Revolutionary Spherical Rhenium Powder for High-Performance Uses
Low MOQ
Provide low minimum order quantity to meet different needs.
OEM & ODM
Provide customized products and design services to meet unique customer needs.
Adequate Stock
Ensure fast order processing and provide reliable and efficient service.
Customer Satisfaction
Provide high quality products with customer satisfaction at the core.
share this article
Table of Contents
Rhenium is often considered one of the rarest and most valuable elements on Earth. With an atomic number of 75, it’s a heavy metal that’s often overshadowed by more common industrial metals like tungsten and molybdenum. But in high-tech industries, rhenium is a true powerhouse, especially when it’s processed into spherical powder.
Why spherical? Because the shape of the powder particles plays a huge role in the performance of additive manufacturing, thermal spraying, and powder metallurgy processes. Spherical particles flow better, pack more densely, and provide more consistent results.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore spherical rhenium powder from every angle. Whether you’re a material scientist, an engineer, or just someone curious about this incredible element, we’ll walk you through the composition, properties, applications, specifications, and even pricing of spherical rhenium powder. And we’ll do it in a way that’s easy to understand, even if you don’t have a Ph.D. in metallurgy.
Overview: What is Spherical Rhenium Powder?
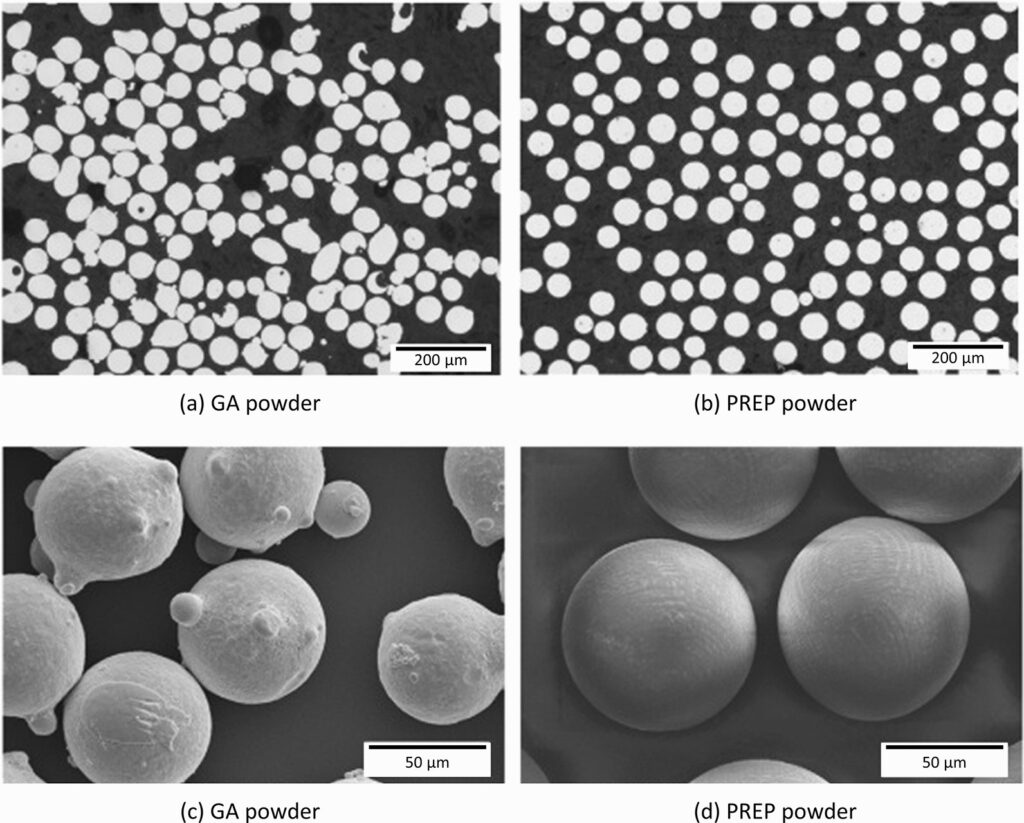
Spherical rhenium powder is a high-purity metal powder in which the particles are shaped like tiny, uniform spheres. This shape is achieved through specialized processes like gas atomization or plasma spheroidization. The spherical shape is crucial because it improves the powder’s flowability, packing density, and consistency in manufacturing processes.
This powder form of rhenium is used in high-temperature applications (think jet engines and rocket nozzles) because it can withstand extreme heat without melting or breaking down. It’s also used in electronics, catalysis, and superalloys where precision and performance are key.
Key Benefits of Spherical Rhenium Powder
- High Melting Point: Rhenium has a melting point of 3,185°C—one of the highest of any metal.
- Excellent Thermal Stability: It maintains its strength and structure even at extreme temperatures.
- Enhanced Flowability: The spherical shape ensures smooth flow in additive manufacturing and powder metallurgy processes.
- Corrosion Resistance: Rhenium resists corrosion, especially in high-temperature and aggressive environments.
- Versatility: Used in everything from jet engine turbines to catalysts for refining petroleum.
Types, Composition, and Properties of Spherical Rhenium Powder
Understanding the types and properties of spherical rhenium powder is crucial for choosing the right material for your application. Rhenium powders can vary in purity, particle size, and production method, all of which affect how they perform in different industrial processes.
Types and Composition of Spherical Rhenium Powder
| Type of Rhenium Powder | Composition | Purity Level | Key Properties |
|---|---|---|---|
| High-Purity Rhenium Powder | 99.99% Rhenium | Ultra-high purity | Ideal for high-temperature and aerospace uses |
| Rhenium Alloy Powder | Rhenium + Tungsten/Nickel | 90-95% Rhenium | Enhanced mechanical properties for superalloys |
| Submicron Rhenium Powder | Rhenium in submicron size | ≥ 99.95% | High surface area, ideal for catalysts |
Each type of spherical rhenium powder has its own specific benefits and is optimized for different high-performance applications.
Physical and Mechanical Properties of Spherical Rhenium Powder
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Density | 21.02 g/cm³ |
| Melting Point | 3,185°C (5,765°F) |
| Thermal Conductivity | 48 W/m·K (at 20°C) |
| Electrical Resistivity | 193 nΩ·m |
| Hardness | 7 Mohs |
| Tensile Strength | 1,000 MPa |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion | 6.2 µm/m·K (at 20°C) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent in high-temperature environments |
Rhenium’s high melting point, combined with its thermal conductivity and resistance to corrosion, makes it an irreplaceable material in industries that demand extreme heat resistance and durability.
Applications of Spherical Rhenium Powder
Because of its unique properties, spherical rhenium powder finds its way into a wide variety of high-tech applications. Whether it’s in the aerospace industry, electronics, or catalysts for chemical reactions, rhenium’s ability to withstand extreme conditions makes it invaluable.
Key Applications of Spherical Rhenium Powder
| Industry | Application | Why Rhenium? |
|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Turbine blades, rocket nozzles | High melting point, excellent thermal stability |
| Electronics | Electrical contacts, thermocouples | High conductivity, corrosion resistance |
| Catalysis | Catalysts for petroleum refining | High catalytic activity, especially in harsh chemical environments |
| Defense | Missile components, advanced armor | Extreme durability, high-temperature resistance |
| Additive Manufacturing | 3D printed precision parts | Excellent flowability and high packing density for consistent results |
| Superalloys | Rhenium-based superalloys for jet engines | Increases strength and durability at high temperatures |
Example: Rhenium in Aerospace Applications
The aerospace industry is a major consumer of spherical rhenium powder. Rhenium’s ability to maintain structural integrity at extreme temperatures makes it a critical component in jet engine turbine blades and rocket nozzles. These components need to withstand thousands of degrees in temperature while maintaining their strength and durability—and rhenium delivers.
In fact, one of the most well-known aerospace applications is the use of rhenium-tungsten alloys in turbine blades. These alloys help engines run hotter and more efficiently, which in turn improves fuel efficiency and performance. In a way, it’s like putting a high-performance racecar engine into an everyday vehicle—suddenly, everything runs smoother, faster, and with more power.
Specifications, Sizes, Grades, and Standards for Spherical Rhenium Powder
When sourcing spherical rhenium powder, it’s important to understand the different specifications, grades, and sizes available. This ensures you’re getting the right material for your specific application, whether it’s for additive manufacturing, thermal spraying, or powder metallurgy.
Common Specifications and Grades of Spherical Rhenium Powder
| Specification | Value |
|---|---|
| Purity | 99.95% – 99.99% |
| Particle Size | 1 µm – 100 µm |
| Flowability | Excellent for 3D printing and thermal spraying |
| Packing Density | High due to spherical shape, ideal for high-density applications |
| Standards | ASTM F3055 (Additive manufacturing), ISO 9001 (Quality Management) |
| Grade | Rhenium Grade Re-1, Re-2 (High-purity rhenium for aerospace and electronics) |
Available Sizes and Forms
The particle size of spherical rhenium powder can vary depending on its intended use. For example, submicron powders are often used in catalysts and electronics, while larger particles (up to 100 µm) are used in powder metallurgy and additive manufacturing.
| Size Range | Application |
|---|---|
| Submicron (<1 µm) | Catalysts, electronics, chemical applications |
| 1-10 µm | Powder metallurgy, sintering |
| 10–50 µm | 3D printing, coatings, thermal spraying |
| 50–100 µm | Additive manufacturing for larger components |
Standards for Spherical Rhenium Powder
To ensure the quality and performance of spherical rhenium powder, several industry standards must be met. These standards guide the manufacturing processes and testing protocols, ensuring that the powder performs consistently across various applications.
- ASTM F3055: This standard covers the specification for additive manufacturing powders used in the aerospace industry.
- ISO 9001: A quality management system standard that ensures consistency in manufacturing processes.
- AMS 7725: Aerospace Material Specification for rhenium used in high-temperature applications, such as turbine blades and rocket nozzles.
These standards help ensure that the spherical rhenium powder you’re purchasing is suited for high-tech and critical applications.
Suppliers and Pricing of Spherical Rhenium Powder
When it comes to sourcing spherical rhenium powder, the market can vary greatly depending on factors like purity, particle size, and production method. Prices can range from affordable to extremely expensive, particularly for high-purity powders used in aerospace and electronics.
Suppliers of Spherical Rhenium Powder
| Supplier | Location | Available Grades | Price per Kg (Approx.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rhenium Alloys, Inc. | USA | High-purity rhenium powders, alloys | $1,200 – $4,500 |
| American Elements | USA | Submicron rhenium powders, high-purity grades | $1,500 – $4,800 |
| Advanced Refractory Metals | USA | Rhenium alloys, high-purity powders | $1,400 – $4,200 |
| Stanford Advanced Materials | USA | High-purity rhenium, rhenium alloys | $1,500 – $5,000 |
| H.C. Starck Tungsten | Germany | Specialty rhenium powders for aerospace | $1,600 – $4,600 |
Factors Influencing the Price of Spherical Rhenium Powder
Several factors influence the pricing of spherical rhenium powder, including purity levels, particle size, and production methods. Here are some of the key factors:
- Purity: Higher-purity powders (99.99% and above) are more expensive due to the additional refining required.
- Particle Size: Submicron powders and highly uniform particles tend to cost more because of the specialized equipment needed to produce them.
- Production Method: Processes like gas atomization and plasma spheroidization add to the cost but result in superior powder quality.
- Volume: Bulk purchases often result in lower per-unit pricing, making it more affordable for larger manufacturing needs.
For example, high-purity spherical rhenium powder used in superalloys for jet engines can be significantly more expensive than powders intended for less demanding applications, like basic catalysis.
Pros and Cons of Spherical Rhenium Powder
Like any material, spherical rhenium powder has its advantages and limitations. Knowing these can help you decide whether it’s the best choice for your high-tech application.
Advantages and Limitations of Spherical Rhenium Powder
| Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|
| High Melting Point: Perfect for extreme heat | Cost: Rhenium is one of the most expensive metals |
| Excellent Thermal Stability: Holds up under high temperatures | Scarcity: Rhenium is rare, making it difficult to source in large quantities |
| Enhanced Flowability: Ideal for additive manufacturing | Processing Challenges: Specialized equipment is required to handle rhenium |
| Corrosion Resistance: Great for harsh environments | Weight: Rhenium is dense, which can be a drawback in lightweight applications |
For example, while spherical rhenium powder is a top choice for aerospace applications because of its thermal stability, its high cost and scarcity might make it less appealing for more cost-sensitive applications.
Spherical Rhenium Powder vs. Other Materials
When deciding whether to use spherical rhenium powder, it’s helpful to compare it to other materials that offer similar properties. Some metals, like tungsten and molybdenum, also have high melting points and thermal stability, making them potential alternatives to rhenium.
Comparison of Spherical Rhenium Powder with Other Materials
| Material | Key Properties | Cost Comparison | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rhenium (Re) | High melting point, excellent thermal stability | More expensive than tungsten | Aerospace, electronics, catalysts |
| Tungsten (W) | Higher density, comparable melting point | Cheaper than rhenium | Aerospace, defense, electronics |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | High thermal conductivity, lower melting point | Cheaper than both rhenium and tungsten | Electronics, powder metallurgy, aerospace |
| Tantalum (Ta) | Superior corrosion resistance, biocompatibility | More expensive than rhenium | Medical devices, chemical processing, electronics |
Compared to tungsten and molybdenum, rhenium stands out for its higher melting point and thermal stability. However, it’s also significantly more expensive, which means that tungsten might be a better choice for applications where cost is a major concern.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Spherical Rhenium Powder
Common Questions About Spherical Rhenium Powder
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is spherical rhenium powder used for? | Spherical rhenium powder is used in aerospace, electronics, catalysis, and additive manufacturing due to its high melting point, thermal stability, and corrosion resistance. |
| Why is rhenium so expensive? | Rhenium is one of the rarest elements on Earth, and its extraction and refining processes are complex and costly, driving up the price. |
| Can rhenium be recycled? | Yes, rhenium can be recycled, especially in applications like turbine blades and electronics where the material is highly valuable. |
| How is spherical rhenium powder made? | Spherical rhenium powder is typically made through processes like gas atomization or plasma spheroidization, which produce uniform, spherical particles. |
| What industries use rhenium the most? | The aerospace and electronics industries are the largest consumers of rhenium, particularly for turbine blades, rocket nozzles, and electrical contacts. |
| How does rhenium compare to tungsten? | Rhenium is less dense than tungsten but has a higher melting point and better thermal stability, making it ideal for high-temperature applications like aerospace turbines. |
| What is the typical particle size for spherical rhenium powder? | Particle sizes typically range from submicron to 100 µm, depending on the application. |
Conclusion: Is Spherical Rhenium Powder Right for Your Project?
In conclusion, spherical rhenium powder is an outstanding material for high-tech applications that require extreme heat resistance, thermal stability, and high durability. Its use in industries like aerospace, electronics, and catalysis highlights its versatility and value.
However, it’s important to weigh the advantages against the costs. While rhenium offers incredible benefits in high-temperature environments, it’s also one of the most expensive metals available, and its scarcity can make sourcing a challenge.
Ultimately, if your project demands precision, performance, and durability at extreme temperatures, spherical rhenium powder could be the perfect solution. But for applications where cost is a limiting factor, you may want to explore alternatives like tungsten or molybdenum.
Get Latest Price
About Met3DP
Product Category
HOT SALE
CONTACT US
Any questions? Send us message now! We’ll serve your request with a whole team after receiving your message.

Metal Powders for 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing
COMPANY
PRODUCT
cONTACT INFO
- Qingdao City, Shandong, China
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- +86 19116340731








