Molybdenum Powder: Discover Its Powerful Role in Modern Technology
Low MOQ
Provide low minimum order quantity to meet different needs.
OEM & ODM
Provide customized products and design services to meet unique customer needs.
Adequate Stock
Ensure fast order processing and provide reliable and efficient service.
Customer Satisfaction
Provide high quality products with customer satisfaction at the core.
share this article
Table of Contents
Molybdenum powder might not be the first material that comes to mind when thinking of industrial applications, but it’s one of the most critical elements in industries ranging from aerospace to electronics. Known for its high melting point, strength, and corrosion resistance, molybdenum powder has become an indispensable part of modern technology.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore molybdenum powder from every angle. Whether you’re a material scientist, an engineer, or someone simply curious about this fascinating material, this article will provide a deep dive into molybdenum powder’s properties, applications, and advantages.
Overview
What is Molybdenum Powder?
Molybdenum powder is a fine, grayish-black powder produced from molybdenum ores or scrap through a multi-step process. The powder is widely used in industries that require materials with high-temperature stability, strength, and resistance to corrosion. Because molybdenum has one of the highest melting points of all elements (around 2,623°C or 4,753°F), it’s often used in applications where other metals would fail.
Imagine a material that can withstand intense heat, pressure, and even corrosive environments. That’s molybdenum powder in a nutshell. From high-performance alloys to electrical contacts, this powder turns up in some of the most demanding environments on Earth.
Composition and Properties
Molybdenum powder’s impressive properties stem from its unique chemical composition and structure. Below, we’ve outlined the key characteristics that give molybdenum powder its strength and versatility.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Chemical Symbol | Mo |
| Atomic Number | 42 |
| Melting Point | 2,623°C (4,753°F) |
| Density | 10.28 g/cm³ |
| Thermal Conductivity | 138 W/m·K (at 20°C) |
| Electrical Conductivity | 1.87 x 10⁶ S/m (at 20°C) |
| Young’s Modulus | 324 GPa |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent in most acidic and basic environments, especially at high temperatures |
| Oxidation Resistance | Oxidizes above 600°C, requiring protective coatings or alloying for higher-temperature applications |
| Tensile Strength | 550 MPa (at room temperature) |
| Recrystallization Temperature | Approximately 1,100°C |
Key Characteristics
- High-Temperature Stability: Molybdenum powder doesn’t lose its strength or structural integrity, even at temperatures that would melt steel.
- Exceptional Corrosion Resistance: It can resist corrosion in highly acidic and basic environments, making it ideal for chemical processing equipment.
- Electrical and Thermal Conductivity: Molybdenum has excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, which makes it a popular choice for electrical contacts and heat sinks.
- Hardness and Strength: Despite being lightweight compared to other metals with similar properties, molybdenum powder exhibits impressive tensile strength.
These properties make molybdenum powder an all-around workhorse in environments where other materials would falter.
Types of Molybdenum Powder Based on Composition and Properties
Molybdenum powder comes in several different types, depending on its purity, grain size, and intended use. Each type offers a slightly different set of characteristics, making it suitable for specific applications.
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| High-Purity Molybdenum Powder | Contains over 99.95% molybdenum, used in high-performance applications such as semiconductors and high-temperature alloys. |
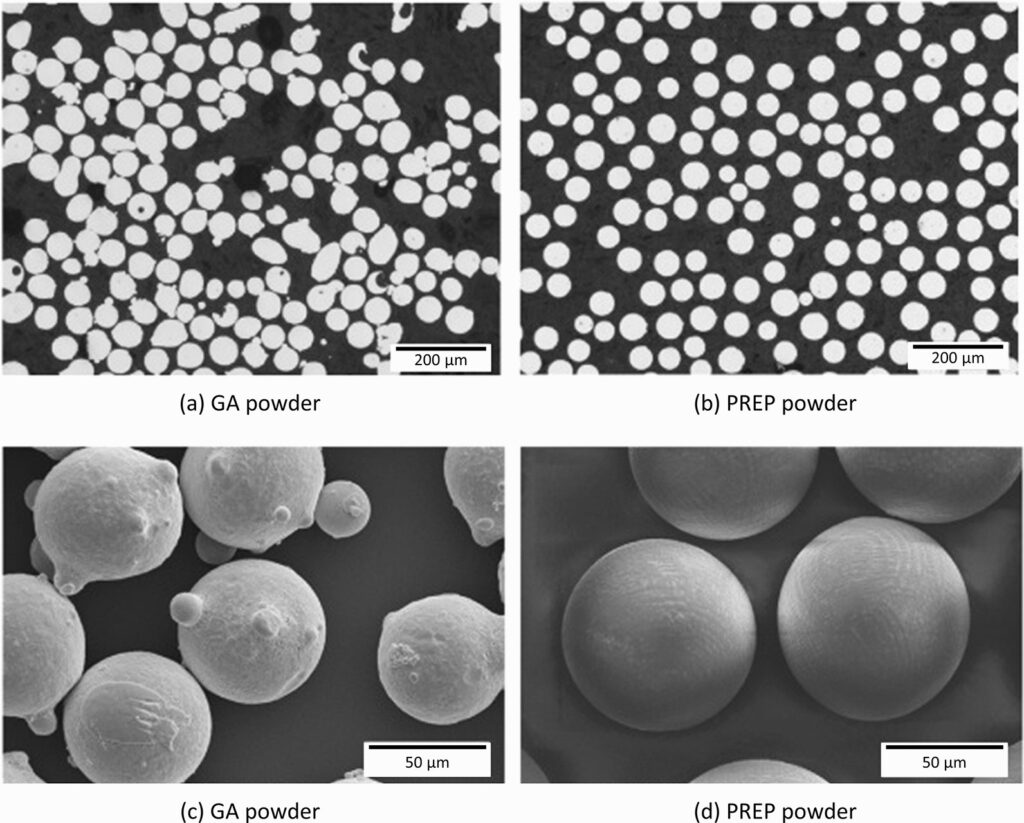
| Spherical Molybdenum Powder | Manufactured into spherical shapes for additive manufacturing, thermal spraying, and powder metallurgy applications. |
| Nano-Molybdenum Powder | Extremely fine particles (measured in nanometers) used in catalysts, batteries, and advanced electronics. |
| Alloyed Molybdenum Powder | Molybdenum mixed with other metals like tungsten or copper to enhance specific properties like oxidation resistance. |
| Molybdenum Disulfide Powder (MoS₂) | A compound of molybdenum and sulfur, widely used as a lubricant due to its low friction and high-temperature stability. |
Each type of molybdenum powder has specialized properties that make it suitable for certain applications. For example, spherical molybdenum powder performs well in thermal spraying because its shape allows for better flow and coating uniformity, while nano-molybdenum powder is prized for its reactivity and potential in cutting-edge technologies like energy storage.
Applications
Molybdenum powder’s versatility means it’s used across a wide range of industries, from high-tech electronics to heavy-duty industrial applications. Below, we look at some of its most common uses.
| Industry | Application |
|---|---|
| Aerospace | Used in high-temperature alloys, rocket engine components, and heat shields due to its ability to withstand extreme temperatures. |
| Electronics | Molybdenum is a key material in semiconductors, transistors, and thin-film transistors for displays (like OLEDs and LCDs). |
| Energy | Found in solar panels, nuclear reactors, and power generation turbines, where high-temperature performance is critical. |
| Metalworking | Used in steel alloys to improve hardness, toughness, and corrosion resistance. Molybdenum powder is also used in powder metallurgy to produce parts with high strength. |
| Chemical Processing | Molybdenum’s corrosion resistance makes it ideal for chemical processing equipment, such as reaction vessels, pipelines, and pumps exposed to acidic or basic environments. |
| Automotive | Used in catalytic converters, engine components, and electrical contacts in vehicles, where heat and wear resistance are necessary. |
| Medical | In the production of medical imaging equipment and x-ray tubes, molybdenum is used due to its ability to absorb x-rays without degrading. |
| Lubrication | Molybdenum disulfide (MoS₂) is widely used as a solid lubricant in environments where traditional liquid lubricants would break down, such as in high-temperature machinery. |
Molybdenum Powder in Aerospace
In the aerospace industry, molybdenum powder is essential for creating high-temperature alloys used in rocket engines and spacecraft components. These components must endure temperatures that would melt most other metals, making molybdenum’s high melting point and strength critical for success. Molybdenum alloys are also used in heat shields to protect spacecraft from the intense heat experienced during reentry into the Earth’s atmosphere.
Molybdenum Powder in Electronics
Molybdenum powder is a key material in the production of semiconductors and transistors, which are the building blocks of modern electronics. Thanks to its high electrical conductivity and thermal stability, molybdenum is used in thin-film transistors in devices like OLED displays, LCD screens, and solar cells. Molybdenum’s ability to conduct electricity without degrading under high temperatures makes it indispensable in these high-tech applications.
Molybdenum Disulfide as a Lubricant
One of the most common applications of molybdenum in powder form is as molybdenum disulfide (MoS₂), a widely used solid lubricant. This powder reduces friction in machinery and equipment, especially in situations where traditional liquid lubricants would fail—like in high-temperature or high-vacuum environments. MoS₂ is commonly used in automotive engines, industrial machinery, and even military applications.
Specifications, Sizes, Grades, and Standards
Choosing the right molybdenum powder for a specific application requires understanding the available specifications, sizes, and grades. These factors can significantly impact performance, depending on the environment and stresses the material will face.
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Particle Sizes | Available in various sizes, ranging from nano-powders (as small as 100 nm) to coarse powders (up to 100 µm). |
| Purity Grades | Ranges from 99.9% purity for high-performance applications to 98% for less demanding industrial uses. |
| Density | Typically 10.28 g/cm³, though it can vary slightly depending on grain size and alloying elements. |
| Hardness (Vickers Scale) | Ranges from 250 to 350 HV, depending on the alloy and processing method. |
| ISO Standards | Certified to meet ISO 9001 for quality management and ISO 4499 for powder metallurgy. |
| ASTM Standards | Conforms to ASTM B386 for molybdenum products and ASTM F2891 for powder metallurgy components. |
Choosing the Right Grade
When selecting molybdenum powder for your project, it’s essential to consider the grade. High-purity molybdenum powder (99.95%) is often required for semiconductors and high-temperature applications, while lower-purity grades are suitable for bulk material in less demanding environments.
Suppliers and Pricing
If you’re in the market for molybdenum powder, there are several factors to consider, including supplier reputation, product quality, and pricing. Prices can vary significantly based on the purity, particle size, and quantity you purchase.
| Supplier | Country | Price Per Kg (USD) | Purity Grades | Special Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H.C. Starck | Germany | $150 – $300 | 99.9% – 99.95% | High-purity molybdenum for electronics and aerospace applications. |
| Kennametal | United States | $200 – $400 | 99.5% – 99.95% | Specializes in powder metallurgy and thermal spraying molybdenum powders. |
| Plansee | Austria | $180 – $350 | 99.9% – 99.95% | Offers molybdenum for semiconductors and high-performance alloys. |
| Luoyang Tongrun Nanotech | China | $100 – $250 | 99.0% – 99.9% | Specializes in nano-molybdenum powders for advanced electronics. |
| American Elements | United States | $120 – $280 | 98% – 99.95% | Offers a wide range of particle sizes, including nano-powders. |
| MolyWorks Materials | United States | $130 – $320 | 99.5% – 99.95% | Focuses on recycled molybdenum powders for sustainable manufacturing. |
Factors Influencing Molybdenum Powder Prices
Several factors influence the price of molybdenum powder, including:
- Purity: Higher-purity molybdenum powder commands a higher price due to the more complex refining processes required.
- Particle Size: Nano-sized molybdenum powder is more expensive than coarser powders because of the additional processing involved.
- Supplier Location: Prices can also vary based on the supplier’s location, with Chinese suppliers often offering lower prices due to lower production costs.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Like any material, molybdenum powder comes with its advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these can help you decide whether it’s the right choice for your application.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| High-Temperature Strength: Maintains strength and structure at extreme temperatures. | Oxidation: Molybdenum oxidizes at high temperatures, requiring protective coatings. |
| Excellent Corrosion Resistance: Withstands acidic and basic environments. | Cost:It is more expensive than other metals like steel or aluminum. |
| Electrical and Thermal Conductivity: Ideal for electronics and heat sinks. | Machinability: Molybdenum can be difficult to machine due to its hardness. |
| Lightweight: Lighter than many high-performance metals like tungsten. | Availability: High-purity molybdenum powders can have long lead times. |
Molybdenum Powder vs. Tungsten
When compared to tungsten, it offers better machinability and is lighter in weight. However, tungsten has a higher melting point, making it more suitable for extremely high-temperature applications such as filaments in light bulbs or radiation shielding. Molybdenum is often the better choice when weight and cost are key factors, while tungsten is favored for applications requiring extreme temperature resistance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
To help clarify some common questions about molybdenum powder, we’ve compiled a list of frequently asked questions below.
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is it used for? | It is used in industries like aerospace, electronics, energy, and metalworking for high-temperature and corrosion-resistant applications. |
| How is it made? | It is produced through a process called powder metallurgy, where molybdenum ore or scrap is reduced and refined into a powder. |
| Can it be recycled? | Yes, it can be recycled, especially in industries focused on sustainability and reducing material waste. |
| What’s the difference between molybdenum and molybdenum disulfide? | It (MoS₂) is a compound used as a lubricant, while pure molybdenum powder is used for structural and high-temperature applications. |
| Is it safe to handle? | It is generally safe to handle, but inhalation of fine particles should be avoided. It’s recommended to use protective equipment when working with it. |
| Why is it expensive? | The cost of molybdenum powder is due to the complexity of refining molybdenum ore and the high demand for its unique properties in advanced industrial applications. |
| How do you choose the right grade of it? | The right grade depends on your application. For electronics, choose high-purity molybdenum; for metalworking, a lower-purity grade may suffice. |
Conclusion
It is more than just a niche material—it’s a critical component in some of the world’s most advanced technologies. Whether you’re looking to strengthen a high-temperature alloy, build a semiconductor, or create a heat-resistant coating, it offers a solution that combines strength, corrosion resistance, and thermal stability. While it may come with a higher price tag than other materials, its performance in extreme environments often makes it well worth the investment.
From aerospace to electronics, molybdenum powder is quietly powering some of the most innovative industries on the planet. So, is molybdenum powder the right choice for your next project? If you need a material that can stand up to heat, corrosion, and wear without breaking down, the answer is almost certainly “yes.”
Get Latest Price
About Met3DP
Product Category
HOT SALE
CONTACT US
Any questions? Send us message now! We’ll serve your request with a whole team after receiving your message.

Metal Powders for 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing
COMPANY
PRODUCT
cONTACT INFO
- Qingdao City, Shandong, China
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- +86 19116340731








