Maraging Steel 350 Powder
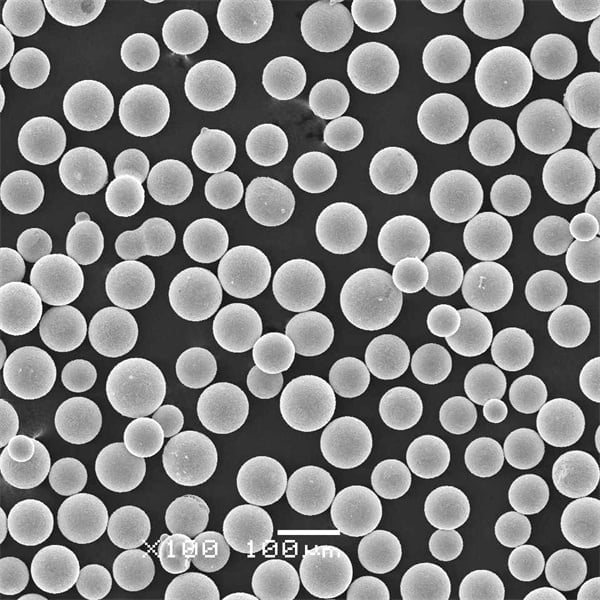
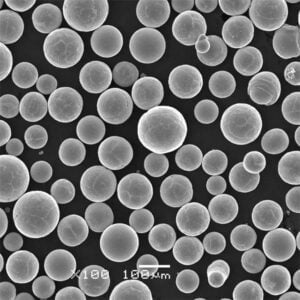
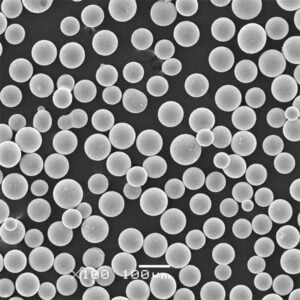
Maraging steel 350 powder is a precipitation-hardenable, martensitic steel powder designed for additive manufacturing, especially for applications requiring high hardness and strength alongside good ductility. It is known for its ultra-high strength from a unique blend of molybdenum, cobalt, nickel, aluminum, titanium and other alloying elements.
Low MOQ
Provide low minimum order quantity to meet different needs.
OEM & ODM
Provide customized products and design services to meet unique customer needs.
Adequate Stock
Ensure fast order processing and provide reliable and efficient service.
Customer Satisfaction
Provide high quality products with customer satisfaction at the core.
share this product
Table of Contents
Overview
Maraging steel 350 powder is a precipitation-hardenable, martensitic steel powder designed for additive manufacturing, especially for applications requiring high hardness and strength alongside good ductility. It is known for its ultra-high strength from a unique blend of molybdenum, cobalt, nickel, aluminum, titanium and other alloying elements.
Maraging steels are unique due to their lower carbon content and higher availability of nickel-aluminum-molybdenum. The low carbon levels prevent segregation or precipitation of carbides, while the strong alloying promotes age hardening within the martensite matrix from the precipitation of intermetallic phases.
Key properties of maraging steel 350 powder:
- Ultra-high tensile yield and ultimate strength
- Good ductility and toughness
- Excellent fracture toughness
- High hardness
- Resistant to over-aging and dimensional changes at moderately high temperatures
- Good weldability
- Heat treatable to tailor properties
- Good machinability and polishability
Maraging steel 350 finds uses across aerospace, aviation, defense, oil and gas, motorsports, tooling, molds, and die components. It allows engineers to reduce weight while maintaining performance and durability.
The ‘350’ designation refers to an ultimate tensile strength of 350 ksi or 2400 MPa from aging treatment. Higher strength variants like maraging steel 300 and maraging steel 550 are also available.
Composition
Maraging steel 350 powder typically has the following composition:
Maraging Steel 350 Powder Composition
| Alloying Element | Weight % |
|---|---|
| Nickel (Ni) | 17-19 |
| Cobalt (Co) | 8-9 |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | 4-5 |
| Titanium (Ti) | 0.6-0.8 |
| Aluminum (Al) | 0.05-0.15 |
| Carbon (C) | ≤ 0.03 |
| Manganese (Mn) | ≤ 0.1 |
| Phosphorus (P) | ≤ 0.01 |
| Sulfur (S) | ≤ 0.01 |
| Silicon (Si) | ≤ 0.1 |
| Iron (Fe) | Balance |
The strength in maraging steels comes from intermetallic precipitates that form during aging treatment, not from carbon-based carbides. Hence the carbon level is deliberately kept low.
Titanium is critical to produce the hardening Ni3Ti precipitates. Aluminum optimizes the activity of titanium by forming Ni3(Al,Ti) precipitates. The high nickel and cobalt content partition more strongly during quenching and enhance the kinetics of age strengthening.
The molybdenum adds solid solution strengthening. Impurities like silicon, manganese, phosphorus and sulfur are minimized as they can reduce fracture toughness.
Properties
Physical and Mechanical Properties of Maraging Steel 350 Powder
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Density | 8 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 1400°C ± 30°C |
| Thermal Conductivity | 10-12 W/m.K |
| Modulus of Elasticity | 190-210 GPa |
| Poisson’s Ratio | 0.28-0.30 |
| Electrical Resistivity | 0.80 microhm-cm |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion | 10-11 x 10-6 /K |
| Hardness | 40-52 HRC, 400-550 HB |
Typical Mechanical Properties of As-Built Parts
| Properties | Maraging Steel 350 |
|---|---|
| Tensile Yield Strength | 235 ksi (1600 MPa) |
| Tensile Strength | 290-330 ksi (2000-2275 MPa) |
| Elongation at break | 3-8% |
| Reduction in area | 30-35% |
Typical Mechanical Properties – Heat Treated and Aged
| Properties | Maraging Steel 350 |
|---|---|
| Tensile Yield Strength | 280-300 ksi (1930-2070 MPa) |
| Tensile Strength | 340-350 ksi (2350-2400 MPa) |
| Elongation at break | 8-13% |
| Reduction in area | 8-15% |
| Fracture Toughness | 75-100 MPa√m |
| Hardness | 50-52 HRC, 475-525 HB |
The remarkable ultra-high strengths are achieved through additional heat treatment and aging cycles which promote precipitation hardening.
Proper temperature and time of aging is critical to achieving the desired level of age hardening – overaging can cause reductions in strength and hardness.
In addition to strength, maraging steel parts also demonstrate good ductility, fracture toughness and resistance to fracture compared to other aerospace alloys. The strength-to-weight ratio is exceptionally high.
Applications
The unparalleled strength-to-weight ratio of maraging steel 350 makes it suitable for:
Maraging Steel 350 Powder Applications
| Sectors | Parts and Components |
|---|---|
| Aerospace | Landing gear components, actuators, fittings, fasteners, gears |
| Avionics | Ruggedized enclosures and housings |
| Defense | Ordnance, gun barrels, ammunition casings, optics |
| Motorsports | Suspension, steering mechanisms |
| Automotive | Precision tooling, injection molds |
| Tool and die | Forming dies, pressing dies, molds, casting dies |
| Oil and gas | Valves, pumps, wirelines |
The lightweight yet exceptionally strong maraging steel 350 parts allow critical weight savings without sacrificing the extreme durability needed under dynamic working loads.
Heat treatment enables tailoring maraging steel properties for different applications – moderately high hardness for wear resistance, maximum yield strength for load-bearing or ballistic uses, or balanced strength and ductility.
By using 3D printing, complex geometries including lattices and cooling channels can be incorporated into maraging steel parts to further cut weight while retaining stiffness and performance. This is increasingly valued by industries like aerospace and motorsports racing.
Specifications, Grades and Standards
Material Specifications
| Specification | Description |
|---|---|
| AMS 6514 | Annealed and precipitation hardened steels bars, forging and billet |
| MIL-S-46850 | High strength maraging steel for aircraft landing gear parts |
| ASTM A564 / A564M | Standard specification for maraging steels |
| AMS 2759 / 2759M | Annealed and precipitation hardened steel plates |
| MIL-S-16216K | Military specification for maraging steel plates |
Available Grades
| Grade | Nominal Tensile Strength |
|---|---|
| Maraging Steel 200 | 200 ksi (1380 MPa) |
| Maraging Steel 250 | 250 ksi (1720 MPa) |
| Maraging Steel 350 | 350 ksi (2400 MPa) |
| Maraging Steel 550 | 550 ksi (3790 MPa) |
The grade indicates the nominal tensile strength achieved after heat treatment and aging. Other variants like maraging 300 steel (2110 MPa) also exist for specific applications.
Industry Standards
- AMS 2772 – Heat treatment of maraging steels
- AMS 2773 – Retreatment of maraging steels
- AMS 2774 – Age hardening of maraging steels
- SAE AMS 7001 – Ultrasonic inspection of maraging steel
- SAE AMS 2655 – Magnetic particle inspection of maraging steel
These standards help producers and end-users to consistently process and quality check maraging steel materials and components.
Maraging Steel 350 Powder Suppliers
Maraging Steel 350 Powder Manufacturers
| Company | Description |
|---|---|
| LPW Technology | Leading metal powder supplier for AM industry |
| Sandvik Osprey | Reputed manufacturer of specialty alloy powders |
| Erasteel | Producer of high performance soft and stainless steels |
| Carpenter Additive | Major producer of customized alloy powders |
| Praxair | Supplies advanced metallic powders to aerospace sector |
| AP&C | Specializes in gas and water atomized metal powders |
Indicative Pricing
| Product Form | Price Range |
|---|---|
| Maraging Steel 350 Powder | $115-145 per kg |
| Maraging Steel 350 Wire | $165-215 per kg |
Prices vary based on order quantities, lead times, quality checks and value-added services provided by the manufacturer. Bulk orders usually avail discounts from powder suppliers.
Value-Added Services
- Sieving and classification
- Blending and custom alloy development
Processing Maraging Steel Powder
Maraging steel powders possess good flowability and packing density, making them suitable for binder-jetting and laser powder bed fusion additive manufacturing.
Parameters need to optimized to achieve high density prints with the desired mechanical properties.
Printing Parameters
| Parameter | Typical Range | Role |
|---|---|---|
| Layer thickness | 20-50 μm | Thinner layers improve resolution |
| Laser power | 100-400 W | Melting of particles for consolidation |
| Scan speed | 100-1000 mm/s | Balances density and build rate |
| Hatch spacing | 80-150 μm | Overlapping hatches for densification |
| Powder bed temp | 100-150°C | Minimizes residual stresses |
Heat Treatment
Solutionizing followed by aging treatment is vital to achieve ultra-high strength in maraging steel 350.
Typical Heat Treatment Schedule
- Solution annealing – Heat at 820-830°C for 1 hour and air cool
- Precipitation hardening – Age at 480°C for 6 hours and air cool to room temperature
The temperatures and duration can be slightly adjusted based on part sizes and furnace limitations.
Most maraging steel parts require additional machining using processes like CNC milling or turning to achieve the tolerance and surface finish requirements demanded by end-use applications, especially in sectors like aerospace.
Comparison with Other Materials
Comparison with Stainless Steels
| Parameter | Maraging Steel 350 | Stainless Steels |
|---|---|---|
| Density | Higher | 7.7-8 g/cm3 |
| Strength | 2-3X higher | Up to 1000 MPa |
| Weldability | Comparable | Excellent |
| Corrosion Resistance | Lower | Extremely high |
| Cost | 5-10x more expensive | Lower cost per kg |
While lacking corrosion resistance, maraging steel provides vastly higher strength compared to all series of stainless steels including Inconel superalloys. This makes it ideal for structural components.
Comparison with Aluminum and Titanium Alloys
| Parameter | Maraging Steel 350 | Al/Ti Alloys |
|---|---|---|
| Density | Similar/Higher | ~4.5/7.8 g/cm3 |
| Strength | Up to 2X higher | 330-1100 MPa |
| Ductility | Lower | Up to 25% elongation |
| Stiffness | Higher | Moderate stiffness |
| Cost | Similar/Lower | Comparable pricing |
Maraging steels compete with the strength-to-weight ratios of aircraft-grade aluminum and titanium while avoiding issues like cracking and distortion seen in those lighter alloys. The higher elastic modulus also makes it more rigid.
Comparison with Other Steels
| Parameter | Maraging Steel 350 | Plate/Tool Steels |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 1.5-2X higher | Up to 300 ksi |
| Toughness | Better | Variable toughness |
| Hardness | 1.5-2X higher | Up to 54 HRc |
| Machinability & polishability | Better | More tool wear |
Maraging steel powder outperforms standard varieties of mold and tool steels in terms of attainable hardness, tensile and yield strengths. This is useful for cutting tooling needing hot hardness.
Applications Case Studies
Aerospace Brackets
- Maraging steel 350 brackets created using AM to mount radar system
- 30% weight reduction over traditional stainless steel 316L parts
- Maintains stiffness in thin regions via topology optimization
Racing Car Gearbox
- Complete H-pattern gearbox housing 3D printed
- Withstood extreme vibration, pressures and temperatures during racing
- 70% lighter than cast aluminium housing
- Reduced lap times and increased fuel efficiency
Injection Molding Tooling
- Maraging steel 350 inserts for plastic injection molding
- UltiMaker sPro 230 used for printing the tool inserts
- Reduced lead times from 26 weeks to 2 weeks
- Inserts lasted 60% longer than tool steel tools
Artillery Projectiles
- Built maraging steel obus shells using laser powder bed fusion
- Achieved 30% increased muzzle velocities from light-weighting
- Withstood firing stresses exceeding 50,000 psi
- Reduced scatter and improved accuracy
Cryogenic Pin Tooling
- Inserts, locators, clamping fixtures printed in maraging steel
- Optimized for subzero conditions down to -150°C
- Handled thermal strains during cryogenic aluminum welding
- Increased tool life by 8X over tool steel parts
These application examples highlight the benefits of maraging steel 350 powder like extreme part strength, reduced weight, design flexibility, part customization and performance gains in challenging operating environments.
Pros and Cons
Advantages
- Exceptional tensile and yield strengths
- High strength-to-weight ratio
- Heat treatable to tailor properties
- Good fracture toughness
- Dimensional stability at higher temperatures
- Excellent machinability and polishability
- Parts can be welded and repaired
Limitations
- More expensive than standard steels
- Lower corrosion resistance
- Prone to cracking if improperly processed
- Requires post-processing and finishing
- Difficult to recycle after use
- Limited commercial availability and experience
Future Outlook
Maraging steel continues to find increasing usage in aerospace, defense, motorsports, tooling and other sectors needing ultra-high strength metallic materials.
Advancements in post-processing and quality assurance promise to increase adoption rates by improving final part quality and reliability.
New spray-forming and condensation manufacturing techniques also seek to increase cost-effectiveness and environmental sustainability of maraging steel powder-based AM.
High initial costs, long lead times and proprietary limitations have hampered more widespread implementation thus far. But continued metallurgical developments, supply chain improvements and standardization efforts aim to make maraging steels more accessible to small and medium sized enterprises as well.
Get Latest Price
About Met3DP
Product Category
HOT SALE
CONTACT US
Any questions? Send us message now! We’ll serve your request with a whole team after receiving your message.

Metal Powders for 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing
COMPANY
PRODUCT
cONTACT INFO
- Qingdao City, Shandong, China
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- +86 19116340731