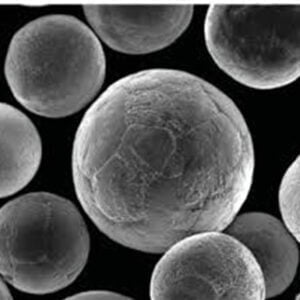
Specific classification of Aluminum Alloy 3D Metal Powder
Table of Contents
Imagine building intricate objects layer by layer, not with bricks and mortar, but with vaporized metal. This is the magic of 3D printing, and aluminum alloy powders are the tiny metallic soldiers that make it happen. But not all aluminum alloy powders are created equal. Delving into their specific classifications is crucial to unlocking the full potential of 3D printed aluminum creations.
Aluminum Alloy 3D Metal Powder Classification based on Chemical Composition
The elements alloyed with pure aluminum significantly influence the final properties of the 3D printed part. Here’s a breakdown of some key classifications:
- AlSi Alloys (Silicon): Imagine adding a dash of baking soda to your bread dough. Silicon in AlSi alloys acts similarly, enhancing fluidity during printing and improving castability. AlSi7Mg0.3 (AA7005) and AlSi10Mg (AA6101) are popular choices, offering a good balance between strength, ductility, and weldability. They’re ideal for automotive components, architectural elements, and even engine blocks.
- AlCu Alloys (Copper): Copper brings high strength to the party. AlCu4Mg1 (2024) is a superstar in this category, boasting excellent strength-to-weight ratio and superior wear resistance. Think aerospace components, high-performance bicycles, and even robotic arms. But here’s the catch: copper makes AlCu alloys less corrosion-resistant.
- AlMg Alloys (Magnesium): Magnesium is a lightweight champion. Alloys like AlMgSi0.5 (AA6061) are known for their excellent workability, corrosion resistance, and ability to be anodised for a decorative finish. They’re perfect for building housings, enclosures, and even decorative art pieces. However, their strength pales in comparison to AlCu alloys.
Composition Comparison Table:
| Alloy Designation | Primary Alloying Element(s) | Key Properties | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| AlSi7Mg0.3 (AA7005) | Silicon (7%), Magnesium (0.3%) | Good fluidity, castability, strength, ductility | Automotive components, architectural elements, engine blocks |
| AlSi10Mg (AA6101) | Silicon (10%), Magnesium | Good fluidity, castability, strength, ductility | Automotive components, architectural elements |
| AlCu4Mg1 (2024) | Copper (4%), Magnesium (1%) | High strength-to-weight ratio, wear resistance | Aerospace components, high-performance bicycles, robotic arms |
| AlMgSi0.5 (AA6061) | Magnesium (0.5%), Silicon | Excellent workability, corrosion resistance | Housings, enclosures, decorative art pieces |
Remember: This is just a glimpse into the vast world of aluminum alloy compositions. Specialty alloys exist for specific needs, like AlLi (Lithium) for aerospace applications requiring extreme lightweight performance.
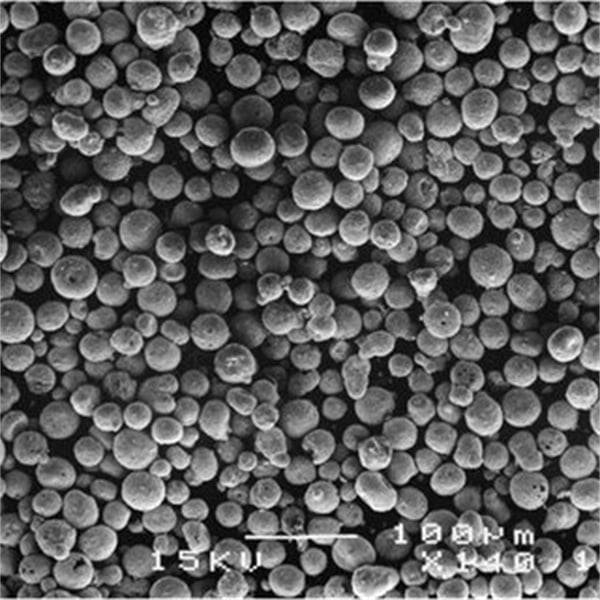
Aluminum Alloy 3D Metal Powder Classification based on Powder Morphology
The shape and surface characteristics of the powder particles significantly impact printability and final part quality. Here’s a breakdown of two key classifications:
- Spherical Powders: Imagine tiny metal ball bearings. Spherical powders offer excellent flowability, leading to more consistent layer deposition during printing. This translates to smoother surfaces and potentially stronger parts. However, the production process for perfectly spherical powders can be more complex, impacting cost.
- Irregular Shaped Powders: Not all powders are created equal! Irregularly shaped powders can have advantages too. Their interlocking nature can sometimes improve packing density, potentially leading to stronger parts. Additionally, the production process for these powders can be simpler, making them potentially more cost-effective. However, irregular shapes can also lead to flowability issues and potentially rougher surface finishes.
Morphology Comparison Table:
| Powder Morphology | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Spherical | Excellent flowability, smoother surfaces, potentially stronger parts | More complex production process, potentially higher cost |
| Irregular Shaped | Potentially improved packing density, stronger parts, simpler production process, potentially lower cost | Flowability issues, rougher surface finishes |
The Takeaway: The ideal morphology depends on the specific application and printing technology. For high-resolution prints with critical surface finishes, spherical powders might be preferred. For applications where maximizing strength and cost are top priorities, irregular shaped powders could be a viable option.
Aluminum Alloy 3D Metal Powder Classification based on Particle Size
The size of the powder particles plays a crucial role in determining printability and final part properties. Here’s a breakdown:
- Fine Powders (< 30 microns): Imagine working with ultra-fine flour. Fine powders offer incredible detail and resolution in the printed parts. Think intricate features and smooth surfaces. But there’s a catch: these tiny particles can be challenging to flow freely, potentially leading to printing inconsistencies. Additionally, fine powders may have a higher surface area, making them more susceptible to oxidation during storage.
- Medium Powders (30 – 100 microns): The Goldilocks zone! Medium sized powders offer a good balance between detail and printability. They flow more readily than their finer counterparts, reducing printing issues. They’re also less prone to oxidation due to lower surface area. This makes them a popular choice for a wide range of 3D printing applications.
- Coarse Powders (> 100 microns): Think of coarse sand. Coarse powders offer the easiest flow characteristics, minimizing printing problems. However, the trade-off is a potential loss of detail and resolution in the final parts. Surfaces might appear rougher, and intricate features may be difficult to achieve.
Particle Size Comparison Table:
| Particle Size Range | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Fine Powders (< 30 microns) | High detail, smooth surfaces | Poor flowability, higher oxidation risk |
| Medium Powders (30 – 100 microns) | Good balance of detail and printability, less prone to oxidation | |
| Coarse Powders (> 100 microns) | Excellent flowability | Lower detail, rougher surfaces |
Choosing the Right Particle Size: The ideal particle size depends on the desired balance between detail, printability, and post-processing requirements. For high-resolution prints with intricate features, fine powders might be preferred despite the printing challenges. Conversely, for applications where strength and rapid printing are priorities, coarser powders could be a better choice.
-
 Ti45Nb Powder for Additive Manufacturing
Ti45Nb Powder for Additive Manufacturing -
 Stainless Steel 316L Powder for Metal 3D Printing
Stainless Steel 316L Powder for Metal 3D Printing -
 TiNb Alloy Powder
TiNb Alloy Powder -
 TiNbZrSn Alloy Powder
TiNbZrSn Alloy Powder -
 Ti6Al4V Powder Titanium Based Metal Powder for Additive Manufacturing
Ti6Al4V Powder Titanium Based Metal Powder for Additive Manufacturing -
 CoCrMoW Powder
CoCrMoW Powder -
 CPTi Powder
CPTi Powder -
 TC18 Powder : Unlocking the Power of Titanium Carbide
TC18 Powder : Unlocking the Power of Titanium Carbide -
 TC11 Powder : A Comprehensive Guide
TC11 Powder : A Comprehensive Guide
Common 3D Metal Powders of Aluminum Alloys
Now that we’ve explored the classification systems, let’s delve into some specific examples of aluminum alloy powders commonly used in 3D printing:
- AA2024: This workhorse AlCu4Mg1 alloy offers a fantastic strength-to-weight ratio, making it ideal for aerospace components, high-performance bicycles, and even robotic arms. However, its lower corrosion resistance necessitates additional surface treatments or post-processing.
- AA6061: A versatile champion, AA6061 (AlMgSi0.5) is known for its excellent workability, corrosion resistance, and ability to be anodised for a decorative finish. This makes it a popular choice for building housings, enclosures, and even decorative art pieces.
- AA7075: When peak strength is the ultimate goal, AA7075 (AlZnMgCu) steps up to the plate. Boasting the highest strength among commonly used aluminum alloys for 3D printing, it’s the go-to material for aerospace applications demanding exceptional structural integrity. The downside? Similar to AA2024, its corrosion resistance is lower.
- AlSi10Mg: Need a good balance of castability, strength, and ductility? AlSi10Mg offers just that. This alloy is a popular choice for automotive components, architectural elements, and even engine blocks.
- AMg6: Magnesium’s lightweight champion, AMg6 shines in applications where minimizing weight is crucial. Think aerospace components and high-performance drones. However, its strength is lower compared to other options on this list.
Beyond the Usual Suspects: While these are some of the most common aluminum alloy powders, the world of 3D printing materials is constantly evolving. Specialty alloys are being developed to meet specific needs, such as:
- AlSi7Mg0.3 (AA7005): This alloy offers a good balance between fluidity, castability, strength, and ductility, making it ideal for various applications.
- AlLi: For aerospace applications demanding extreme lightweight performance, AlLi (Lithium) alloys are making waves. These innovative materials offer significant weight savings compared to traditional aluminum alloys.
Choosing the Right Alloy Powder: The selection process hinges on the desired properties for the final part. Consider factors like:
- Strength: How much stress will the part experience?
- Weight: Is minimizing weight a priority?
- Corrosion Resistance: Will the part be exposed to harsh environments?
- Printability: How critical are surface finish and detail?
- Post-processing requirements: Some alloys might require additional treatments like heat treatment or anodization to achieve the desired properties. Consider the impact on time and cost.
Remember: Material selection is an iterative process. Consulting with a 3D printing expert can be invaluable in choosing the perfect aluminum alloy powder for your specific application.
Aluminum Alloy 3D Metal Powder Specifications, Sizes, Grades, and Standards
Understanding the technical specifications of aluminum alloy powders is crucial for making informed decisions. Here’s a breakdown of key parameters:
- Chemical Composition: The exact percentages of elements like silicon, copper, and magnesium will significantly influence the final properties of the printed part. Refer to industry standards like ASTM International (ASTM) or Aluminum Association (AA) for detailed specifications.
- Particle Size Distribution: As discussed earlier, particle size plays a vital role in printability and final part properties. Most manufacturers provide a particle size distribution chart indicating the range and percentage of particles within different size ranges.
- Powder Flowability: Measured by specific tests, flowability determines how easily the powder moves during the printing process. Good flowability is essential for consistent layer deposition and avoiding printing issues.
- Apparent Density and Tap Density: These values indicate how tightly packed the powder particles are. Apparent density refers to the density of the powder in its loose state, while tap density reflects the density after a standardized tapping process. The difference between these values can indicate the powder’s flow characteristics.
Aluminum Alloy Powder Specifications Table (for illustrative purposes):
| Parameter | Description | Example Value |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition (as per ASTM or AA standard) | AlSi7Mg0.3 (AA7005) | |
| Particle Size Distribution (D10, D50, D90) | Range of particle sizes with corresponding percentages | D10: 15 microns (10% of particles below 15 microns), D50: 45 microns (50% of particles below 45 microns), D90: 75 microns (90% of particles below 75 microns) |
| Flowability (by standardized test method) | Measured in seconds/gram | 25 sec/gram |
| Apparent Density | Density of loose powder | 2.5 g/cm³ |
| Tap Density | Density of powder after tapping | 2.8 g/cm³ |
Note: The example values provided are for illustrative purposes only and may vary depending on the specific aluminum alloy powder. Always refer to the manufacturer’s technical datasheet for accurate specifications.
Suppliers and Pricing of Aluminum Alloy 3D Metal Powders
The landscape of aluminum alloy powder suppliers is vast. Here are some factors to consider when choosing a supplier:
- Material Portfolio: Does the supplier offer the specific aluminum alloy powder you need?
- Powder Quality: Reputation and certifications can indicate the powder’s consistency and adherence to specifications.
- Pricing: Powder prices can vary depending on factors like the specific alloy, particle size, and minimum order quantity.
- Delivery Timelines: Lead times can impact your project schedule. Consider the turnaround time offered by the supplier.
Here’s a (hypothetical) list of some potential suppliers to get you started (replace placeholders with real suppliers after thorough research):
| Supplier | Location | Website (replace with placeholder) |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier A | North America | [Supplier A Website] |
| Supplier B | Europe | [Supplier B Website] |
| Supplier C | Asia | [Supplier C Website] |
Pricing Considerations:
Unfortunately, providing specific pricing details for aluminum alloy powders is challenging due to several factors:
- Market Fluctuations: The cost of raw materials like aluminum can fluctuate, impacting powder prices.
- Minimum Order Quantities: Prices may vary depending on the quantity you purchase. Smaller quantities might come at a premium.
- Custom Requirements: Specific needs like tighter particle size distribution or special handling can influence pricing.
For accurate pricing information, it’s best to contact potential suppliers directly and request a quote based on your specific requirements.
Pros and Cons of Aluminum Alloy 3D Metal Powders
Advantages:
- Excellent Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Aluminum alloys offer a fantastic balance between strength and weight, making them ideal for applications demanding lightweight yet robust parts.
- Good Corrosion Resistance: Many aluminum alloy powders boast inherent corrosion resistance, especially those with high magnesium content.
- High Formability: Aluminum alloys are generally known for their good formability, allowing for complex geometries to be achieved through 3D printing.
- Recyclability: Aluminum is a highly recyclable material, making aluminum alloy powders an eco-friendly choice compared to some other 3D printing materials.
- Wide Range of Alloys: The vast selection of aluminum alloy powders allows for tailoring material properties to specific application needs.
Disadvantages:
- Cost: Compared to some plastics commonly used in 3D printing, aluminum alloy powders can be more expensive.
- Printability Challenges: Aluminum alloy powders can be trickier to print compared to some materials due to factors like flowability and potential oxidation. Optimizing printing parameters might be necessary.
- Post-Processing Requirements: Some aluminum alloys might require additional post-processing steps like heat treatment or surface finishing, adding to production time and cost.
- Limited High-Temperature Performance: While some aluminum alloys offer good heat resistance, they generally don’t perform as well as high-temperature materials like certain steels or nickel alloys.
FAQ
Q: What are the safety precautions for handling aluminum alloy powders?
A: Aluminum alloy powders can be flammable and pose inhalation risks. Always follow the manufacturer’s safety data sheet (SDS) for proper handling procedures. This may include using personal protective equipment like gloves, respirators, and eye protection while working with the powder.
Q: How long can aluminum alloy powders be stored?
A: The shelf life of aluminum alloy powders depends on factors like the specific alloy, storage conditions, and moisture exposure. Generally, storing the powder in a cool, dry, and sealed container can help maximize its shelf life. Refer to the manufacturer’s recommendations for specific storage guidelines.
Q: Can aluminum alloy powders be recycled?
A: Yes, aluminum itself is a highly recyclable material. However, the specific recycling process for used aluminum alloy powders might differ depending on the printing technology and post-processing involved. Consult with your powder supplier or a specialized recycling facility for proper procedures.
Q: What are some emerging trends in aluminum alloy powders for 3D printing?
A: The development of new aluminum alloy powders with improved properties like higher strength, better printability, and enhanced corrosion resistance is an ongoing area of research. Additionally, there’s a growing focus on developing aluminum alloys suitable for multi-material 3D printing, allowing for combining aluminum with other materials in a single printed part.
Conclusion
Aluminum alloy powders are a powerful tool in the 3D printing arsenal. Understanding their classifications, properties, and supplier landscape empowers you to make informed decisions for your next project. By carefully considering factors like desired part properties, printability, and post-processing requirements, you can unlock the full potential of aluminum alloy powders to create innovative and functional 3D printed parts.
Share On
MET3DP Technology Co., LTD is a leading provider of additive manufacturing solutions headquartered in Qingdao, China. Our company specializes in 3D printing equipment and high-performance metal powders for industrial applications.
Inquiry to get best price and customized Solution for your business!
Related Articles
About Met3DP
Recent Update
Our Product
CONTACT US
Any questions? Send us message now! We’ll serve your request with a whole team after receiving your message.

Metal Powders for 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing
COMPANY
PRODUCT
cONTACT INFO
- Qingdao City, Shandong, China
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- +86 19116340731