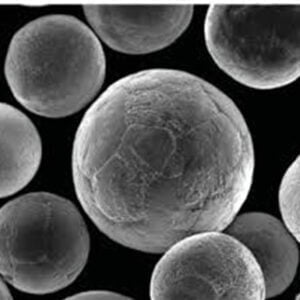
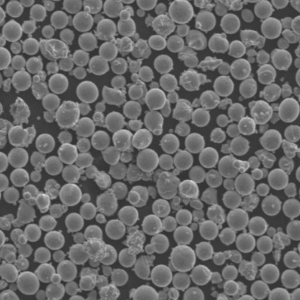
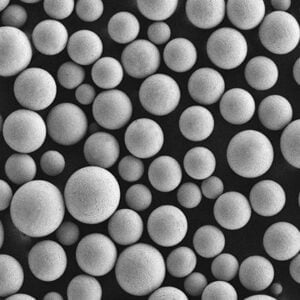
Atomisation Plant
Table of Contents
Overview of Atomisation Plants
Atomisation plants play a pivotal role in the production of metal powders, which are essential components in various industries such as aerospace, automotive, and electronics. These plants employ a sophisticated process to convert molten metal into fine powder particles, each with specific properties tailored for different applications.
Atomisation involves spraying molten metal through a high-pressure gas or liquid stream, causing the metal to break into small droplets that solidify into powder. This method ensures high purity, uniform particle size distribution, and superior material properties, making it indispensable for manufacturing advanced materials.
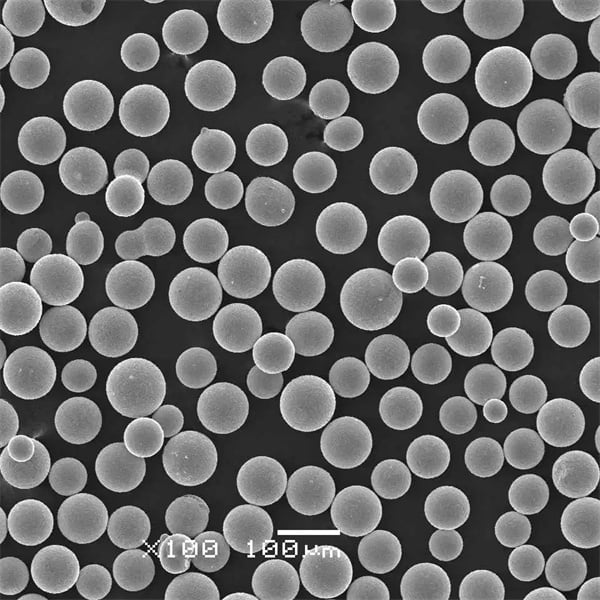
Key Details of Atomisation Plants
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process | High-pressure gas or liquid atomisation of molten metal |
| Materials Processed | Metals such as steel, aluminum, copper, titanium, and their alloys |
| Applications | Aerospace components, automotive parts, electronics, additive manufacturing, coatings, and more |
| Advantages | High purity, uniform particle size, versatility in powder characteristics, scalability |
| Challenges | High energy consumption, complex equipment, need for precise control over process parameters |
Types of Metal Powders and Their Characteristics
1. Stainless Steel Powders
Stainless steel powders are commonly used in applications requiring high strength and corrosion resistance. These powders are essential for producing durable and reliable components in various industries.
| Model | Composition | Properties | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| SS304 | 18% Chromium, 8% Nickel | Corrosion resistance, good weldability | Kitchenware, medical devices |
| SS316 | 16% Chromium, 10% Nickel, 2% Molybdenum | Superior corrosion resistance, especially in chloride environments | Marine equipment, chemical processing |
2. Aluminum Powders
Aluminum powders are lightweight and exhibit excellent conductivity and corrosion resistance. They are widely used in lightweight structures and electronic applications.
| Model | Composition | Properties | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Al6061 | 98% Aluminum, 1% Magnesium, 0.5% Silicon | High strength-to-weight ratio, good machinability | Aerospace components, automotive parts |
| Al7075 | 90% Aluminum, 5.6% Zinc, 2.5% Magnesium | Very high strength, good fatigue resistance | Aircraft structures, high-stress parts |
3. Copper Powders
Copper powders are known for their excellent electrical and thermal conductivity. They are essential for electrical components and thermal management applications.
| Model | Composition | Properties | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cu-ETP | 99.9% Copper | High electrical conductivity, good solderability | Electrical connectors, heat sinks |
| Cu-DHP | 99.9% Copper, 0.04% Phosphorus | Good thermal conductivity, high ductility | Plumbing components, heat exchangers |
4. Titanium Powders
Titanium powders are lightweight and possess high strength and excellent corrosion resistance, making them ideal for aerospace and medical applications.
| Model | Composition | Properties | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ti-6Al-4V | 90% Titanium, 6% Aluminum, 4% Vanadium | High strength, excellent biocompatibility | Aerospace fasteners, medical implants |
5. Nickel-Based Powders
Nickel-based powders offer high temperature and corrosion resistance, essential for high-performance applications in extreme environments.
| Model | Composition | Properties | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inconel 625 | 58% Nickel, 20% Chromium, 8% Molybdenum | Excellent high-temperature strength and corrosion resistance | Gas turbines, chemical processing |
| Hastelloy C276 | 57% Nickel, 16% Molybdenum, 15% Chromium | Outstanding corrosion resistance in harsh environments | Chemical processing, waste treatment |
6. Iron-Based Powders
Iron-based powders are widely used in various industries for their versatility and cost-effectiveness.
| Model | Composition | Properties | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fe-C | 99% Iron, 1% Carbon | Good strength and hardness | Automotive components, structural parts |
| Fe-Ni | 90% Iron, 10% Nickel | Improved toughness and wear resistance | Tooling, heavy machinery parts |
7. Cobalt-Based Powders
Cobalt-based powders are crucial for high wear resistance and high-temperature applications, particularly in cutting tools and aerospace industries.
| Model | Composition | Properties | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stellite 6 | 60% Cobalt, 28% Chromium, 4% Tungsten | High wear resistance, good corrosion resistance | Cutting tools, turbine blades |
| Stellite 21 | 60% Cobalt, 27% Chromium, 5% Molybdenum | Excellent wear resistance at high temperatures | Valve seats, bearing surfaces |
8. Tungsten Carbide Powders
Tungsten carbide powders are renowned for their hardness and wear resistance, making them indispensable in cutting and wear-resistant applications.
| Model | Composition | Properties | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| WC-Co | 90% Tungsten Carbide, 10% Cobalt | Extremely hard, high wear resistance | Cutting tools, mining equipment |
| WC-Ni | 90% Tungsten Carbide, 10% Nickel | High hardness, improved toughness | Wear-resistant parts, tool bits |
9. Magnesium Powders
Magnesium powders are valued for their lightweight and high strength, particularly in the automotive and aerospace industries.
| Model | Composition | Properties | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mg-Al-Zn | 90% Magnesium, 9% Aluminum, 1% Zinc | Lightweight, good strength-to-weight ratio | Automotive components, aircraft parts |
| Mg-Zr | 99% Magnesium, 1% Zirconium | Excellent corrosion resistance, high strength | Aerospace structures, electronics |
10. Silver Powders
Silver powders are known for their superior electrical conductivity and antimicrobial properties, widely used in electronics and medical applications.
| Model | Composition | Properties | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ag-Pure | 99.9% Silver | Highest electrical conductivity, antimicrobial | Electrical contacts, medical devices |
| Ag-Cu | 92% Silver, 8% Copper | Good conductivity, improved hardness | Electrical connectors, brazing alloys |
Applications of Atomisation Plants
Atomisation plants find applications across a diverse range of industries due to the versatility and high quality of the metal powders they produce.
| Industry | Applications |
|---|---|
| Aerospace | High-strength, lightweight components, turbine blades, structural parts |
| Automotive | Engine components, lightweight structures, brake pads |
| Electronics | Conductive pastes, electronic connectors, heat sinks |
| Additive Manufacturing | 3D printing of complex parts, rapid prototyping |
| Medical | Biocompatible implants, surgical instruments |
| Coatings | Thermal spray coatings, anti-corrosion coatings |
| Tooling | Cutting tools, wear-resistant parts |
| Chemical Processing | Corrosion-resistant equipment, catalytic converters |
Advantages of Atomisation Plants
Atomisation plants offer numerous advantages that make them a preferred choice for metal powder production.
- High Purity: Atomisation produces powders with minimal contamination, ensuring high purity and superior material properties.
- Uniform Particle Size: The process allows for precise control over particle size distribution, leading to consistent and predictable behavior in applications.
- Versatility: Atomisation can be applied to a wide range of metals and alloys, providing flexibility in material selection.
- Scalability: Atomisation plants can be scaled to meet varying production demands, from small-scale research to large-scale manufacturing.
- Customization: Powders can be tailored to specific requirements, including particle shape, size, and composition, to meet diverse application needs.
Disadvantages of Atomisation Plants
Despite their many advantages, atomisation plants also have certain drawbacks that need to be considered.
- High Energy Consumption: The process requires significant energy input, making it less efficient compared to some other powder production methods.
- Complex Equipment: Atomisation plants involve sophisticated machinery and controls, leading to higher initial investment and maintenance costs.
- Process Control: Precise control over process parameters is essential to achieve desired powder characteristics, which can be challenging to maintain consistently.
- Limited Materials: Some metals and alloys may be difficult or uneconomical to process using atomisation, limiting its applicability.
Specifications, Sizes, and Standards
When selecting metal powders for specific applications, it’s crucial to consider the specifications, sizes, and standards that define their quality and suitability.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Particle Size | Typically ranges from 1 to 150 microns, depending on the application |
| Purity | Generally above 99%, with specific impurities controlled based on application needs |
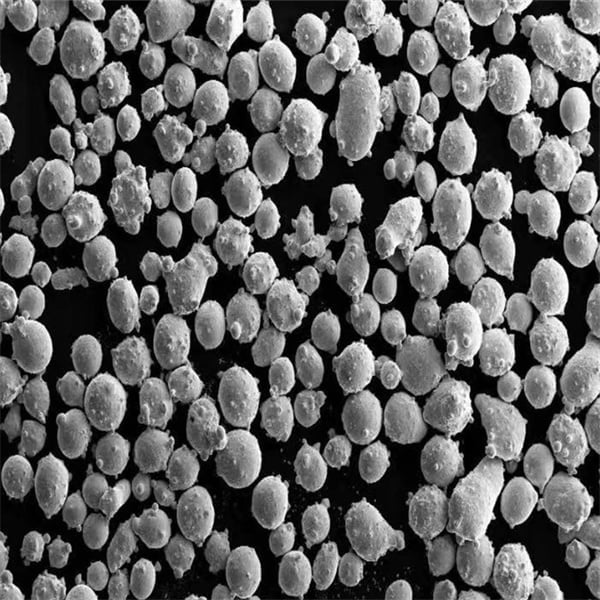
| Morphology | Spherical, irregular, or dendritic shapes, influencing flowability and packing density |
| Standards | ISO, ASTM, and other industry-specific standards ensuring consistent quality |
| Packaging | Available in various sizes, from small laboratory quantities to large industrial volumes |
Suppliers and Pricing Details
Selecting the right supplier is crucial for obtaining high-quality metal powders at competitive prices.
| Supplier | Materials Offered | Pricing (per kg) | Additional Services |
|---|---|---|---|
| ABC Metals | Stainless steel, aluminum, copper | $50 – $200 | Custom alloy development, technical support |
| PowderTech | Titanium, nickel-based, cobalt-based powders | $100 – $500 | Rapid prototyping, bulk discounts |
| Metal Powders Inc. | Iron-based, tungsten carbide, silver | $20 – $300 | Quality assurance, tailored packaging |
| Global Powders | Wide range of metal powders | $30 – $400 | International shipping, on-site consultation |
Comparison of Metal Powders
When choosing metal powders for specific applications, it’s essential to compare their properties, advantages, and limitations.
| Metal Powder | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Corrosion resistance, good strength | Higher cost compared to regular steel |
| Aluminum | Lightweight, good conductivity | Lower strength compared to some other metals |
| Copper | Excellent electrical and thermal conductivity | Susceptible to oxidation |
| Titanium | High strength, biocompatibility | Expensive, challenging to process |
| Nickel-Based | High-temperature and corrosion resistance | Higher cost, complex processing |
| Iron-Based | Cost-effective, versatile | Lower corrosion resistance |
| Cobalt-Based | High wear resistance, temperature stability | Expensive, limited availability |
| Tungsten Carbide | Extremely hard, high wear resistance | Brittleness, high cost |
| Magnesium | Lightweight, good strength-to-weight ratio | Flammability, corrosion issues |
| Silver | Superior conductivity, antimicrobial properties | High cost, tarnishes easily |
FAQ
What is an atomisation plant?
An atomisation plant is a facility that converts molten metal into fine powder using high-pressure gas or liquid streams. This process ensures high purity and uniform particle size, making the powders suitable for various industrial applications.
What metals can be processed in an atomisation plant?
Atomisation plants can process a wide range of metals, including stainless steel, aluminum, copper, titanium, nickel-based alloys, iron, cobalt, tungsten carbide, magnesium, and silver.
Why is particle size important in metal powders?
Particle size affects the flowability, packing density, and overall performance of metal powders in applications such as additive manufacturing, coatings, and sintering processes. Uniform particle size distribution ensures consistent and predictable behavior.
What are the main applications of metal powders produced in atomisation plants?
Metal powders are used in aerospace, automotive, electronics, additive manufacturing, medical devices, coatings, tooling, and chemical processing industries due to their tailored properties and high performance.
What are the advantages of using atomised metal powders?
Atomised metal powders offer high purity, uniform particle size, versatility in material selection, scalability for different production volumes, and customization to meet specific application needs.
What are the challenges associated with atomisation plants?
Challenges include high energy consumption, complex equipment and controls, precise process parameter maintenance, and limited applicability for some metals and alloys.
How are metal powders priced?
The pricing of metal powders depends on the material type, purity, particle size, and supplier. Prices can range from $20 to $500 per kilogram, with additional services such as custom alloy development and technical support influencing the cost.
Can atomisation plants produce custom alloy powders?
Yes, many suppliers offer custom alloy development to meet specific application requirements, ensuring that the metal powders possess the desired properties for optimal performance.
Conclusion
Atomisation plants are at the forefront of metal powder production, enabling the creation of high-quality powders essential for modern manufacturing. By understanding the various types of metal powders, their applications, and the advantages and limitations of atomisation, industries can make informed decisions to harness the full potential of these advanced materials. Whether in aerospace, automotive, electronics, or medical fields, the versatility and performance of atomised metal powders continue to drive innovation and excellence.
Share On
MET3DP Technology Co., LTD is a leading provider of additive manufacturing solutions headquartered in Qingdao, China. Our company specializes in 3D printing equipment and high-performance metal powders for industrial applications.
Inquiry to get best price and customized Solution for your business!
Related Articles
About Met3DP
Recent Update
Our Product
CONTACT US
Any questions? Send us message now! We’ll serve your request with a whole team after receiving your message.

Metal Powders for 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing
COMPANY
PRODUCT
cONTACT INFO
- Qingdao City, Shandong, China
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- +86 19116340731