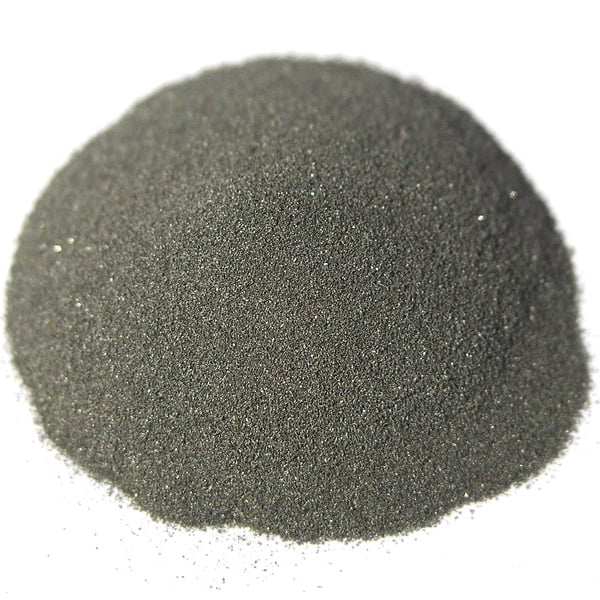
Nickel Alloy 52 Powder
Nickel Alloy 52 powder, also known as Nicrofer 5220h or 2.4631 powder, is a nickel-chromium alloy powder used for additive manufacturing and metal 3D printing applications. This alloy stands out due to its high strength properties coupled with outstanding corrosion and oxidation resistance at elevated temperatures.
Low MOQ
Provide low minimum order quantity to meet different needs.
OEM & ODM
Provide customized products and design services to meet unique customer needs.
Adequate Stock
Ensure fast order processing and provide reliable and efficient service.
Customer Satisfaction
Provide high quality products with customer satisfaction at the core.
share this product
Table of Contents
Nickel Alloy 52 powder, also known as Nicrofer 5220h or 2.4631 powder, is a nickel-chromium alloy powder used for additive manufacturing and metal 3D printing applications. This alloy stands out due to its high strength properties coupled with outstanding corrosion and oxidation resistance at elevated temperatures.
Overview of Nickel Alloy 52 Powder
Nickel Alloy 52 powder has the following key characteristics:
- Composition: Nickel, Chromium, Iron, Molybdenum
- High temperature strength and creep resistance
- Excellent corrosion and oxidation resistance
- Used for additive manufacturing, 3D printing
- Applications in aerospace, power generation, chemical processing
Table 1: Nickel Alloy 52 powder properties
| Properties | Details |
|---|---|
| Composition | Ni: Balance, Cr: 22%, Fe: 22%, Mo: 3% |
| Density | 8.3 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 1390°C |
| Ultimate tensile strength | 850-1000 MPa |
| Yield strength (at 20°C) | 450 MPa |
| Elongation | 30-35% |
| Thermal conductivity | 11 W/m-K |
| Thermal expansion coefficient | 16 x 10-6/K |
| Corrosion resistance | Excellent in oxidizing and reducing environments up to 1100°C |
| Oxidation resistance | Excellent isothermal oxidation resistance in air up to 1100°C |
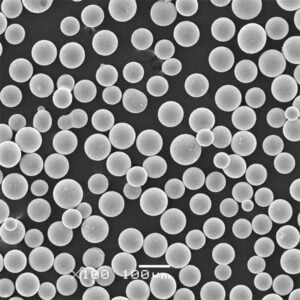
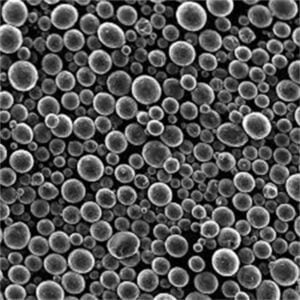
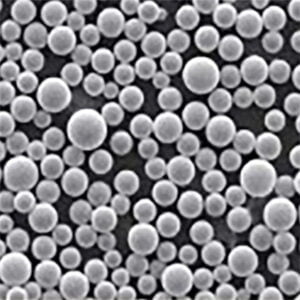
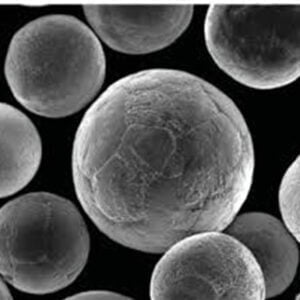
Table 2: Nickel Alloy 52 powder sizes
| Powder size | Range | Particle shape |
|---|---|---|
| Fine grade | 15-45 μm | Spheroidal |
| Coarse grade | 45-150 μm | Spheroidal |
Table 3: Nickel Alloy 52 powder pricing
| Powder grade | Pricing |
|---|---|
| Fine grade (<45 μm) | $100/kg |
| Coarse grade (45-150 μm) | $90/kg |
Composition of Nickel Alloy 52 Powder
The composition of Nickel Alloy 52 consists primarily of nickel along with substantial amounts of chromium, iron and a small percentage of molybdenum.
Nickel is the main element which makes up the balance of the composition after the other alloying elements. Nickel imparts corrosion resistance, ductility and high temperature mechanical properties.
Chromium (Cr) constitutes 22% of Nickel Alloy 52 powder. The addition of chromium significantly enhances oxidation and corrosion resistance. It also provides solid solution strengthening.
Iron (Fe) is added up to 22% to improve high temperature strength through solid solution strengthening without impairing ductility or workability.
Molybdenum (Mo) constitutes 3% of the alloy composition. Molybdenum further improves elevated temperature strength, creep resistance and stability of the alloy.
This optimized chemical composition allows Nickel Alloy 52 powder to demonstrate an exceptional combination of high temperature strength, creep resistance, weldability, and corrosion/oxidation resistance.
Properties and Characteristics
Nickel Alloy 52 stands out due to its impressive mechanical properties coupled with excellent high temperature corrosion and oxidation resistance, as summarized below:
High strength: Nickel Alloy 52 powder can achieve an ultimate tensile strength exceeding 1000 MPa and a yield strength over 450 MPa at room temperature. This means printed parts have very high strength capable of withstanding high mechanical loads.
Good ductility: Despite its high strength, Nickel Alloy 52 still retains decent elongation of 30-35% allowing some flexibility and resistance to fracture.
Excellent creep resistance: The alloy has outstanding creep rupture strength up to 850°C owing to its solid solution strengthening and precipitate formation. This allows durability against deformation under sustained loading over time.
Resistant to thermal fatigue and cycling: Nickel Alloy 52 powder can endure rapid heating and cooling cycles without cracking or premature failure. This is critical for components seeing fluctuating temperatures.
Corrosion resistant: The high chromium and molybdenum content enables exceptional resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion in oxidizing, neutral and reducing environments up to temperatures exceeding 1000°C.
Oxidation resistance: A very adherent chromium-rich oxide layer protects the material from oxidation damage in air environments up to 1100°C. It resists breakaway oxidation even after extensive service.
Overall, the combination of strength, ductility, creep resistance together with corrosion/oxidation resistance at extreme temperatures make Nickel Alloy 52 a versatile high performance material for metal AM and powder bed fusion 3D printing.
Applications of Nickel Alloy 52 Powder
Nickel Alloy 52 is used in critical applications across aerospace, power generation, chemical processing and other harsh environment industries where the capability to withstand extreme temperatures and corrosion affects component life and safety.
Table 4: Applications of Nickel Alloy 52 powder in various sectors
| Sector | Components | Demand drivers |
|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Turbine blades and vanes, rocket nozzles, combustion liners | High temperature strength for propulsion systems |
| Power generation | Heat exchangers, fasteners | Corrosion resistance for fossil fuel plants |
| Chemical and petrochemical | Valves, reactors, heat exchangers | Oxidation resistance for processes involving superheated steam |
| Marine | Exhaust components | Corrosion resistance in marine environments |
Some specific applications include:
- Aerospace engine components like blades, nozzles, housings, and casings
- Industrial gas turbine hot section parts
- Rocket engine nozzles
- Heat exchanger tubing for chemical refineries and offshore platforms
- Valves and processing equipment for corrosive chemicals
- Exhaust components and turbochargers in marine engines
The ability to 3D print intricate, customizable geometries otherwise impossible through conventional manufacturing further expands potential applications of Nickel Alloy 52 across industries.
Metal 3D Printing Using Nickel Alloy 52 Powder
Nickel Alloy 52 powder is primarily used as feedstock material for powder bed fusion (PBF) based metal additive manufacturing processes including selective laser melting (SLM) and direct metal laser sintering (DMLS).
The typical 3D printing process involves:
- Spreading a uniform layer of Nickel Alloy 52 powder on build platform
- Selectively melting powder to solidify cross section using laser
- Lowering platform and spreading new layer of powder
- Repeating layer-by-layer until the part is complete
Table 5: Typical 3D printing parameters for Nickel Alloy 52 powder
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Layer thickness | 20-50 μm |
| Laser power | Up to 500 W |
| Scan speed | 750-3500 mm/s |
| Hatch spacing | 80-200 μm |
| Inert gas | Argon or nitrogen |
The excellent flowability and high density of Nickel Alloy 52 powder enables uniform spreadability along with good absorption and retention of laser energy resulting in great printability.
Proper annealing treatments relieve internal stresses from the rapid solidification inherent in AM processes allowing metal parts to meet design requirements.
Compared to casting/forging, benefits of additive manufacturing Nickel Alloy 52 components include:
- Complex geometries not possible otherwise
- Reduced assembly parts through consolidated designs
- Shorter development times
- Lower costs for smaller batch production
- High strength-to-weight ratios
- Excellent reproducibility part-to-part
However, limitations of metal AM need consideration:
- Higher cost for large production volumes
- Constrained maximum part envelope size
- Additional post-processing may be required
- Anisotropic material properties
Overall, 3D printing delivers game-changing advantages over conventional techniques for small niche applications where factors like design complexity, customization, costs and lead times are critical.
Nickel Alloy 52 Powder Suppliers
Some leading global suppliers offering Nickel Alloy 52 powder specifically for metal additive manufacturing include:
Table 6: Nickel Alloy 52 powder manufacturers
| Company | Location |
|---|---|
| Sandvik Osprey | Wales, UK |
| Carpenter Additive | Virginia, USA |
| Höganäs | Sweden |
| Praxair | Indiana, USA |
| Sentient Jet | California, USA |
Factors differentiating powder producers involve quality control in:
- Chemical composition conformity to strict aerospace standards
- Spheroidal particle shape distribution
- Strict handling procedures to prevent contamination
- Range of particle sizes available
- Consistent powder morphology from batch-to-batch
So it’s essential for 3D printing shops to select a reliable supplier that provides complete quality assurance certification for Nickel Alloy 52 powder suited to their exact build process parameters and requirements.
Nickel Alloy 52 Powder Costs
Nickel alloy powders are more expensive than conventional stainless steel powders due to the proprietary compositions involving higher nickel and chromium contents.
Comparisons With Other Nickel Alloy Powders
Nickel Alloy 52 powder delivers substantially better high temperature mechanical properties and corrosion resistance compared to entry-level nickel alloys, but it is more expensive.
Table 7: Comparison of Nickel Alloy 52 with other nickel alloy powders
| Alloy | Strength | Oxidation Resistance | Corrosion Resistance | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nickel Alloy 52 | Highest | Up to 1100°C | Excellent up to 1100°C | High |
| Inconel 718 | Medium | Up to 700°C | Moderate up to 700°C | Medium |
| Inconel 625 | Lowest | Up to 980°C | Good up to 980°C | Low |
Inconel 718 is a cheaper alternative nickel alloy powder, but it starts softening over 650°C so cannot match the 1100°C temperature capability of Nickel Alloy 52. It also has lower corrosion and oxidation resistance at extreme temperatures.
Inconel 625 provides good oxidation resistance in continuous service up to 980°C. However, it lacks sufficient high temperature strength for dynamic loading applications. The strength diminishes rapidly over 700°C.
For extreme environments involving temperatures exceeding 1000°C along with hot corrosion or oxidation, Nickel Alloy 52 clearly outperforms alternatives at an increased cost premium. But for less demanding applications Inconel 718 or 625 may provide sufficient performance at lower powder price points.
Standards and Grades for Nickel Alloy 52 Powder
Nickel Alloy 52 powder for AM applications is manufactured to conform to the following international material specifications:
- ASTM B466: Standard for Nickel-Chromium-Molybdenum-Columbium Alloy Castings
- AMS 5832: Nickel Alloy, Corrosion and Heat Resistant, Bars, Forgings, and Rings 52.5Ni – 22Cr – 22Fe – 3Mo
- DIN 2.4631 / NiCr22Fe19Mo3: Heat Resisting Alloy Casting
These specifications define the acceptable standards for composition, mechanical properties, grain structure, surface finish and quality processes across global supply chains.
Table 8: Nickel Alloy 52 powder certification types
| Certification | Description |
|---|---|
| AS9100D Aerospace | Meets airworthiness quality management standards for flight-critical aerospace applications |
| ISO 9001 | Verifies quality management system process compliance across production and supply chain |
| ISO 13485 | Confirms stringent regulations for medical devices are achieved |
Leading metal AM powder manufacturers have their Nickel Alloy 52 powders certified to these specifications, giving customers confidence in receiving defect-free high quality materials suited for regulated applications in sectors like aerospace, defense, energy and medical.
Best Practices For Print parameter Development
Since Nickel Alloy 52 is relatively new to metal 3D printing applications, effective print parameters have not yet been standardized. Print shops should collaborate closely with their powder suppliers and printer OEMs to develop optimized build parameters on a trial-and-error basis accounting for factors like:
- Laser power, scan speed, hatch spacing
- Inert gas flow settings
- Preheating and base plate heating temperatures
- Part orientation and support structures
- Annealing cycles
Extensive material characterization is imperative using test geometries to quantify achievable material properties for sufficient part performance. Microstructure, hardness measurements, tensile testing, and microscopy should be performed to compare sample coupon builds before investing in expensive final part production runs.
Table 9: Print parameter development guidelines for Nickel Alloy 52
| Objective | Method | Metrics | Target |
|---|---|---|---|
| Density optimization | Parameter matrix experiments | Relative density | >99.5% |
| Residual stress reduction | Modified scan patterns, pre/post heating | Deformation, XRD, modeling | Minimized distortion |
| Mechanical properties | Tensile/fatigue testing | UTS, yield strength, elongation % | Match target properties |
| Microstructure control | Parameter variations | Grain size, phase analysis | Uniform, fine grains |
| Cost minimization | Volume packing analysis | Part quantity per build | Maximized |
With rigorous testing protocols leveraging these best practices, users can dial in optimal settings to exploit the full potential of Nickel Alloy 52 in their specific applications. Consult closely with experts from material suppliers, printer OEMs and third party service providers to implement such development procedures effectively.
FAQ
Here are some common FAQs answered related to metal 3D printing using Nickel Alloy 52 powder:
What particle size range is best suited for laser powder bed fusion printing of Nickel Alloy 52?
A particle size range between 15-45 microns is recommended as the finest grade powder for precision scanning of thin layers. Coarser powders from 45-100 microns may also provide good printability at faster speeds by reducing laser reflectivity.
What kind of post processing is required on AM Nickel Alloy 52 parts?
As printed Nickel Alloy 52 components have residual stresses from the localized melting and rapid solidification inherent in 3D printing. Stress relieving heat treatments between 700°C to 1000°C based on HIP or vacuum furnace annealing are vital to eliminate internal stresses and enhance mechanical properties. Additional hot isostatic pressing can further maximize density. Minimal machining or grinding may also be applied to achieve dimensional accuracy and desired surface finish quality.
Is Nickel Alloy 52 compatible with multi-material printing or alloying using metal AM?
Yes, nickel alloy composites or functionally graded materials containing gradual transitions from Nickel Alloy 52 to other powder alloys like stainless steel are quite feasible without extensive material science modifications. The binder alloy elements and base nickel composition readily allow compatible alloying or intermixing capabilities within AM build volumes.
Can you weld or additively repair AM Nickel Alloy 52 components?
Yes, powder bed fusion printed Nickel Alloy 52 parts can be sucessfully welded or repaired using directed energy deposition based AM processes like laser metal deposition (LMD) or electron beam additive manufacturing. Compatible nickel filler material must be utilized to build up worn areas or join subcomponents while maintaining the desired chemistry, mechanicals and high temperature performance.
What design principles should be followed when modeling parts using Nickel Alloy 52 for metal AM?
Design guidelines for powder bed fusion processes need to be implemented that account for factors like optimal part orientation, minimal overhang angles, sufficient wall thicknesses, appropriate support structures, and transition radii to enable sound builds. Considering manufacturing constraints and potential postprocessing upfront in the CAD model is key to fabricating fully functional Nickel Alloy 52 components via 3D printing.
Get Latest Price
About Met3DP
Product Category
HOT SALE
CONTACT US
Any questions? Send us message now! We’ll serve your request with a whole team after receiving your message.

Metal Powders for 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing
COMPANY
PRODUCT
cONTACT INFO
- Qingdao City, Shandong, China
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- +86 19116340731