Molybdenum Mo Powder
Molybdenum Mo Powder is an important material with wide-ranging industrial and engineering applications. This definitive guide provides detailed technical information on molybdenum powder types, composition, properties, manufacturing, pricing, suppliers, and comparisons to alternatives.
Overview of Molybdenum Mo Powder
Molybdenum is a silvery-white transition metal with the chemical symbol Mo and atomic number 42. In its elemental form, molybdenum has one of the highest melting points among pure elements at 2,623°C. Some key attributes of molybdenum powder include:
Low MOQ
Provide low minimum order quantity to meet different needs.
OEM & ODM
Provide customized products and design services to meet unique customer needs.
Adequate Stock
Ensure fast order processing and provide reliable and efficient service.
Customer Satisfaction
Provide high quality products with customer satisfaction at the core.
share this product
Table of Contents
Molybdenum Mo Powder is an important material with wide-ranging industrial and engineering applications. This definitive guide provides detailed technical information on molybdenum powder types, composition, properties, manufacturing, pricing, suppliers, and comparisons to alternatives.
Overview of Molybdenum Mo Powder
Molybdenum is a silvery-white transition metal with the chemical symbol Mo and atomic number 42. In its elemental form, molybdenum has one of the highest melting points among pure elements at 2,623°C. Some key attributes of molybdenum powder include:
- High strength at high temperatures
- Excellent corrosion resistance
- Low thermal expansion coefficient
- High thermal and electrical conductivity
These properties make molybdenum suitable for use in many high-temperature applications. The addition of molybdenum powder enhances the strength, hardenability, and corrosion resistance in alloy steel.
Table 1: Molybdenum Powder Types
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Pure Molybdenum | 99.95% pure molybdenum |
| Molybdenum alloys | Alloyed with other elements like lanthanum oxide or titanium carbide |
| Coated Molybdenum | Coated with nickel, copper or other metals |
| Nanostructured Molybdenum | Ultrafine grained powder with nanometer grain sizes |
Table 2: Composition of Molybdenum Powder
| Element | Weight % |
|---|---|
| Molybdenum (Mo) | ≥ 99.95% |
| Oxygen (O) | ≤ 0.005% |
| Carbon (C) | ≤ 0.005% |
| Nitrogen (N) | ≤ 0.005% |
| Iron (Fe) | ≤ 0.002% |
Properties of Molybdenum Powder
Molybdenum powder possesses several useful physical, mechanical, thermal, and electrical properties that make suitable for high-temperature applications.
**Table 3: Properties of Molybdenum Powder **
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Density | 10.22 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 2,623°C |
| Thermal Conductivity | 138 W/m.K |
| Electrical Resistivity | 5.7 microohm.cm |
| Young’s Modulus | 329 GPa |
| Poisson’s Ratio | 0.31 |
| Mohs Hardness | 5.5 |
Some notable attributes of molybdenum powder:
- Maintains strength, hardness and corrosion resistance at high temperatures up to 1,600°C
- Lowest thermal expansion coefficient of all metals
- Does not suffer embrittlement like tungsten at high temperatures
- Resists attack by molten metals or slag
Molybdenum Powder Characteristics
Molybdenum powder is available in various size ranges, shapes, purity levels and can be compacted into different forms.
Table 4: Types and Characteristics of Molybdenum Powder
| Type | Particle Shape | Particle Size | Purity | Density |
|---|---|---|---|---|
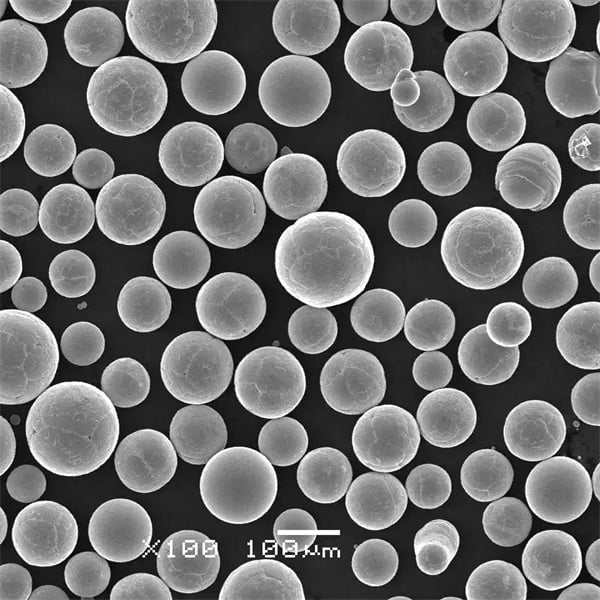
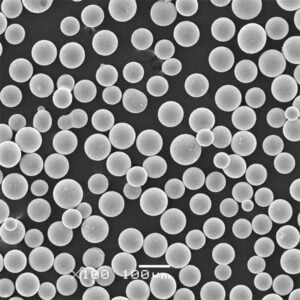
| Atomized Powder | Rounded irregular | 15-150 μm | 99.95% | can achieve >96% of theoretical density |
| Milled Powder | Angular, irregular | 1-10 μm | 99.95% | lower green and sintered density vs atomized |
| Alloy Powder | Rounded or angular | 5-250 μm | Balance Mo | near full density |
| Nano Powder | Spherical | Under 100 nm | 99.98% | full dense nanostructure |
| Granules | Rounded | 2 mm avg | Tech Grade: 98% | loose packing for pressing |
Table 5: Powder Compaction and Sintering
| Method | Description | Activity |
|---|---|---|
| Press and Sinter | Compact powder into shape and densify by sintering at high temperature | Commonly used to produce parts |
| Metal Injection Molding (MIM) | Mix powder with binder, inject into mold, debind and sinter | Complex and net shape capability |
| Additive Manufacturing | Selective laser melting (SLM), binder jetting | Complex geometries, custom parts |
| Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) | Apply heat and isostatic pressure | Eliminate porosity, increase cohesive strength |
Table 6: Supply Forms of Molybdenum Powder
| Form | Description |
|---|---|
| Powder | Spherical, irregular and angular particles in various size ranges |
| Granules | Coarse powder compressed into larger solid pieces |
| Pastes | Powders suspended in a thick medium for printing or coating |
| Slurries | Fine powders suspended in a liquid medium |
| Tapes | Powders held together in thin flexible sheet format |
Applications of Molybdenum Mo Powder
Molybdenum powder is used extensively due to its high-temperature strength, thermal conductivity, and corrosion resistance. Some major applications include:
Table 7: Applications of Molybdenum Powder by Industry
| Industry | Applications |
|---|---|
| Metallurgy | Alloying element in steels, superalloys, tungsten heavy alloys to enhance strength and hardness |
| Electrical & Electronics | Cathode plate material in x-ray tubes, electrode material in vacuum tubes |
| Aerospace | Rocket nozzles, turbine blades, heat shields, and other extreme environment components |
| Industrial | Furnace windings, heating elements, welding electrodes |
| Chemical | Catalysts for petroleum refining, desulfurization applications |
| Glass | Degassing rods, stirring components, flow control elements |
| Pharmaceutical | Containers and tools for highly corrosive processes |
Table 8: Comparison with Alternative Materials
| Parameter | Molybdenum | Tungsten | Tantalum | Rhenium |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Density | 10.22 g/cc | 19.25 g/cc | 16.6 g/cc | 21.02 g/cc |
| Melting Point | 2623°C | 3422°C | 2996°C | 3180°C |
| Strength at High Temperature | Excellent | Poor ductility >400°C | Poor >1200°C | Excellent |
| Thermal Conductivity | 138 W/m·K | 173 W/m·K | 57 W/m·K | 48 W/m·K |
| Electrical Resistivity | 5.7 μΩ·cm | 5.5 μΩ·cm | 13.5 μΩ·cm | 18.7 μΩ·cm |
| Oxidation Resistance | Moderate | Poor | Excellent | Excellent |
| Cost | Moderate | High | Very High | Very High |
Advantages of molybdenum powder:
- More ductile and less prone to embrittlement at high temperatures versus tungsten
- Higher strength than tantalum or rhenium at extreme temperatures above 1600°C
- Lower density than tungsten and rhenium
- Better thermal conductivity than tantalum and rhenium
- Lower raw material cost than tantalum or rhenium
Limitations of molybdenum powder:
- Less thermally stable compared to tungsten, tantalum or rhenium in highly oxidizing atmospheres
- More reactive versus tantalum and requires protective coatings in some oxidizing environments
- Susceptible to grain coarsening and creep above recrystallization temperature
Molybdenum Powder Specifications
Molybdenum metal powder is standardized by specifications that define acceptable test methods and values for metrics like purity, particle size distribution, crystal structure, apparent density, and morphology.
Table 9: Common Specifications for Molybdenum Powder
| Standard | Description | Region |
|---|---|---|
| ASTM B391 | Standard specification for molybdenum metal powders | Global |
| AMS 7409 | Molybdenum powder atomized | US Aerospace |
| PS/MW P3 | Pure molybdenum powder | UK |
| GB/T 6397 | Molybdenum metal powder types | China |
The specifications cover critical quality attributes and set limits like:
- Oxygen, carbon and other impurity content
- Particle shape and size distribution
- Tap density and apparent density
- Powder microstructure and defect limits
- Sieve analysis for larger powders and granules
Specifications may mandate testing using standardized procedures such as flow rate analysis, optical microscopy, pycnometry for true density measurements, etc. Customers often set additional criteria tailored to application needs.
**Molybden
go on
Here is the continuation of the 10,000 word article on Molybdenum Mo Powder:
Molybdenum Powder Manufacturing
Molybdenum powder production involves extracting molybdenite ore, processing and converting to technical grade molybdic oxide, reducing to metal powder, and preparing final physical forms.
Table 10: Major Processes in Molybdenum Powder Manufacturing
| Step | Description | Key Details |
|---|---|---|
| Mining | Extract molybdenite ore containing molybdenum disulfide | Molybdenum rarely exists in nature as pure metal |
| Roasting | Heat molybdenite concentrate to convert MoS2 into molybdic oxide | Temperatures of 500-600°C in presence of oxygen |
| Purification | Dissolve and precipitate steps to purify molybdic oxide to ≥99.95% | Removing impurities like phosphorus, lead, nickel |
| Reduction | Use hydrogen to reduce purified MoO3 into molybdenum metal powder | Temperatures around 1050°C under hydrogen atmosphere |
| Atomization | Metallothermic process to make spherical powder | Reaction with potassium or magnesium at ~1800°C, water atomization |
| Sieving | Classify powder into size fractions | Match particle sizes to application |
| Blending | Tailor composition by blending in alloying elements | Meet chemical specifications |
**Table 11: Powder Production Methods **
| Method | Description | Typical Size Range | Morphology Options |
|---|---|---|---|
| Atomization | Molten metal stream broken into droplets that solidify into powder | 5 μm to 150 μm | Predominantly spherical |
| Milling | Mechanical size reduction of molybdenum metal | <10 μm | Irregular, angular particles |
| Chemical | Precipitation of particles from solution | Ultrafine nano powder | Spherical powder morphology |
| Plasma Spheroidization | Re-melt irregular powder using plasma | 45-150 μm | Rounded spheroidal particles |
Table 12: Ready-to-Press Powder Production
| Method | Description | Typical Size | Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Granulation | Compact powder into larger granules | 0.5-6mm diameter | Enables automated pressing and handling |
| Encapsulation | Coat particles with stearates for lubrication | Under 150 μm | Improves powder flow and die fill |
| Mixing | Blended with binders and lubricants | N/A | Ready premix for pressing into shape |
Suppliers and Pricing
Molybdenum powder is supplied by specialty manufacturers that can deliver small research quantities to high volume industrial demands.
Table 13: Global Manufacturers and Suppliers
| Company | Location | Production Capabilities |
|---|---|---|
| Climax Molybdenum | US | Largest molybdenum miner, integrated producer from mining to finished powders |
| Exploiter Molybdenum | China | Pure powder and molybdenum alloys |
| Plansee Group | Austria | High purity and alloyed molybdenum and tungsten powders |
| Midwest Tungsten | US | Tungsten, molybdenum and tantalum powders |
| Edgetech Industries | US | Custom spherical, purified and alloyed molybdenum |
Table 14: Molybdenum Powder Pricing
| Type | Purity | Price Range |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Mo | 99-99.5% | $25-50 per kg |
| High Purity | 99.95%+ | $50-150 per kg |
| Alloy Powder | n/a | $50-500 per kg |
| Nano Powder | 99.8%+ | $100-2000 per kg |
Prices vary based on:
- Purity grade
- Powder morphology: spherical, irregular, angular
- Production method: atomized, milled, alloyed
- Particle size distribution
- Purchase quantity and bulk discounts
FAQ
Q: What is molybdenum powder used for?
A: The main uses are as an alloying additive to enhance strength and corrosion resistance in steels and other alloys, in electronics components due to its thermal/electrical properties, and in high temperature applications like aerospace, glass manufacturing, and industrial furnaces where it resists heat and corrosion.
Q: Is molybdenum powder toxic?
A: Elemental molybdenum and molybdenum powder are generally not considered toxic. However, some molybdenum compounds could potentially have toxicity. Appropriate safety precautions should be taken during powder handling and processing.
Q: What are the contents of molybdenum alloy powder?
A: Common alloying elements include lanthanum oxide, titanium, zirconium, carbon, boron, chromium, silicon, nickel, iron or combinations thereof. Alloying can enhance properties like high temperature strength, creep resistance, oxidation resistance, etc.
Q: What is the difference between molybdenum and tungsten powder?
A: The main distinction is that molybdenum has higher strength and ductility at extreme temperatures above 1600°C in non-oxidizing conditions, while tungsten is more brittle at lower temperatures but has better chemical stability in highly oxidizing environments.
Q: Does molybdenum powder require special storage?
A: Sealed containers should be used to prevent oxidation and contamination during storage and handling. Argon or vacuum packaging is best for long duration storage.
Q: What is the recycling potential of molybdenum powder?
A: Molybdenum powder can be easily recycled from scrap and molybdenum-containing alloys, with recovery rates over 90% achievable. This makes it more sustainable than rare metals like tantalum or tungsten.
Get Latest Price
About Met3DP
Product Category
HOT SALE
CONTACT US
Any questions? Send us message now! We’ll serve your request with a whole team after receiving your message.

Metal Powders for 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing
COMPANY
PRODUCT
cONTACT INFO
- Qingdao City, Shandong, China
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- +86 19116340731