Metal powders suitable for SLM
Table of Contents
Selective Laser Melting (SLM) has revolutionized manufacturing, enabling the creation of complex, high-performance metal parts directly from digital models. But at the heart of this technology lies a crucial ingredient: metal powders. These meticulously engineered materials play a pivotal role in determining the success and quality of SLM-produced components.
The Characteristics of Metal Powders Suitable for SLM
SLM powders possess unique characteristics that set them apart from conventional metal powders. Here’s a closer look:
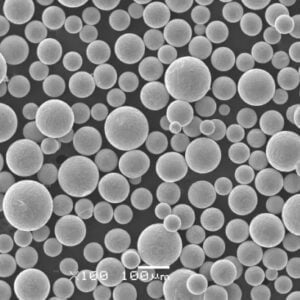
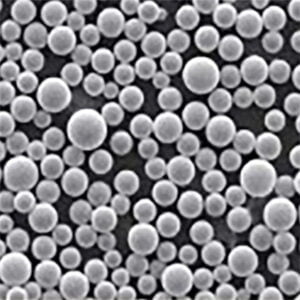
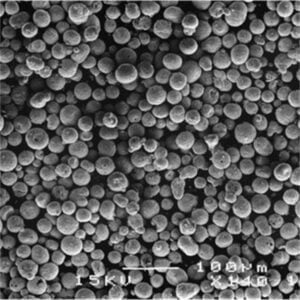
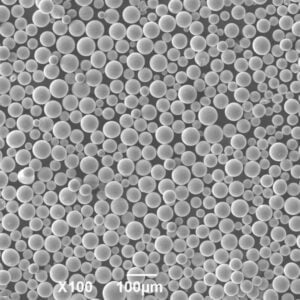
- Particle size and distribution: SLM powders are incredibly fine, typically ranging from 15 to 45 microns in diameter. This ensures efficient laser melting and layer-by-layer build-up during the SLM process. A narrow particle size distribution, where most particles fall within a specific size range, is crucial for consistent material flow and good packing density in the powder bed.
- Sphericity: Ideally, SLM powders should be spherical or near-spherical in shape. This minimizes surface area and promotes optimal flowability, which is essential for even distribution within the build chamber and smooth layer formation.
- Chemical composition: The specific composition of the metal powder directly influences the properties of the final printed part. SLM powders are often high-purity metals or precisely formulated alloys to achieve desired mechanical strength, corrosion resistance, and other performance characteristics.
- Flowability: Excellent flowability is essential for ensuring consistent powder spreading and layer formation during the SLM process. Poor flowability can lead to irregularities, defects, and even build failures.

Applications of Metal Powders in SLM
Selective Laser Melting (SLM) has revolutionized manufacturing with its ability to create complex, high-performance parts directly from digital models. But the magic behind SLM lies not just in the technology, but also in the materials used: metal powders. These meticulously crafted powders hold the key to unlocking a vast array of applications across diverse industries.
Taking Flight in Aerospace:
In the aerospace industry, where every gram counts, SLM powders shine. Their ability to be transformed into lightweight, yet incredibly strong components for aircraft, spacecraft, and propulsion systems is a game-changer. Compared to traditional manufacturing methods, these components offer significant weight reductions, leading to enhanced fuel efficiency and improved performance. Imagine lighter airplanes requiring less fuel, translating into longer flight ranges, increased payload capacity, and reduced environmental impact.
Healing and Empowering in Medical and Dental Fields:
The medical and dental fields have witnessed a paradigm shift with the introduction of biocompatible SLM powders. These powders, often made of titanium or cobalt-chrome, are used to create implants, prosthetics, and dental restorations that seamlessly integrate with the human body. Their excellent biocompatibility ensures minimal rejection, while their osseointegration (fusion with bone) properties promote long-term functionality. Additionally, their mechanical properties closely mimic natural bone tissue, providing patients with a natural feel and improved functionality.
Shifting Gears in the Automotive Industry:
The automotive industry is constantly striving for increased fuel efficiency and performance. SLM powders are stepping up to the challenge by enabling the creation of complex, lightweight engine components, gears, and other parts. These components not only reduce weight, but also offer improved design freedom, allowing for the creation of parts with optimized shapes and functionalities, leading to a significant boost in overall vehicle performance.
Advantages and Considerations of Using Metal Powders in SLM
Advantages:
- Design freedom: SLM allows for the creation of complex geometries and internal features that are impossible with traditional manufacturing methods.
- Lightweighting: The use of metal powders enables the production of lightweight components, crucial for applications in aerospace, automotive, and other weight-sensitive industries.
- Performance optimization: The ability to tailor the composition of metal powders allows for the creation of parts with specific mechanical properties, such as high strength, corrosion resistance, or biocompatibility.
- Reduced waste: SLM minimizes material waste compared to traditional methods like machining, as unused powder can be recycled and reintroduced into the process.
Considerations:
- Cost: SLM technology and metal powders can be expensive compared to traditional manufacturing methods. This is often mitigated by the benefits of design freedom, performance optimization, and lightweighting.
- Process complexity: SLM requires expertise in machine operation, powder handling, and process optimization to achieve consistent quality and desired part properties.
- Surface roughness: SLM parts can exhibit a slightly rougher surface finish compared to some traditional methods. However, post-processing techniques like polishing or machining can be used to achieve smoother surfaces.
Metal Powders: A Diverse Landscape
A fascinating aspect of SLM is the vast array of available metal powders, each offering unique properties and catering to specific applications. Here are ten prominent examples, along with their key characteristics and applications:
1. 316L Stainless Steel:
- Composition: Stainless steel alloy with chromium, nickel, and molybdenum, offering excellent corrosion resistance, biocompatibility, and good strength.
- Applications: Medical and dental implants, aerospace components, chemical processing equipment.
2. Inconel 625:
- Composition: Nickel-chromium-based superalloy known for its high-temperature
3. Titanium Grade 2:
- Composition: Commercially pure titanium, prized for its excellent biocompatibility, low density, and good corrosion resistance.
- Applications: Medical implants, aerospace components, sporting goods.
4. Aluminum Si10Mg:
- Composition: Aluminum alloy with silicon and magnesium, offering a good balance of strength, ductility, and weight savings.
- Applications: Automotive components, consumer electronics, prototypes.
5. Cobalt Chrome (CoCr):
- Composition: Alloy of cobalt and chromium, known for its high strength, wear resistance, and biocompatibility.
- Applications: Medical implants, dental restorations, cutting tools.
6. Nickel (Ni):
- Composition: Pure nickel, offering good electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and corrosion resistance.
- Applications: Electrical components, heat exchangers, chemical processing equipment.
7. Copper (Cu):
- Composition: Pure copper, known for its excellent electrical conductivity and thermal conductivity.
- Applications: Heat sinks, electrical conductors, electromagnetic components.
8. Tooling Steel (H13):
- Composition: Alloy steel formulated for tool and die applications, offering high strength, wear resistance, and hot hardness.
- Applications: Molds, dies, punches, tooling inserts.
9. Maraging Steel:
- Composition: Low-carbon, high-nickel steel known for its exceptional strength and toughness after aging at low temperatures.
- Applications: Aerospace components, high-performance tools, firearm components.
10. Tantalum (Ta):
- Composition: Rare earth metal prized for its high melting point, excellent corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility.
- Applications: Medical implants, chemical processing equipment, high-temperature crucibles.

Conclusion
Metal powders play a critical role in unlocking the potential of Selective Laser Melting. Their unique characteristics and diverse range cater to a growing number of industries and applications, pushing the boundaries of design, performance, and efficiency. As SLM technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more advancements in metal powder development, further expanding the possibilities of this transformative manufacturing method.
FAQs
What is Selective Laser Melting (SLM)?
SLM is an additive manufacturing technology that uses a high-powered laser to selectively melt and fuse metal powder layer-by-layer to create complex three-dimensional objects from a digital model.
What materials can be used in SLM?
A wide range of metal powders can be used in SLM, including:
Titanium and its alloys: Commonly used in aerospace and medical applications due to their high strength, light weight, and biocompatibility.
Stainless steel: Versatile and widely used in various industries due to its strength, corrosion resistance, and affordability.
Nickel and its alloys: Used in high-temperature and high-stress applications due to their excellent heat resistance and mechanical properties.
Aluminum and its alloys: Valued for their lightweight properties and used in applications where weight reduction is crucial.
Precious metals: Used in creating jewelry and other high-value applications.
What are the advantages of using SLM?
Design freedom: SLM allows for the creation of complex geometries and intricate features that are difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional manufacturing methods.
Lightweight parts: SLM-produced parts are often lighter than traditionally manufactured components, leading to improved fuel efficiency and performance in applications like aerospace and automotive.
Customization: SLM enables the production of customized parts and one-off pieces efficiently.
Reduced waste: Compared to traditional subtractive manufacturing methods, SLM produces minimal waste material.
What are the limitations of SLM?
Cost: SLM equipment and materials can be expensive, making it less suitable for mass production of simple parts.
Surface roughness: SLM-produced parts can have a rougher surface finish compared to some traditional methods, requiring additional post-processing.
Limited material selection: While the range of compatible materials is expanding, it is still not as extensive as with traditional methods.
What are some applications of SLM?
SLM is used in various industries, including:
Aerospace: Lightweight and high-strength components for aircraft, spacecraft, and propulsion systems.
Medical and dental: Biocompatible implants, prosthetics, and dental restorations.
Automotive: Complex and lightweight engine components, gears, and other parts.
Consumer goods: Jewelry, sporting goods, and customized consumer electronics.
Share On
MET3DP Technology Co., LTD is a leading provider of additive manufacturing solutions headquartered in Qingdao, China. Our company specializes in 3D printing equipment and high-performance metal powders for industrial applications.
Inquiry to get best price and customized Solution for your business!
Related Articles
About Met3DP
Recent Update
Our Product
CONTACT US
Any questions? Send us message now! We’ll serve your request with a whole team after receiving your message.

Metal Powders for 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing
COMPANY
PRODUCT
cONTACT INFO
- Qingdao City, Shandong, China
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- +86 19116340731