Copper C11000 Powder
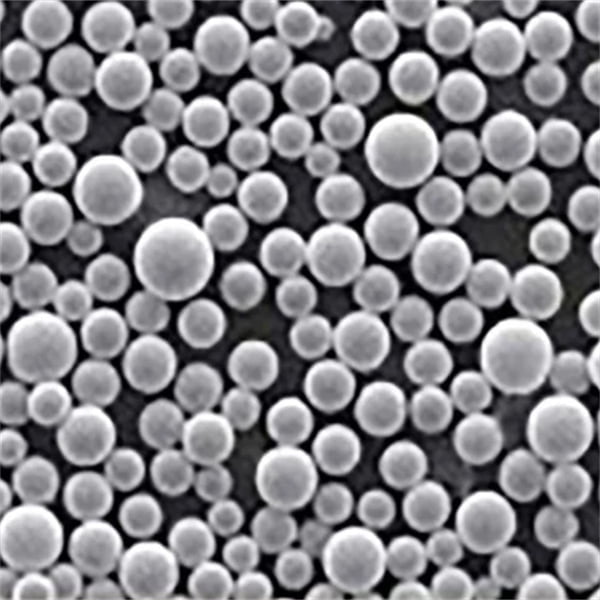
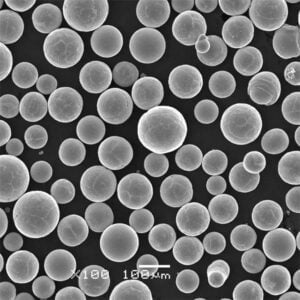
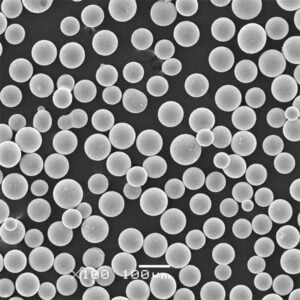
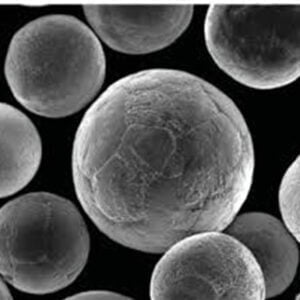
Copper C11000 powder, also known as electrolytic tough pitch (ETP) copper powder, is a high purity copper powder produced through electrolytic processes. It has a minimum copper content of 99.9% and is known for its combination of purity, outstanding electrical and thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance, and workability.
Low MOQ
Provide low minimum order quantity to meet different needs.
OEM & ODM
Provide customized products and design services to meet unique customer needs.
Adequate Stock
Ensure fast order processing and provide reliable and efficient service.
Customer Satisfaction
Provide high quality products with customer satisfaction at the core.
share this product
Table of Contents
Overview
Copper C11000 powder, also known as electrolytic tough pitch (ETP) copper powder, is a high purity copper powder produced through electrolytic processes. It has a minimum copper content of 99.9% and is known for its combination of purity, outstanding electrical and thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance, and workability.
Some key properties and characteristics of Copper C11000 powder include:
Copper C11000 Powder Properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Composition | 99.9% minimum copper content |
| Particle Shape | Spherical, spongy, or dendritic |
| Particle Size | From under 10 microns to over 150 microns |
| Apparent Density | Around or above 4 g/cm3 |
| Tap Density | Up to 5.5 g/cm3 |
| Purity | 99.9% Cu minimum, low oxygen and trace metals |
| Conductivity | High electrical and thermal conductivity |
Copper C11000 powder owes its properties to its purity and production process which creates a porous structure with high surface area ideal for applications like brazing, welding, friction materials, additive manufacturing, and more.
The base metal properties combined with controllable particle size distribution, morphology, apparent density, and flow characteristics allow the powder to be tailored to specific uses across industries.
Applications and Uses
Copper C11000 powder’s unique combination of purity, conductivity, and workability make it suitable for the following applications:
Major Applications of Copper C11000 Powder
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Brazing and Soldering | Used to join metals through capillary action of filler metal |
| Friction Materials | Blended with resins/fibers to create brake pads, clutch discs |
| Welding | Added to improve weldability of steel, aluminum, and other alloys |
| Additive Manufacturing | Used in bound metal deposition, selective laser melting, etc. |
| EMI Shielding | Blended into polymers, coatings to block electromagnetic interference |
| Copper Infiltration | Impregnated into porous metal parts to enhance properties |
| Diamond Tools | Added to metal matrix of diamond cutting tools |
| Other | Conductive adhesives, inks, greases, cosmetics, pyrotechnics |
The high purity, spherical morphology, and electrical conductivity of the powder enable excellent performance across this wide range of uses when blended with other metals, alloys, polymers, and base materials.
Specifications and Grades
Copper C11000 powder is available in various particle size distributions categorized as granules and powders. Common size ranges include:
Copper C11000 Powder Sizes
| Size Classification | Mesh Size | Micron Size |
|---|---|---|
| Coarse Granules | 8 – 50 mesh | 2000 – 300 microns |
| Medium Granules | 50 – 140 mesh | 300 – 100 microns |
| Fine Granules | 140 – 325 mesh | 100 – 40 microns |
| Coarse Powder | 325 – 500 mesh | 40 – 20 microns |
| Fine Powder | -500 mesh | Under 20 microns |
Additionally, the powder can be segmented into classification grades which determine characteristics like purity, oxide levels, particle morphology, and more.
Popular standard grades of copper C11000 powder include:
- Grade 1 – High purity, low oxide
- Grade 2 – General purpose grade with good purity
- Grade 3 – Industrial grade with higher oxide levels
The grade chosen depends on application requirements and powder properties needed. Custom particle sizes and property optimization is also possible through toll processing.
Manufacturing Process
The predominant production method for Copper C11000 powder is through electrolytic reduction and refining of copper. The process involves:
- Dissolution of copper anodes into electrolytes like copper sulfate
- Electrolytic plating of 99.9% pure copper onto cathodes
- Removal and processing of powder deposit through crushing, grinding, and sieving
Additional steps like deoxidation, annealing, screening, and blending are used to achieve target powder characteristics. High productivity, purity, and flexibility make electrolytic copper powder ideal for industry applications.
Alternative methods like atomization of molten copper can also produce Copper C11000 powder but are less common.
Suppliers and Pricing
As a widely used industrial material, Copper C11000 powder is available from metal powder suppliers and specialty chemical distributors globally. Pricing varies based on:
- Particle size
- Packing format (bulk bags, drums, cans, etc.)
- Quantity and lot size
- Grade and purity levels
- Chemistry conformity certifications
Indicative pricing for Copper C11000 powder in US$ per kg:
Copper Powder Pricing
| Grade | 20 mesh | 150 mesh | -325 mesh |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grade 1 | $12-15 | $15-18 | $18-22 |
| Grade 2 | $10-13 | $13-16 | $15-19 |
| Grade 3 | $8-12 | $11-14 | $13-17 |
Custom toll processing services for special particle sizes, morphology, and property enhancement are also available at premiums to base pricing.
Comparison With Alternatives
Key differences of Copper C11000 powder versus potential alternatives:
VS Brass and Bronze Powders
- Higher purity and conductivity
- Lower cost than many copper alloys
- Less prone to dezincification
VS Other Copper Powders
- More economical than CuOFE, CuFHC powders
- Higher conductivity than atomized/reduced copper powder
- Lower oxygen and impurities than Cu powder from scrap
VS Silver Powder
- Significantly lower cost
- Oxidation and migration resistance weaker than silver
- Thermal/electrical conductivity slightly below silver
VS Aluminum Powder
- Higher density and melting point
- Superior conductivity but more expensive
- Slower oxidation kinetics in reactive environments
So while other powder options exist, Copper C11000 offers the best balance of purity, performance, availability, and cost for most industrial uses.
Advantages and Limitations
Advantages
- High purity and copper content
- Excellent conductivity and corrosion resistance
- Good workability and manufacturing flexibility
- Cost advantage over alloys/noble metals
- Readily available from variety of suppliers
Limitations
- Surface oxidation under heat or long storage
- Limited high temperature properties vs alloys
- Lower strength-to-weight ratio than aluminum
- Not biocompatible for medical devices
- Heavy weight increases shipping costs
Proper handling as well as protective coatings/atmospheres help mitigate limitations while retaining beneficial powder characteristics.
Standards and Compliance
Globally accepted standards for electrolytic copper powder’s chemistry specifications include:
- ASTM B602 – Standard Specification for Copper Powder and Flakes
- EN 13601 – Copper and copper alloys – Copper powder
- GB/T 467 – Copper and Copper Alloy Powder
These standards regulate critical elements like particle size distribution, apparent density, purity levels, loss on ignition limits, sieve residue percentages, and more.
Reputable copper powder suppliers test and certify to such standards while also supporting additional customer requirements as needed through internal QA/QC practices. Compliance certifications like ISO 9001 demonstrate systemic quality assurance across production and supply chains.
FAQs
Q: Does Copper C11000 powder oxidize rapidly in air?
A: Yes, copper powder can slowly oxidize during exposure to ambient conditions. The fine particle size and porous structure leads to growing oxide scale. Proper sealed storage with oxygen absorbers is recommended for preventing extensive oxidation over long durations.
Q: Can this powder be mixed with polymers like nylon?
A: Copper C11000 powder can be blended into various plastics through techniques like melt-mixing or twin screw extrusion compounding. Addition levels up to 70% by weight are possible for some engineered plastics, allowing EMI shielding or thermal conductivity benefits while retaining mechanical properties.
Q: What is the bulk density range of copper C11000 powder?
A: In loose poured form, apparent densities from around 2.5 – 4 g/cm3 are common. Under compaction/vibration the tap density can go up to 5 – 5.5 g/cm3. Particle size distribution and morphology governs density ranges. Fine powders tend to have lower densities.
Q: Does welding with Copper C11000 powder increase joint strength?
A: Yes, adding pure copper powder to steel/aluminum welds through processes like cold metal transfer welding and laser cladding improves mechanical properties. This is achieved by bonding base metals with the high purity copper particles through dissolution and re-deposition.
Get Latest Price
About Met3DP
Product Category
HOT SALE
CONTACT US
Any questions? Send us message now! We’ll serve your request with a whole team after receiving your message.

Metal Powders for 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing
COMPANY
PRODUCT
cONTACT INFO
- Qingdao City, Shandong, China
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- +86 19116340731