Nickel Coated Graphite Powder
Table of Contents
Overview
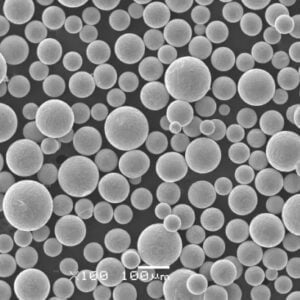
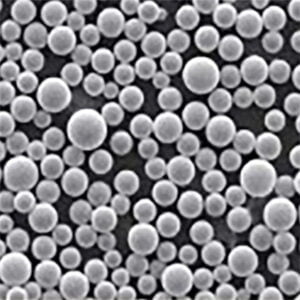
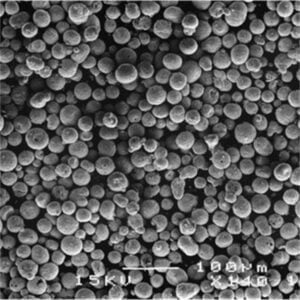
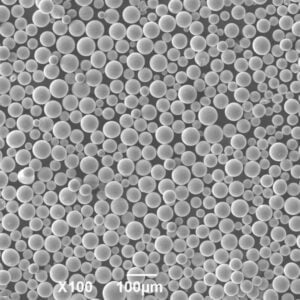
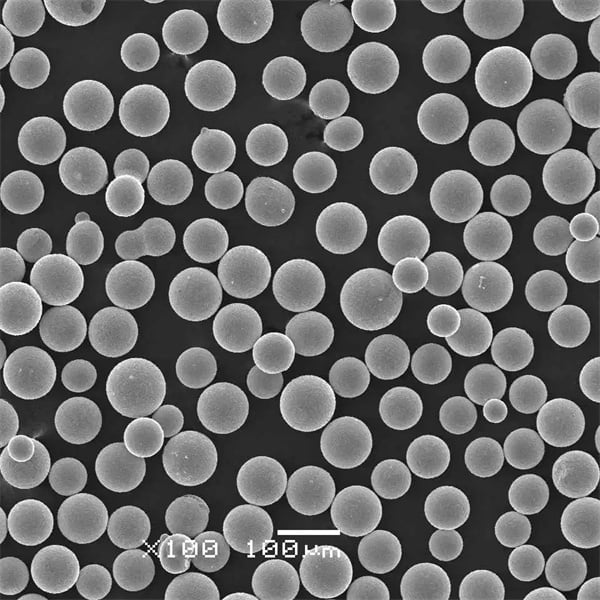
Nickel coated graphite powder is a specialty powder material consisting of graphite particles that are coated with a layer of metallic nickel. The nickel coating provides several enhanced properties and benefits compared to regular graphite powder.
Some key features of nickel coated graphite powder include:
- High electrical and thermal conductivity
- Improved lubricity and anti-seizing properties
- Increased corrosion resistance
- Higher heat resistance
- Better solderability and wettability
The nickel coating thickness can range from less than 1 micron up to over 50 microns. The thickness impacts properties like conductivity and lubrication. Popular uses for nickel coated graphite are in the automotive, electronics, energy, and industrial manufacturing industries.

Types of Nickel Coated Graphite Powder
| Type | Description | Nickel Coating Thickness | Particle Size Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type 1 | Light nickel coating for improved conductivity | < 1 micron | 1 – 10 microns |
| Type 2 | Medium nickel coating for good lubricity | 1 – 5 microns | 5 – 20 microns |
| Type 3 | Heavy nickel coating for corrosion resistance | > 10 microns | 15 – 50 microns |
- Nickel coating thickness and graphite particle size can be customized
- Finer graphite powder allows thinner nickel coatings
- Coarser graphite powder used for thicker nickel coatings
Composition of Nickel Coated Graphite
| Component | Weight % | Role |
|---|---|---|
| Graphite | 80-95% | Provides base structure and core properties |
| Nickel | 5-20% | Enhances conductivity, lubricity, heat resistance etc. |
- High purity graphite powder is used
- Nickel provides exterior coating on each graphite particle
- The nickel fully encapsulates the graphite particle
- Overall purity exceeds 98% for most nickel coated graphite
Properties of Nickel Coated Graphite Powder
Electrical Conductivity
- Nickel coating increases electrical conductivity
- Enables stable performance in friction applications
- Maintains conductivity between graphite particles
- Improves conductivity in polymer composites
Thermal Conductivity
- Thermal conductivity higher than pure nickel
- Between 140-180 W/mK for most varieties
- Heat dissipation maintained during friction use
- Permits use in thermally conductive composites
Lubricity and Anti-Seize Properties
- Coefficient of friction ranges from 0.10 to 0.25
- Significantly lower than pure nickel
- Graphite provides low friction surface
- Nickel binding reduces material transfer
- Prevents seizing up of interfaces
Corrosion Resistance
- Nickel coating resists corrosion
- Protects graphite in oxidizing environments
- Stable lubricity performance over time
- Suitable for sea water, fuel, and chemical use
Heat Resistance
- Uses high purity graphite powder substrate
- Handles temperatures over 2400°C in inert atmosphere
- Oxidation resistance to over 600°C in air
Compare properties to Standard Graphite Powder:
| Property | Nickel Coated Graphite | Standard Graphite Powder |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | Higher | Lower |
| Thermal Conductivity | Higher | Lower |
| Lubricity | Equal | Equal |
| Corrosion Resistance | Higher | Lower |
| Heat Resistance | Equal | Equal |
Applications of Nickel Coated Graphite Powder
Automotive Industry
- Transmission clutch plates
- Water pump seals
- Lock cylinders and ignition parts
- Ball joints and other friction surfaces
Electronics Industry
- Conductive coatings and gaskets
- Heat dissipation composites
- Dry film lubricant layers
Energy Sector
- Lubricant in high pressure valves
- Seals in pumps for corrosive fluids
- Components in renewable energy systems
Industrial Manufacturing
- Anti-seize lubricant for metal forming
- Metal injection molding additive
- High temperature molds and dies
- Powder metallurgy additive
Compare application suitability:
| Application | Nickel Coated Graphite | Standard Graphite |
|---|---|---|
| Transmission clutches | Excellent | Poor |
| Conductive coatings | Good | Poor |
| Corrosion resistance | Excellent | Poor |
| Mold release agent | Excellent | Good |
The nickel binding gives nickel coated graphite powder enhanced suitability in applications that undergo friction or corrosive conditions. The improved properties expand its usage into new industrial sectors.
Specifications of Nickel Coated Graphite Powder
Nickel coated graphite powder is available in a wide range of specifications targeted at different industries and customized applications:
Particle Sizes Available
| Size Range | Typical Uses |
|---|---|
| 1 – 10 microns | Electronics coatings, polymer fillers |
| 5 – 20 microns | Anti-seize lubricants, metal composites |
| 15 – 50 microns | High temperature lubricants, friction plates |
- Narrower size distributions available for tailored performance
- Optimal sizes depend on coating thickness and usage
- Finer sizes used for thin coatings and larger for thicker
Nickel Coating Thickness Options
| Thickness Range | Typical Uses |
|---|---|
| < 1 micron | Thermal interface materials, electronics |
| 1 – 5 microns | Lock cylinders, water pump seals |
| > 10 microns | Clutches, metal processing, valves |
- Coating thickness impacts conductivity, lubricity, and corrosion resistance
- Thicker coatings used in demanding friction and anti-seize uses
- Thinner coatings optimize conductivity for composites
Grade Standards
| Grade | Properties |
|---|---|
| Grade 1 | Basic purity and sizing |
| Grade 2 | Higher purity levels |
| Grade 3 | Precision particle distribution |
- Grade standards designate overall powder quality
- Higher grades have more controlled specifications
- Custom grades available for specialized applications
Suppliers and Pricing
Nickel coated graphite powder is sold by specialty chemical and powder metallurgy suppliers. Some leading global providers include:
Major Nickel Coated Graphite Manufacturers
| Supplier | Location |
|---|---|
| Asbury Carbons | USA |
| Mersen | France |
| SGL Carbon | Germany |
| JFE Chemical | Japan |
Pricing for nickel coated graphite powder varies based on:
- Supplier/manufacturer
- Grade and powder specification
- Purchase quantity and bulk order size
- Regional availability
| Type | Price Range per Kg |
|---|---|
| Basic Grade | $25 – $75 |
| High Purity Grade | $50 – $150 |
| Ultrafine Grade | $150 – $500 |
Larger 20 tonne bulk orders can be over 50% less per kg. Recent supply chain issues have increased lead times and pricing volatility worldwide.

Pros and Cons of Nickel Coated Graphite Powder
Advantages
- Increased corrosion resistance
- Enhanced electrical conductivity
- Higher thermal conductivity
- Maintains lubricity during friction
- Withstands higher temperatures
Disadvantages
- More expensive than standard graphite powder
- Heavier density than uncoated graphite
- Dark colored nickel coating
- Requires further processing for coating
- Longer lead times for custom grades
For critical applications where performance outweighs cost, nickel coated graphite powder delivers value through longer component lifetime, reduced failures, lower replacement rates, and greater energy efficiency over time.
Nickel Coated vs Metal Coated Graphite
Other metal coatings for graphite powder besides nickel include copper, silver, tin, zinc and precious metals.
Compare nickel coating with alternatives:
| Coating Material | Pros | Cons | Best Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nickel | Corrosion resistant, conductive, lubricious | Expensive, dark colored | Transmissions, electronics, valves |
| Copper | Highly conductive, cheaper | Oxidizes easily | Conductive composites, EMI shielding |
| Tin | Lower friction, more lubricious | Less strong bonding | Low friction lubricants |
| Silver | Excellent conductivity, stable coating | Very expensive | Thermal interface materials |
- Nickel offers the best all-around performance enhancement
- Alternative metal coatings better suited for specific uses
- Copper competes when electrical conductivity is critical
- Silver only viable for premium niche applications
Combinations of graphite coated with both nickel and copper give tunable optimization between improved conductivity, lubricity, and corrosion resistance.
The Future of Nickel Coated Graphite
Ongoing innovation in materials technology will open up new possibilities for nickel coated graphite powder over the next 5-10 years:
Demand Growth Projections
- Global graphite market projected to grow 6-8% annually
- Nickel coated subset forecast for 9-12% annual growth
- Electric vehicle adoption driving higher volumes
- Expanding high performance applications
Emerging Technologies
- Graphene and graphite nanoplatelet coatings
- Gradient density coatings
- Embedded particle coatings e.g. with MoS2, hBN
- Advanced purification and production techniques
Market Opportunities
- Recycling nickel coated powders
- Lower cost production methods
- New application development e.g biomedical
- Grades tailored for customer criteria
Continued strong industrial demand combined with material and manufacturing improvements will make nickel coated graphite powder an essential advanced functional material over the next decade.
FAQs
What is nickel coated graphite powder?
Nickel coated graphite powder consists of micron-sized graphite particles encapsulated by a metallic nickel exterior coating. The nickel forms a jacket around the graphite core, enhancing properties.
Why coat graphite powder with nickel?
Nickel coatings improve graphite powder’s electrical and thermal conductivity, lubrication, corrosion and heat resistance for wider industrial uses.
What industries use nickel coated graphite powder?
Major industrial applications are in the automotive, electrical, energy, and general manufacturing sectors. Significant growth potential also exists in emerging technologies.
What thickness of nickel coating is typical?
Coating thickness ranges from less than 1 micron to over 50 microns. 1-10 microns is common. Thicker coatings provide more corrosion protection and lubricity. Thinner coatings optimize conductivity.
Does nickel coated graphite powder achieve better heat transfer?
Yes, the nickel coating boosts thermal conductivity above standard graphite. This enables better dissipation in high temperature friction applications.
Is nickel coated graphite powder expensive?
Nickel coated graphite powder costs between 5-10x more than standard grades per unit weight. However the enhanced performance justifies higher costs for critical applications.
Is custom nickel coated graphite powder available?
Yes, leading suppliers offer custom particle sizes, size distribution, coating thickness and specifications tailored to individual customer requirements.
Can nickel coated graphite be recycled?
Nickel and graphite are recyclable commodities. Recovering used powder can provide cost savings and sustainability incentives for manufacturers.
Share On
MET3DP Technology Co., LTD is a leading provider of additive manufacturing solutions headquartered in Qingdao, China. Our company specializes in 3D printing equipment and high-performance metal powders for industrial applications.
Inquiry to get best price and customized Solution for your business!
Related Articles
About Met3DP
Recent Update
Our Product
CONTACT US
Any questions? Send us message now! We’ll serve your request with a whole team after receiving your message.

Metal Powders for 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing
COMPANY
PRODUCT
cONTACT INFO
- Qingdao City, Shandong, China
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- +86 19116340731