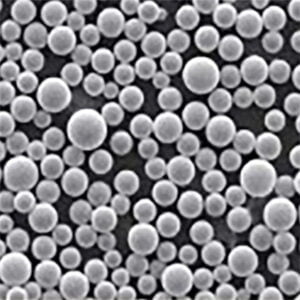
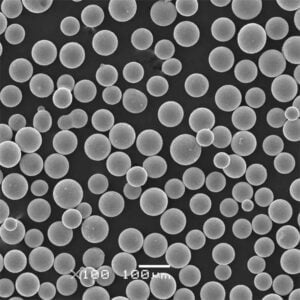
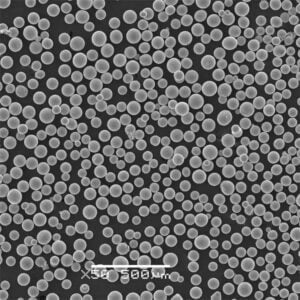
Titanium Sponge Powder
Table of Contents
Titanium sponge powder is a key material used as the feedstock for manufacturing titanium metal components and products. This powder metallurgy route offers several benefits over extraction from mineral ores. This article provides an overview of titanium sponge including its composition, key characteristics, processing methods, applications, suppliers, and more.
Overview of Titanium Sponge Powder
Titanium sponge is the porous form of unalloyed titanium that is the raw material used in powder metallurgy to produce titanium metal components. It is prepared by reducing titanium tetrachloride (TiCl4) derived from mineral ores using magnesium or sodium.
The sponge particles have high surface area and reactivity, allowing them to be easily converted into powders, ingots, mill products, and parts using processes like vacuum arc remelting (VAR), hot isostatic pressing (HIP), additive manufacturing, metal injection molding, and powder forging.
Below is a summary of titanium sponge powder’s properties, applications, global production, pricing, and more.
Titanium Sponge Powder – Key Details
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Composition | Unalloyed titanium (>99% titanium) |
| Particle shape | Porous, irregular shaped sponge particles |
| Particle size | Typically <15 mm size |
| Purity | >=98%, can be up to 99.9% |
| Density | 2.2 – 2.7 g/cc |
| Melting point | 1668°C |
| Key properties | Low density, high strength, excellent corrosion resistance even at high temperatures |
| Main applications | Feedstock for titanium metal powders, mill products, additive manufacturing |
| Annual global production | ~300,000 tonnes with 75,000 tonnes in USA and 100,000 tonnes in China |
| Cost | ~$8-15 per kg for CP-Ti grade sponge |
Titanium sponge enables the economical production of titanium components using near-net shape and powder metallurgy techniques compared to traditional ingot metallurgy involving multiple melt-mill-weld steps with high material waste.
Next, we examine the composition and characteristics of titanium sponge powder in more detail.
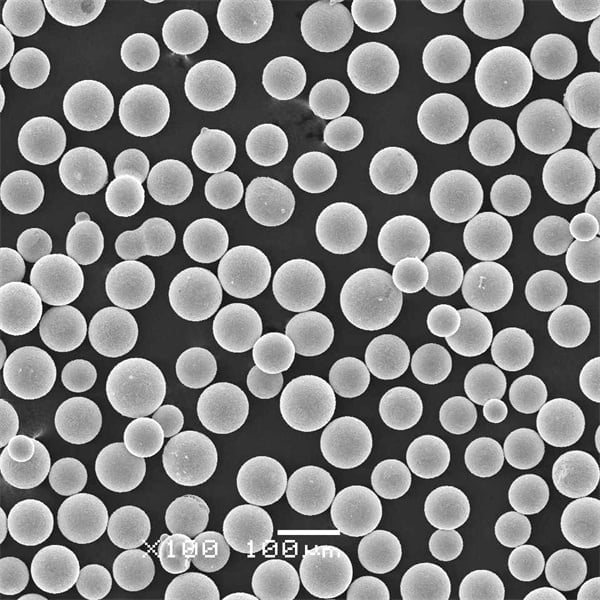
Composition of Titanium Sponge Powder
Titanium sponge powder consists of porous aggregates of titanium metal containing small amounts of impurities like chlorides, magnesium, iron, silicon, nitrogen, carbon, and oxygen. High purity sponge with low O and N content is required for critical aerospace applications.
Titanium Sponge Composition
| Element | Weight % |
|---|---|
| Titanium (Ti) | 98 – 99.9% |
| Oxygen (O) | 0.08 – 0.45% |
| Nitrogen (N) | 0.02 – 0.15% |
| Carbon (C) | 0.04 – 0.16% |
| Iron (Fe) | 0.15 – 0.5% |
| Chloride (Cl) | 0.10 – 0.30% |
The ASTM International standard ASTM B837 specifies the requirements for commercial purity unalloyed titanium sponge based on the sponge grade as follows:
ASTM Specification for Titanium Sponge Grades
| Grade | Titanium Content | Oxygen Content | Iron Content | Nitrogen Content |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CP Ti Grade 1 | 99.2% min | 0.40% max | 0.20% max | 0.03% max |
| CP Ti Grade 2 | 98.9-99.5% | 0.25% max | 0.30% max | 0.05% max |
| CP Ti Grade 3 | 98.3-99.2% | 0.35% max | 0.30% max | 0.05% max |
| CP Ti Grade 4 | 97.75-99.2% | 0.40% max | 0.50% max | 0.05% max |
Higher purity sponge powder with controlled low levels of O and N is required for critical applications like aircraft engine components. This is when grades with 99.5%+ titanium like Ti-6Al-4V Grade 5 or Grade 23 are specified.
Next, we look at the key properties of titanium sponge that make it an excellent engineering material across industries.
Properties of Titanium Sponge Powder
Titanium is valued for its unique combination of low density coupled with high strength retention even at elevated temperatures beyond 500°C. It also offers excellent corrosion resistance in harsh environments.
Key properties of titanium sponge powder are:
Properties of Titanium Metal Sponge
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| Density | 4.5 g/cm3, almost half that of steel and nickel alloys |
| Tensile strength | 340-450 MPa for CP grades, higher for Ti alloys |
| Yield strength (proof strength) | 170-380 MPa for CP grade sponges |
| Melting point | 1668 ± 10°C |
| Young’s modulus | 100-115 GPa, lower than steel |
| Poisson’s ratio | 0.32-0.34 |
| Coefficient of thermal expansion | 8.5 x 10<sup>-6</sup> /K (20-100°C) |
| Thermal conductivity | 6.7-21 W/m.K at 20°C |
| Electrical resistivity | 420-470 nΩ.m at 20°C |
| Magnetism | Non-magnetic |
| Corrosion resistance | Excellent due to protective oxide layer |
| Biocompatibility | Highly bioinert material |
The combination of low weight, high strength at low and high temperatures, corrosion and heat resistance makes titanium indispensable across aerospace, chemical, power generation, automotive, marine, and biomedical industries among others.
Next, we examine some of the major applications and uses of titanium sponge powder across industries.
Applications of Titanium Sponge Powder
The main industrial applications of titanium sponge include the following sectors:
Applications of Titanium Sponge Powder
| Sector | Applications |
|---|---|
| Aerospace | Jet engine and airframe components, blades, fasteners, landing gear |
| Power generation | Components for steam and gas turbines, heat exchangers |
| Chemical processing | Tanks, vessels, heat exchangers, pipes, pumps |
| Marine | Components for ships, submarines, offshore platforms |
| Automotive | Connecting rods, valves, springs, fasteners, exhausts |
| Biomedical | Implants, prostheses, surgical instruments, devices |
| Petroleum | Drill strings, wellhead system components |
| Sporting goods | Golf clubs, tennis rackets, bicycles |
| Military | Aircraft, vessels, armour products |
| Desalination | Heat exchangers, pressure vessels, tubes |
Titanium usage continues to grow at 8-10% CAGR in industries like aerospace, chemical processing, power generation, and seawater desalination. Market demand is forecast to increase from 300,000 tonnes currently to around 575,000 tonnes by 2030.
Let’s look at the various product forms derived from titanium sponge powder.
Titanium Powder Types and Forms
Titanium metal powder and mill products are manufactured from sponge feedstock using processes like vacuum arc remelting (VAR), hot isostatic pressing (HIP), additive manufacturing (AM), metal injection molding (MIM), and others.
Titanium Powder Products Derived from Sponge
| Form | Details |
|---|---|
| Hydride-dehydride (HDH) powder | Irregular shaped <150 μm size powder |
| Gas atomized spherical powder | Spherical 15-150 μm size used in AM |
| Alloyed prealloyed powders | Ti-6Al-4V, Ti-6Al-2Sn-4Zr-6Mo etc. |
| VAR ingots, billets | Remelted ingots and wrought products |
| HIP powder metallurgy products | Custom near-net shape parts |
| Metal injection molding feedstock | Powders for MIM process |
| Powder forged connecting rods | Automotive, marine applications |
| Additive manufacturing feedstock | Laser powder bed, direct laser deposition |
These mill products are further fabricated into finished components and end products across industries.
Next, we examine the manufacturing process and supply chain aspects of titanium metal sponge powder.
Manufacturing Process of Titanium Sponge
Titanium sponge powder is commercially produced by reducing titanium tetrachloride (TiCl4) using sodium or magnesium under strict process controls. TiCl4 itself is produced
Links provided by Claude may not always be valid or up to date. We appreciate your patience as we work to improve link accuracy.
The basic steps for titanium sponge production are:
Titanium Sponge Manufacturing Process
- Extract titanium dioxide (TiO2) from mineral ores
- Convert TiO2 to titanium tetrachloride (TiCl4) using the chloride process
- Reduce TiCl4 with magnesium/sodium under vacuum at 800-850°C
- Diffuse out the salts and condense pure titanium
- Process the porous titanium sponge by crushing, cleaning and sieving
The titanium sponge powder is highly reactive and pyrophoric. So it is handled and stored under inert atmospheres like argon to prevent ignition and explosion hazards.
The porous irregular shaped sponge particles have very high surface area to volume ratio, allowing efficient degassing, compaction and alloying during subsequent melt and powder consolidation steps.
About 75% of titanium sponge output is used to manufacture titanium mill products. The remaining 25% is utilized to produce titanium powders for additive manufacturing and powder metallurgy applications.
Global Production and Leading Suppliers
Currently, global titanium sponge production is around 300,000 metric tons annually. The geography is concentrated with USA and China accounting for almost 60% of world output.
Some of the major titanium sponge manufacturers globally include:
Key Titanium Sponge Manufacturers
| Company | Location | Capacity |
|---|---|---|
| VSMPO-Avisma | Russia | 52,000 mt |
| Western Titanium | USA | 30,000 mt |
| Toho Titanium | Japan | 20,000 mt |
| UKTMP JV | Kazakhstan | 30,000 mt |
| Northwest Institute of NTM | China | 20,000 mt |
| ZTMC | China | 15,000 mt |
USA has proposed restrictions on titanium exports to Russia and China due to strategic concerns in the aerospace sector. This may restructure supply chains and boost production expansions in other regions.
Overall, there is increased installed capacity expected globally with growth opportunities for titanium sponge manufacturers and traders serving various user industries.
Cost Analysis and Pricing Trends
Titanium sponge powder prices vary in the range of $8-16 per kg based on supplied quantity, grade/quality, geography, delivery schedules, long term contracts, and other commercial factors.
Titanium Sponge Price Range
| Grade | Price per kg |
|---|---|
| CP Grade 1 | $8 – 12 |
| CP Grade 2 | $10 – 14 |
| CP Grade 3 | $12 – 15 |
| CP Grade 4 | $10 – 16 |
| Ti 6Al-4V Grade 5, Grade 23 | $14 – 20 |
Prices rose sharply in 2022 due to strong demand recovery across aerospace and other sectors post-pandemic, as well rising energy, feedstock, and logistics costs.
However, some easing is expected from mid-2023 with global sponge capacity rising. Overall industry outlook remains positive with titanium sponge demand forecast to grow steadily at 6-8% CAGR over the next decade.

FAQs
Q. What is titanium sponge?
Titanium sponge is a porous form of high purity titanium metal in powder form that is used as feedstock to manufacture titanium mill products, powders, and parts across industries.
Q. How is titanium sponge powder produced?
It is produced commercially by reducing titanium tetrachloride (TiCl4) derived from mineral ores using magnesium or sodium metal under strictly controlled conditions.
Q. What are the applications of titanium sponge?
Key applications are in aerospace engines and airframes, power generation plants, chemical plants, marine hardware, biomedical implants and devices. It serves industries needing high strength, low weight and corrosion resistant metal components.
Q. What are the advantages of titanium vs. steel?
Compared to steel, titanium offers higher strength-to-weight ratio, superior high temperature properties, non-magnetic response, and much better corrosion resistance benefiting demanding applications.
Q. Who are leading manufacturers of titanium sponge?
Major global producers include VSMPO-Avisma, Western Titanium, Toho Titanium, UKTMP JV, Northwest Institute of NTM, ZTMC with capacities spanning from 15,000 to 50,000 metric tons per annum currently.
Q. What is the price range for titanium sponge per kg?
Prices vary from $8-16 per kg based on grade, order size, geographies, delivery schedule and other commercial factors. Multi-year contracts also impact effective realized pricing for buyers and sellers.
Share On
MET3DP Technology Co., LTD is a leading provider of additive manufacturing solutions headquartered in Qingdao, China. Our company specializes in 3D printing equipment and high-performance metal powders for industrial applications.
Inquiry to get best price and customized Solution for your business!
Related Articles
About Met3DP
Recent Update
Our Product
CONTACT US
Any questions? Send us message now! We’ll serve your request with a whole team after receiving your message.

Metal Powders for 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing
COMPANY
PRODUCT
cONTACT INFO
- Qingdao City, Shandong, China
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- +86 19116340731