FGH95 Powder: The Strongest Superalloy for Challenging Conditions
Low MOQ
Provide low minimum order quantity to meet different needs.
OEM & ODM
Provide customized products and design services to meet unique customer needs.
Adequate Stock
Ensure fast order processing and provide reliable and efficient service.
Customer Satisfaction
Provide high quality products with customer satisfaction at the core.
share this article
Table of Contents
In the world of advanced materials, FGH95 powder stands out as a high-performance superalloy powder designed to withstand extreme conditions. Whether you’re working in aerospace, power generation, or industrial turbines, this material is engineered for high-temperature strength, corrosion resistance, and long-term durability.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll take a deep dive into FGH95 powder, exploring its composition, mechanical properties, applications, and industry standards. We’ll break down the benefits of using this material, compare it to alternatives, and provide useful insights into sourcing and pricing. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of whether FGH95 powder is the right material for your project.
Overview of FGH95 Powder
FGH95 powder is a nickel-based superalloy known for its outstanding high-temperature performance and creep resistance. This alloy is designed for applications that require long-term stability under extreme stress, such as jet engines, gas turbines, and nuclear power plants. It belongs to a family of nickel-based superalloys that are used in environments where oxidation resistance and mechanical strength are critical.
The FGH95 powder is typically used in additive manufacturing, powder metallurgy, and thermal spray coatings, allowing for the production of complex parts with high precision and durability. Its ability to maintain mechanical properties at elevated temperatures makes it ideal for critical components that must endure harsh operational conditions.
Key Features
- Outstanding High-Temperature Strength: Performs well in applications above 1,000°C.
- Excellent Creep Resistance: Maintains mechanical integrity under long-term stress.
- Corrosion and Oxidation Resistance: Provides protection in oxidizing environments.
- Versatile Applications: Widely used in aerospace, power generation, and oil & gas industries.
- Compatibility with Additive Manufacturing: Ideal for 3D printing and metal injection molding (MIM).
Composition of FGH95 Powder
The unique properties of FGH95 powder are primarily due to its carefully balanced chemical composition. The powder is made up of a combination of nickel (Ni), chromium (Cr), molybdenum (Mo), cobalt (Co), and other alloying elements that provide creep resistance, oxidation protection, and high-temperature stability.
FGH95 Powder Composition Breakdown
| Element | Percentage (%) | Functional Role |
|---|---|---|
| Nickel (Ni) | 55-65% | Base metal providing high-temperature strength and corrosion resistance. |
| Chromium (Cr) | 15-20% | Enhances oxidation resistance and contributes to overall corrosion resistance. |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | 3-5% | Adds to creep resistance and solid-solution strengthening. |
| Cobalt (Co) | 8-12% | Improves high-temperature strength and contributes to phase stability. |
| Aluminum (Al) | 4-5% | Aids in forming a protective oxide layer for oxidation resistance and strengthens the alloy. |
| Titanium (Ti) | 2-3% | Strengthens the alloy by forming precipitates that resist deformation at high temperatures. |
| Tungsten (W) | 4-6% | Enhances high-temperature performance, particularly creep resistance. |
| Tantalum (Ta) | 0.5-1.5% | Improves oxidation resistance and creep strength. |
The combination of nickel, chromium, molybdenum, and other elements gives FGH95 powder the ability to maintain its mechanical properties in environments where other alloys would fail due to creep, oxidation, or corrosion.
Properties and Characteristics of FGH95 Powder
The performance of FGH95 powder is defined by its mechanical and thermal properties, which make it suitable for high-stress, high-temperature applications. Below, we explore its key properties, including creep strength, oxidation resistance, and thermal expansion.
Key Properties
| Property | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 8.3 g/cm³ | Provides a balance between strength and weight. |
| Melting Point | 1,350°C – 1,380°C | High melting point ensures stability at elevated temperatures. |
| Yield Strength | ~950 MPa at 1,000°C | Exceptional strength even at elevated temperatures. |
| Tensile Strength | ~1,200 MPa | Maintains excellent strength under tensile loads. |
| Creep Strength | Superior at 950°C | Designed to resist deformation under long-term stress at high temperatures. |
| Thermal Expansion | 13 x 10⁻⁶ /°C | Low thermal expansion minimizes the risk of thermal fatigue. |
| Oxidation Resistance | High up to 1,100°C | Retains oxidation resistance in high-temperature environments. |
| Fatigue Life | Long life under cyclic loads | The alloy’s microstructure improves fatigue resistance at elevated temperatures. |
Mechanical Strength and Durability
FGH95 powder is known for its outstanding mechanical properties, particularly in high-temperature environments. Its ability to maintain tensile strength and creep resistance at temperatures above 1,000°C makes it an excellent candidate for aerospace turbine blades and power generation components.
Oxidation Resistance
The high chromium and aluminum content in FGH95 forms a protective oxide layer that prevents oxidation at elevated temperatures. This feature is crucial for applications in gas turbines or jet engines, where exposure to oxygen-rich environments at high temperatures can degrade materials over time.
Applications of FGH95 Powder
Thanks to its exceptional high-temperature stability, FGH95 powder has found its way into several critical industries. Its ability to maintain strength and resist creep deformation at elevated temperatures makes it ideal for gas turbines, jet engines, and other high-stress applications.
FGH95 Powder Applications by Industry
| Industry | Application | Why FGH95 is Used |
|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Turbine blades, jet engine components | High creep resistance and oxidation resistance at high temperatures. |
| Power Generation | Gas turbine components, steam turbines | Long-term performance in high thermal stress environments. |
| Oil & Gas | Downhole tools, valves, pumps | Excellent corrosion resistance in harsh chemical environments. |
| Automotive | Turbocharger components, exhaust systems | Ability to withstand extreme heat and mechanical stress. |
| Industrial | High-temperature furnace components, heat shields | Durability and thermal stability under continuous high-heat operation. |
Aerospace Industry
The aerospace industry is one of the largest consumers of FGH95 powder. The material is commonly used in manufacturing turbine blades and jet engine components that must endure extreme temperatures and cyclic stress. These components operate in environments where oxidation and creep can lead to material failure, making FGH95 an ideal choice due to its superior high-temperature performance.
Power Generation
In power generation, FGH95 powder is used in gas turbines and steam turbines, where components are exposed to high thermal loads over extended periods. The material’s creep resistance ensures that turbine components maintain their shape and function, even under continuous stress at elevated temperatures.
Specifications, Sizes, and Standards for FGH95 Powder
To ensure that FGH95 powder meets the needs of various industries, it must adhere to specific standards and specifications. This section covers the common specifications and sizes available on the market for FGH95 powder.
Common Specifications and Available Sizes
| Specification/Standard | Description |
|---|---|
| ASTM F75 | Standard specification for nickel-based superalloys used in high-temperature applications. |
| ISO 9001 | Certification ensuring quality management in the production of metal powders. |
| Particle Size | Available in 15 to 150 microns, depending on the intended application. |
| Purity | Typically 99.5% or higher, ensuring minimal impurities for critical applications. |
| Form | Available as powder, bars, billets, sheets, and wires. |
Available Grades and Forms
| Grade | Application |
|---|---|
| FGH95 Standard | Ideal for aerospace and power generation applications. |
| FGH95 Fine Powder | Optimized for additive manufacturing and 3D printing applications. |
| FGH95 Coarse Powder | Primarily used in thermal spraying and coatings for wear resistance. |
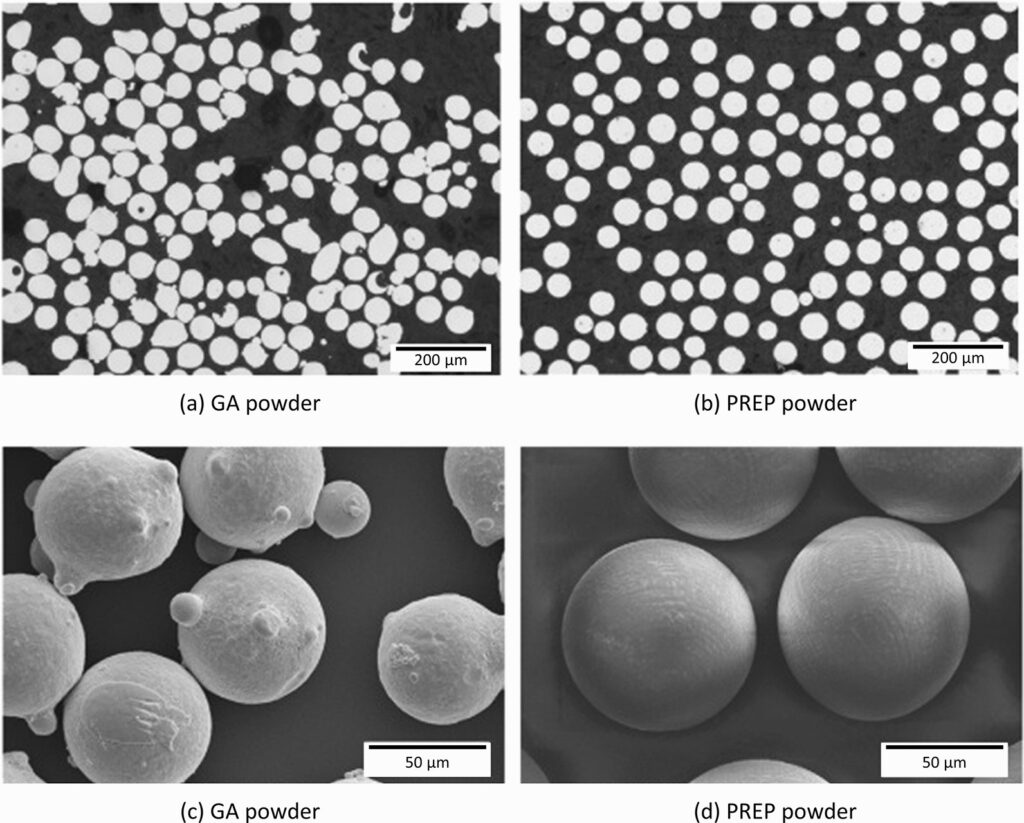
The particle size of FGH95 powder is an important consideration, depending on the manufacturing process used. Fine powders (15-45 microns) are typically used in additive manufacturing and metal injection molding, while coarser powders (75-150 microns) are more suitable for thermal spraying and coatings.
Suppliers and Pricing of FGH95 Powder
There are multiple suppliers of FGH95 powder globally, each offering various grades, particle sizes, and purity levels. The pricing of FGH95 powder can vary depending on several factors, such as purity, grade, and supplier reputation.
Top Suppliers and Price Range
| Supplier | Price Range (per kg) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Höganäs AB | $700 – $1,100 | Specializes in high-quality metal powders for additive manufacturing. |
| Sandvik Materials Technology | $750 – $1,150 | Known for precise particle sizing for 3D printing and thermal spraying. |
| Carpenter Technology | $800 – $1,200 | Provides high-performance superalloys for aerospace and power generation. |
| ATI Metals | $850 – $1,300 | Leading supplier of nickel-based superalloys for gas turbines. |
| Kennametal Stellite | $700 – $1,100 | Offers wear-resistant alloys and powders for industrial coatings. |
Factors Influencing the Cost
Several factors can affect the price of FGH95 powder, including:
- Grade: Higher performance grades with tighter specifications tend to be more expensive.
- Purity: Powders with higher purity levels, particularly for aerospace or medical applications, cost more.
- Particle Size: Finer powders used for 3D printing or additive manufacturing are priced higher than coarser powders.
- Supplier Reputation: Established suppliers with strong quality control and reliability often charge a premium.
Advantages and Limitations of FGH95 Powder
Like any other material, FGH95 powder has its advantages and drawbacks. Understanding these will help you decide if this superalloy fits your project’s requirements.
Advantages
| Advantage | Why It’s Important |
|---|---|
| High Creep Resistance | Ideal for long-term use in high-stress environments without deformation. |
| Excellent Oxidation Resistance | Performs well in oxidizing environments up to 1,100°C. |
| High-Temperature Stability | Maintains strength and corrosion resistance at temperatures exceeding 1,000°C. |
| Versatile Applications | Suitable for use in aerospace, power generation, oil & gas, and industrial sectors. |
Limitations
| Limitation | Why It’s a Concern |
|---|---|
| High Cost | Higher cost compared to traditional alloys like stainless steel or Inconel. |
| Processing Complexity | Requires specialized heat treatments and manufacturing processes to unlock its full potential. |
| Limited Availability | Fewer suppliers compared to more common alloys, which can lead to longer lead times. |
FGH95 Powder vs Other Nickel-Based Superalloys
When comparing FGH95 powder to other nickel-based alloys, such as Inconel 718 or Hastelloy X, it’s important to look at factors like temperature resistance, creep strength, and cost-effectiveness.
Comparing FGH95 Powder to Other Nickel-Based Alloys
| Alloy | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|
| FGH95 | Exceptional creep resistance, high-temperature strength, and oxidation resistance. | Higher cost and complex processing requirements. |
| Inconel 718 | Excellent corrosion resistance and reasonable cost. | Lower creep resistance compared to FGH95. |
| Hastelloy X | Superior oxidation resistance and weldability. | Lower high-temperature strength and creep resistance. |
FGH95 powder offers the best creep resistance and high-temperature performance compared to other nickel-based alloys, but it also comes at a higher cost due to its advanced properties.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is FGH95 powder used for? | It is used in aerospace, power generation, and oil & gas industries for critical components that require high-temperature strength and creep resistance. |
| How much does FGH95 powder cost? | The price of FGH95 powder typically ranges from $700 to $1,300 per kg, depending on factors like purity and particle size. |
| Can FGH95 powder be used in 3D printing? | Yes, FGH95 powder is widely used in additive manufacturing and metal injection molding (MIM) to create complex, high-strength parts. |
| What industries commonly use FGH95 powder? | FGH95 powder is commonly used in aerospace, power generation, oil & gas, and industrial sectors. |
| Is FGH95 powder suitable for thermal spraying? | Yes, FGH95 powder is excellent for thermal spraying applications where wear resistance and high-temperature stability are required. |
| How does FGH95 compare to Inconel? | FGH95 offers better creep resistance and high-temperature strength than Inconel, but it is also more expensive and requires more complex processing. |
Conclusion: Is FGH95 Powder the Right Material for Your Application?
In summary, FGH95 powder is one of the most advanced nickel-based superalloys in the industry, offering exceptional performance in high-temperature, high-stress environments. Its creep resistance, oxidation resistance, and thermal stability make it an ideal choice for components in aerospace, power generation, and oil & gas applications.
However, it’s important to weigh the cost and complexity of processing against the performance benefits. While FGH95 powder outperforms many other alloys, it may not always be the most cost-effective solution for every project, especially when budget constraints or lead times are a concern.
If your application demands high-temperature strength, long-term durability, and the ability to withstand extreme stress, FGH95 powder is an excellent material choice.
Get Latest Price
About Met3DP
Product Category
HOT SALE
CONTACT US
Any questions? Send us message now! We’ll serve your request with a whole team after receiving your message.

Metal Powders for 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing
COMPANY
PRODUCT
cONTACT INFO
- Qingdao City, Shandong, China
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- +86 19116340731








