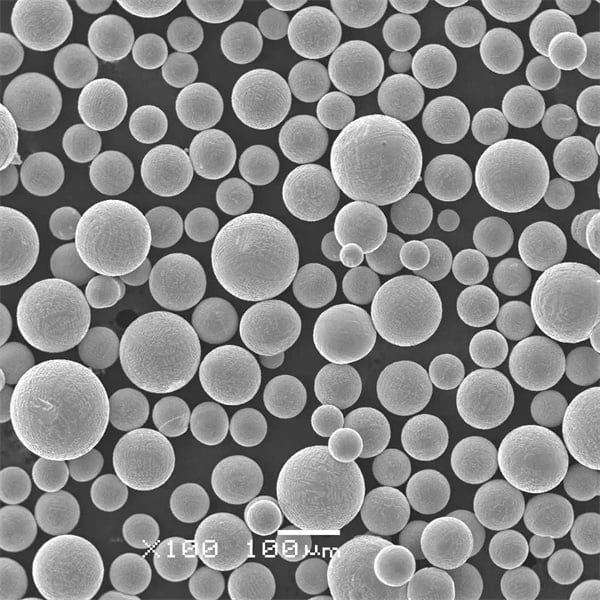
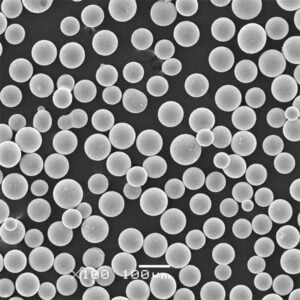
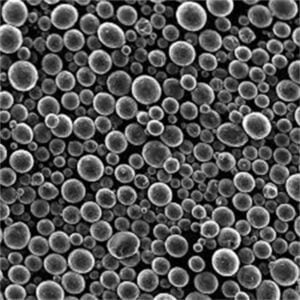
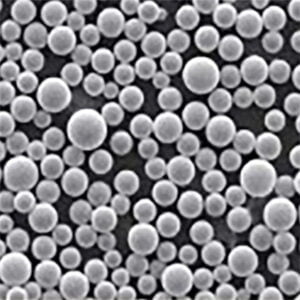
H13 tool steel powder
H13 tool steel powder is an incredibly versatile and durable grade of tool steel powder commonly used to make tooling for hot work processes. This article provides a comprehensive overview of H13 powder metallurgy including composition, properties, processing, specifications, applications, advantages/disadvantages, and suppliers.
Low MOQ
Provide low minimum order quantity to meet different needs.
OEM & ODM
Provide customized products and design services to meet unique customer needs.
Adequate Stock
Ensure fast order processing and provide reliable and efficient service.
Customer Satisfaction
Provide high quality products with customer satisfaction at the core.
share this product
Table of Contents
H13 tool steel powder is an incredibly versatile and durable grade of tool steel powder commonly used to make tooling for hot work processes. This article provides a comprehensive overview of H13 powder metallurgy including composition, properties, processing, specifications, applications, advantages/disadvantages, and suppliers.
Overview
H13 tool steel powder is a versatile chromium-molybdenum-vanadium alloy steel that possesses excellent thermal shock and thermal fatigue resistance properties. It also demonstrates good ductility in hot working applications, high hardenability, and is exceptionally tough.
H13 resists softening at temperatures up to 1000°F (540°C) making it an exceptional choice for manufacturing tooling that will withstand the rigors associated with aluminum die casting, forging dies, extrusion tooling, and more.
When manufactured using powder metallurgy techniques, H13 powder delivers improved overall properties compared to conventionally produced H13 tool steel. Key advantages include:
- Fine, homogeneous microstructure
- Lack of segregation
- Superior mechanical properties
- Better dimensional control
- Higher hardness penetration
- Excellent polishability
Composition
Tool steel H13 is considered a chromium hot work tool steel. Here is a look at the chemical composition in weight percentage:
| Element | Composition % |
|---|---|
| Carbon (C) | 0.32-0.45 |
| Chromium (Cr) | 4.75-5.50 |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | 1.10-1.75 |
| Vanadium (V) | 0.80-1.20 |
| Manganese (Mn) | 0.20-0.50 |
| Silicon (Si) | 0.80-1.20 |
| Iron (Fe) | Balance |
The combination of chromium, molybdenum, and vanadium carbides in the microstructure give H13 excellent wear resistance at elevated temperatures up to 1000°F.
Properties
Here is an overview of the key physical and mechanical properties exhibited by H13 tool steel powder:
Physical Properties
- Density: 7.3 g/cm3
- Melting Point: 2785°F (1530°C)
Mechanical Properties
- Tensile Strength:
- Annealed: 131,000 psi (900 MPa)
- Hardened & Tempered: 300,000 psi (2070 MPa)
- Yield Strength:
- Annealed: 76,000 psi (525 MPa)
- Hardened & Tempered: 262,000 psi (1800 MPa)
- Elongation: 8%
- Reduction of Area: 35%
- Hardness:
- Annealed: 217 HB
- Hardened & Tempered: 54 HRC
The properties make H13 an exceptional choice for hot work dies and tooling. It maintains high strength and hardness at elevated temperatures.
Processing
H13 tool steel is available as conventional and powder metallurgy barstock as well as standard powders for additive manufacturing techniques.
Here is an overview of how H13 powder is manufactured and processed to create dies, tooling, and components:
1. Atomization
Vacuum induction melting is used to create a liquid form of H13 that is then atomized into fine spherical powders. Common powder sizes range from 10 μm to 45 μm.
2. Compaction
The H13 powders are compacted into a die using presses delivering up to 100 tons of pressure. This forms a dense green compact ready for sintering.
3. Sintering
Green compacts are fired at temperatures between 2150-2300°F (1175-1260°C). This fuses the steel particles together creating >90% dense H13 tool steel parts.
4. Heat Treatment
Like wrought H13 tool steel, powder metallurgy H13 undergoes anneal, hardening, and tempering to achieve the desired mechanical properties.
5. Finishing
Sintered H13 products are machined, ground, and polished to final tolerances using conventional or EDM techniques.
Proper heat treatment and finishing ensures parts have suitable compatibility with aluminum, zinc, lead, tin, copper, iron, nickel, and titanium alloys commonly used in hot work applications.
Specifications
H13 tool steel powder products are manufactured to meet various classifications:
- ASTM A681
- ISO 4957 X40CrMoV5-1
- DIN 1.2344
Typical size ranges include:
| Form | Sizes |
|---|---|
| Powders | 10-45 μm |
| Green compacts | Up to 40” x 20” x 6” |
| Sintered parts | Varied based on application |
Applications
Here are some of the common applications which leverage the unique properties of H13 tool steel powder:
Hot Work Tooling
- Aluminum Die Casting
- Forging Dies
- Extrusion Tooling
Plastic Mold Tooling
- Injection Molds
- Blow Molds
- Vacuum Forming
High Temperature Processing
- Handling Molten Materials
- Holding Thermal Energy
H13 powder tool steel proves highly effective for any tooling, dies, or components needing to withstand the extreme environment inside hot work machinery and equipment.
H13 Powder vs Cast H13 Tool Steel
There are a few key differences between H13 produced using conventional casting methods versus H13 fabricated with powder metallurgy techniques:
| Parameter | H13 Cast | H13 Powder |
|---|---|---|
| Composition control | Less consistent composition | Very consistent composition |
| Segregation | High degree of segregation | No segregation |
| Uniformity | Not homogeneous | Very homogeneous |
| Density | 90-92% | Up to 100% density |
| Typical hardness | 50-51 HRC | Up to 56 HRC |
| Dimensional accuracy | +/- 0.5% | +/- 0.1% or better |
| Surface finish polishing | Moderate | Excellent |
The molecular consistency and regularity of H13 steel powders enable superior overall mechanical properties. As a result, powder-based H13 tool steel provides better performance and longer life compared to cast tooling-grade products.
Suppliers
Here is a table highlighting some of the major global suppliers offering H13 tool steel powder products:
| Company | Product Grades | Lead Times |
|---|---|---|
| Hoeganaes | AncorSteel 1000, AncorSteel 2000, AncorSteel 3000, AncorSteel 5000 | 4-6 weeks |
| Höganäs | Digital Metals 47-H13 | 10 business days |
| Sandvik | Osprey H13 | Stock to 8 weeks |
| Praxair | TAFA 95HS, 98HS, 88HS, 99HS | 6-8 weeks |
| Carpenter Powder Products | CP 800, CP 1000 | 6-12 weeks |
H13 Tool Steel Powder Pricing
Pricing for H13 tool steel powder varies quite a bit depending on:
- Supplier
- Order volume
- Lead times
- Customization
- Product grade
- Additional value-added services
That said, here is an overview of price ranges:
| Form | Price Range |
|---|---|
| H13 Powders | $14-22/lb |
| H13 Green Compacts | $18-26/lb |
| H13 Sintered Parts | $22-35/lb |
Keep in mind costs can fluctuate over time due to changes in raw material pricing, demand, and general market conditions. Be sure to request formal quotes for budgetary planning purposes.
FAQs
Q: What’s the difference between H11, H12, H13, and H14 tool steel grades?
A: The primary differences relate to chemical composition resulting in varied heat and wear resistance. H13 offers a good balance of toughness, hardness, and thermal properties for most hot work requirements.
Q: Can you 3D print with H13 tool steel powder?
A: Yes, H13 is readily weldable using laser powder bed fusion and binder jetting additive techniques to fabricate complex geometries impossible with conventional methods.
Q: Is H13 tool steel powder corrosion resistant?
A:H13 tool steel is known for its impressive strength and hardness, which is why it’s often used in high-stress applications like injection molding and die casting. However, when it comes to corrosion resistance, H13 isn’t particularly notable. It’s not as vulnerable as some other steels, but it’s not highly resistant either.
Get Latest Price
About Met3DP
Product Category
HOT SALE
CONTACT US
Any questions? Send us message now! We’ll serve your request with a whole team after receiving your message.

Metal Powders for 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing
COMPANY
PRODUCT
cONTACT INFO
- Qingdao City, Shandong, China
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- +86 19116340731