizes |
| Crushers | Limited impact (may introduce some contamination from crushing media) | Similar to grinders | Similar to grinders |
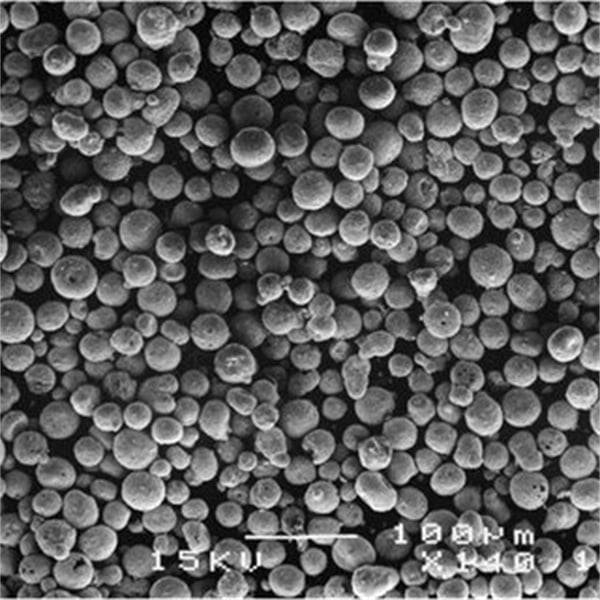
| Mills | May introduce contamination from grinding media | Can achieve very fine particle sizes with a narrower size distribution | Powders tend to be more uniform in shape and size |
| Micronizers | Limited impact | Can achieve extremely fine and uniform particle sizes | Powders have a very high degree of uniformity in size and shape |
| Air Classifiers | No impact (separation technique) | Allows for precise control of particle size distribution | Powders can be tailored to have specific size ranges for optimal performance in different applications |
Applications Of Powder-Making Equipment
The applications of powder-making equipment are as vast as human ingenuity itself. Here are just a few examples:
- Food Industry: From powdered sugar and cocoa for our desserts to spices and coffee grounds, grinders and mills are the backbone of the food industry’s powdered ingredients.
- Pharmaceutical Industry: Micronizers play a crucial role in creating life-saving medications. By precisely controlling particle size, they ensure the uniform distribution and absorption of drugs in our bodies.
- Cosmetics Industry: Powders are essential components of makeup, pigments, and skincare products. Air classifiers and micronizers help achieve the smooth textures and consistent colors we expect from these products.
- Chemical Industry: A wide range of chemicals, from pigments for paints to catalysts for industrial processes, are produced in powdered form. Powder-making equipment allows for precise control over particle size and properties, crucial for optimal chemical reactions.
- Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing): The burgeoning field of 3D printing relies on specialized powder-making equipment to create the fine metallic or plastic powders used in the printing process.
Different Types Of Powder-Making Equipment
Metal Powder Maker Models: Unveiling the Powerhouses
Now, let’s delve deeper into the world of metal powder-making equipment. Here are ten specific models, each with its strengths and applications:
- High-Energy Ball Mill: This workhorse grinder utilizes a rotating cylindrical chamber filled with balls (or grinding media) made from a material harder than the target metal. As the chamber spins, the balls collide with the metal feedstock, pulverizing it into a fine powder. High-energy ball mills are known for their versatility, handling a wide range of metals and achieving a broad spectrum of particle sizes. They’re ideal for producing powders for applications like metal injection molding (MIM) and additive manufacturing.
- Attritor Mill: Imagine a high-speed paint shaker on an industrial scale. Attritor mills employ a rotating shaft with agitators that stir the metal feedstock along with grinding media (often ceramic beads) within a chamber. The intense shearing action breaks down the metal particles, resulting in a finer and more uniform powder compared to ball mills. Attritor mills are well-suited for producing metal powders for applications like brazing and thermal spraying, where a narrow particle size distribution is crucial.
- Jet Mill: Taking a high-tech approach, jet mills utilize a pressurized gas stream to propel the metal feedstock particles against each other at high velocities. This collisional grinding process creates a very fine and uniform powder. Jet mills excel at producing high-purity metal powders for applications like electronics and aerospace, where precise particle size and minimal contamination are essential.
- Fluidized Bed Jet Mill: This innovative mill combines the principles of fluidization and jet milling. The metal feedstock is suspended in a turbulent air stream within the chamber, and then a focused jet stream of gas further breaks down the particles. This technique minimizes inter-particle contact, reducing contamination and achieving exceptionally fine and uniform powders. Fluidized bed jet mills are particularly valuable for producing metal powders for applications like pyrotechnics and pharmaceuticals, where purity and precise particle size are paramount.
- Cryogenic Grinding: This ultra-low temperature approach takes metal powder production to a whole new level. The metal feedstock is first embrittled by subjecting it to extremely cold temperatures (often using liquid nitrogen). Then, it’s pulverized using conventional grinding techniques like ball milling or jet milling. Cryogenic grinding minimizes heat generation during the process, which can be detrimental to certain temperature-sensitive metals. This method is particularly useful for producing metal powders for applications like superconductors and magnetic alloys, where preserving the material’s properties is critical.
Advantages And Limitations Of Powder-Making Equipment
Advantages:
- Versatility: Powder-making equipment can handle a wide range of materials, from soft pharmaceuticals to tough metals.
- Controllability: Different machines offer precise control over particle size, size distribution, and other powder properties.
- Scalability: Equipment is available in various sizes to cater to small-scale research labs or large-scale industrial production.
- Efficiency: Modern powder-making equipment is highly efficient, minimizing waste and maximizing production output.
Limitations:
- Cost: Advanced equipment, particularly micronizers and jet mills, can be expensive investments.
- Complexity: Operating some machines requires specialized training and expertise.
- Contamination: Certain grinding media or milling processes can introduce unwanted contamination into the powder.
- Heat Generation: The grinding process can generate heat, potentially altering the properties of some temperature-sensitive materials.
Choosing the Right Equipment: A Balancing Act
Selecting the most suitable powder-making equipment hinges on several factors:
- Material Properties: The type of metal and its hardness significantly influence the choice of equipment.
- Desired Particle Size and Distribution: The required fineness and uniformity of the powder dictate the grinding technology needed.
- Production Volume: The scale of your operation – from a research lab to a full-blown manufacturing facility – determines the equipment size and capacity.
- Budget: The cost of the equipment needs to be factored into the overall production economics.
FAQ
What is the difference between a crusher and a grinder?
Crushers are typically used for breaking down large chunks of material into smaller, coarser pieces. Grinders, on the other hand, take those smaller pieces and pulverize them into a much finer powder.
How can I control the particle size of the powder?
The type of equipment used, grinding media selection, and process parameters like grinding time and speed all play a role in determining the final particle size. Air classifiers can further refine the powder by separating particles based on size.
What kind of powder making equipment is there?
The type of equipment you need depends on the material you’re working with and the desired characteristics of the final powder. Here are two main categories:
- Grinding equipment: This category breaks down larger materials into finer particles. Examples include hammer mills, ball mills, and fluidized bed jet mills.
- Atomization equipment: This category creates powder from molten materials. Examples include melt atomizers, spray dryers, and plasma atomizers.
What are some important factors to consider when choosing powder making equipment?
- Material properties: The hardness, friability, and moisture content of your material will all affect the type of equipment you need.
- Desired particle size and distribution: How fine do you need the powder to be? How consistent should the particle sizes be?
- Production capacity: How much powder do you need to produce per hour or day?
- Budget: Powder making equipment can range in price from a few thousand dollars to millions of dollars.
Are there different types of powder filling machines?
Yes, there are two main types of powder filling machines:
- Auger fillers: These machines use a screw mechanism to accurately measure and dispense powder into containers. They are versatile and can handle a wide range of powder types.
- Volumetric fillers: These machines use a cup or other volume-based system to fill containers. They are less accurate than auger fillers but may be suitable for some applications.
What safety precautions should I take when working with powder making equipment?
- Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as safety glasses, dust mask, and hearing protection.
- Be aware of the potential for explosions, especially when working with flammable powders.
- Ensure proper ventilation to prevent dust buildup.
- Follow all safety guidelines and procedures outlined in the equipment manual.
Share On
MET3DP Technology Co., LTD is a leading provider of additive manufacturing solutions headquartered in Qingdao, China. Our company specializes in 3D printing equipment and high-performance metal powders for industrial applications.
Inquiry to get best price and customized Solution for your business!
Related Articles
About Met3DP
Recent Update
Our Product
CONTACT US
Any questions? Send us message now! We’ll serve your request with a whole team after receiving your message.

Metal Powders for 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing
COMPANY
PRODUCT
cONTACT INFO
- Qingdao City, Shandong, China
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- +86 19116340731

















