Nickel Alloy Powders
Table of Contents
Nickel alloys refer to a broad range of heat and corrosion resistant materials where nickel constitutes over 40% of the composition. This guide provides an overview of various nickel alloy powder types, manufacturing methods, key applications, specifications, pricing, comparisons, and frequently asked questions for procurement.
Compositions of Nickel Alloy Powder
| Alloy Family | Major Alloying Elements | Common Grades |
|---|---|---|
| Superalloys | Cr, Co, Mo, Ti, Al | Inconel 718, 625, Haynes 282 |
| High temp alloys | Cr, Mo, W | Haynes 230, 188, HR-120 |
| Corrosion resistant | Cr, Mo | Alloy C-276, 20Cb-3, G-35-1 |
| Electrical / Electronic | Fe, Cu, Cr | Alloy 42, Kovar |
| Shape memory | Ti, Hf | Nitinol (NiTi) |
Various alloying elements like chromium, cobalt, iron, copper etc. added to tune mechanical properties, improve fabrication, and enhance corrosion and wear resistance.
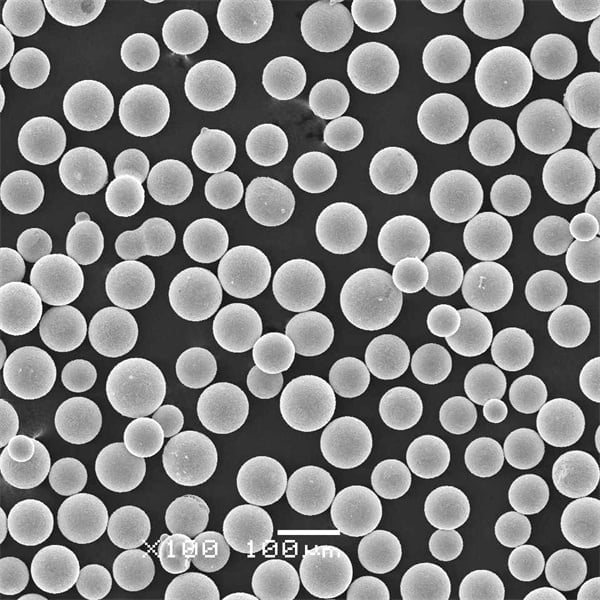
Key Characteristics and Powder Properties
| Attribute | Typical Values |
|---|---|
| Particle shape | Spherical |
| Size range | 10 – 150 microns |
| Oxygen ppm | Below 500 ppm |
| Hall flow rate | Around 25 secs for 50g |
| Apparent density | 2 – 5 g/cc |
| Surface oxide | Thin passivated chromia film |
Particle characteristics tailored to suit production method – additive manufacturing needs spherical powders below 100 microns whereas cold spray better with larger particles.
Production Methods for Nickel Alloy Powder
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Gas Atomization | Inert gas disintegrates molten metal into droplet powder |
| Water Atomization | High pressure water breaks up melt stream |
| Plasma Atomization | Very clean, small production volumes |
| Carbonyl Process | Chemical precipitation from nickel carbonyl |
Gas atomization best suited for reactive alloys like superalloys, titanium etc. Water atomization more economical for high volumes above 30 microns. Plasma atomization and carbonyl route produce specialty powders.
Applications of Nickel Alloy Powder
| Industry | Common Components |
|---|---|
| Aerospace | Turbine blades, discs, transitions |
| Oil & Gas | Wellhead equipment, valves, fasteners |
| Automotive | Exhaust system parts, fuel cells |
| Chemical Process | Heat exchangers, reaction vessels |
| Medical | Implants, surgical tools |
| Additive Manufacturing | Bi-metal parts, lattices, topology optimized designs |
Nickel alloys serve critical applications needing combination of high strength and corrosion resistance at elevated temperatures.
Specifications for Nickel Alloy Powder
| Standard | Description |
|---|---|
| ASTM B162 | Nickel plating grade specifications |
| ASTM B214 | Porous nickel strip |
| ASTM B351 | Wrought superalloy product forms |
| ASTM B777 | Powder metallurgy (PM) nickel alloys |
No universal powder specifications exist. Application and intended production method instead determines acceptance norms.
-
 Ti45Nb Powder for Additive Manufacturing
Ti45Nb Powder for Additive Manufacturing -
 TiNb Alloy Powder
TiNb Alloy Powder -
 TiNbZrSn Alloy Powder
TiNbZrSn Alloy Powder -
 Ti6Al4V Powder Titanium Based Metal Powder for Additive Manufacturing
Ti6Al4V Powder Titanium Based Metal Powder for Additive Manufacturing -
 CPTi Powder
CPTi Powder -
 TC18 Powder : Unlocking the Power of Titanium Carbide
TC18 Powder : Unlocking the Power of Titanium Carbide -
 TC11 Powder : A Comprehensive Guide
TC11 Powder : A Comprehensive Guide -
 TC4 ELI Powder
TC4 ELI Powder -
 Best Ti-6Al-4V powder (TC4 Powder)for additive manufacturing
Best Ti-6Al-4V powder (TC4 Powder)for additive manufacturing
Nickel Alloy Powder Suppliers and Pricing
| Vendor | Lead time | Price Range ($/kg) |
|---|---|---|
| Sandvik Osprey | 10-16 weeks | $25 – $500 |
| Atlantic Equipment | 12-18 weeks | $30 – $450 |
| TLS Technik | 16-20 weeks | $35 – $480 |
Pricing varies widely depending on alloy composition, powder quantity, size range and quality level specified.
Pros and Cons of Nickel Alloy Powder
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| High strength at elevated temps | Expensive alloy raw materials |
| Withstand harsh environments | Limited suppliers and availability |
| Custom alloys for tailored properties | Strict quality procedures to ensure purity |
| Flexible production methods | Safety hazards with fine metal powders |
| Complex shapes from AM technology | Post processing often essential after AM builds |
Nickel alloy powders enable fabrication of high performance components but require significant expertise to manufacture and handle safely.

FAQ
What is the difference between superalloys, high temp alloys and stainless alloys?
Superalloys have highest strength thanks to gamma prime precipitate strengthening. High temp alloys beat oxidation. Stainless alloys focus on corrosion resistance.
What particle size range works best for binder jet printing?
Around 20 to 50 microns needed for binding process. Too fine powders inhibit liquid saturation and binder spread. Ensure narrow distribution for packing density.
What causes contamination during atomization?
Oxygen pickup from air leads to oxide inclusions. Minor element loss by vaporization possible. Other sources are tundish liners, melt crucibles. Use high purity inert gas and starting materials.
Why is gas atomized powder preferred over water atomized?
Water atomization leads to oxygen pickup degrading powder quality. Cooling rates slower leading to carbide networks which lower corrosion resistance. Avoid for reactive alloys.
What are common defects when printing nickel alloys?
Lack of fusion defects due to poor energy density. Residual stress cracking. Powder trapped inside enclosed volumes. Porosity from gas entrapment. Require integrated solution development.
Conclusion
Nickel alloy powders provide extreme environments capability essential in critical applications, with customized compositions and particle properties available through specialized manufacturing processes. Careful specification and testing ensures suitability for production methods like additive manufacturing, thermal spray, or powder injection molding.
Share On
MET3DP Technology Co., LTD is a leading provider of additive manufacturing solutions headquartered in Qingdao, China. Our company specializes in 3D printing equipment and high-performance metal powders for industrial applications.
Inquiry to get best price and customized Solution for your business!
Related Articles
About Met3DP
Recent Update
Our Product
CONTACT US
Any questions? Send us message now! We’ll serve your request with a whole team after receiving your message.

Metal Powders for 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing
COMPANY
PRODUCT
cONTACT INFO
- Qingdao City, Shandong, China
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- +86 19116340731
















