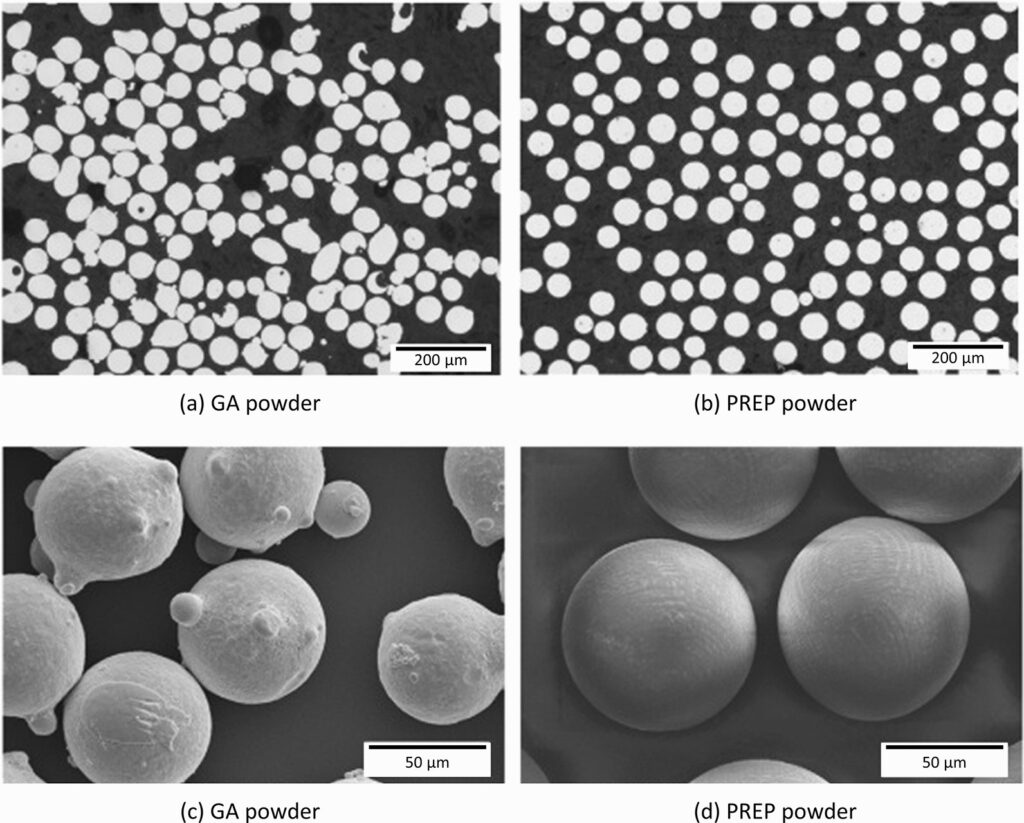
Spherical Bismuth Powder: Unlock New Possibilities in Additive Manufacturing
Low MOQ
Provide low minimum order quantity to meet different needs.
OEM & ODM
Provide customized products and design services to meet unique customer needs.
Adequate Stock
Ensure fast order processing and provide reliable and efficient service.
Customer Satisfaction
Provide high quality products with customer satisfaction at the core.
share this article
Table of Contents
If you’re working with advanced materials, you’ve probably heard of spherical bismuth powder. It’s a unique material that’s gaining traction across a variety of industries, from pharmaceuticals to metallurgy and electronics. But what makes this powder so special? Why should you consider using it in your next project?
In this in-depth guide, we’ll dive deep into spherical bismuth powder—its properties, applications, specifications, and pricing. We’ll also explore its pros and cons, along with a breakdown of suppliers and industry standards. Whether you’re a manufacturer, a researcher, or someone simply curious about this material, this guide is for you.
Overview: What is Spherical Bismuth Powder?
Bismuth (element symbol Bi) is a brittle, crystalline metal with a lustrous silver appearance. It’s known for its low toxicity compared to other heavy metals and its unique physical and chemical properties. But when processed into a spherical powder, bismuth unlocks even more potential, especially in pharmaceuticals, additive manufacturing, and electronic components.
Why Spherical?
The spherical shape offers several distinct advantages:
- Better Flowability: Spherical particles flow more easily, which is a huge plus in processes like 3D printing and powder metallurgy.
- Higher Packing Density: The uniform shape allows for tighter packing, making it ideal for densely packed components and metal injection molding.
- Consistent Performance: Spherical particles provide more predictable performance in both chemical reactions and physical applications.
Key Characteristics of Spherical Bismuth Powder
- Non-toxic: Unlike many heavy metals, bismuth is non-toxic, making it suitable for medical applications and cosmetics.
- Low Melting Point: With a melting point of 271°C (520°F), it’s used in low-temperature fusible alloys and solders.
- Environmental Friendly: Bismuth is often hailed as an eco-friendly alternative to lead in various applications.
- Good Electrical Conductivity: While not as conductive as copper or silver, bismuth still has decent electrical properties, making it useful in electronics.
Types, Composition, and Properties of Spherical Bismuth Powder
There are various forms and grades of spherical bismuth powder, each tailored to specific applications. Understanding the composition and properties of these powders will help you make an informed decision when selecting the right material for your needs.
Types and Composition of Spherical Bismuth Powder
| Type | Composition | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| High-Purity Bismuth Powder | ≥ 99.9% Bismuth | Pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and electronics |
| Alloyed Bismuth Powder | Bismuth blended with tin, lead, or indium | Solders, low-melting alloys, and metallurgy |
| Industrial-Grade Bismuth | 98-99.9% Bismuth | Coatings, catalysts, and additive manufacturing |
Key Properties of Spherical Bismuth Powder
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Particle Size | Typically ranges from 1 µm to 100 µm, depending on the application. |
| Purity | Available in 99.5% to 99.99% purity grades. |
| Shape | Spherical, offering better flow and packing. |
| Density | 9.78 g/cm³, which is relatively high, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. |
| Melting Point | 271°C (520°F), ideal for low-temperature soldering and fusible alloys. |
| Electrical Conductivity | Moderate, useful in electronic components. |
| Toxicity | Non-toxic, making it safe for medical and cosmetic use. |
| Environmental Impact | Considered environmentally friendly, especially as a lead substitute. |
Applications of Spherical Bismuth Powder
One of the reasons spherical bismuth powder is so popular is its versatility. Whether you’re working on metal alloys, pharmaceuticals, or 3D-printed components, this material can likely serve a role.
Common Applications of Spherical Bismuth Powder
| Industry | Application |
|---|---|
| Pharmaceuticals | Used in medical compounds, radiopaque agents, and cosmetics. |
| Metallurgy | Incorporated in low-melting alloys and used as a lead substitute. |
| Soldering | Essential in lead-free solders, often alloyed with tin or silver. |
| 3D Printing | Utilized in additive manufacturing for metal parts and prototypes. |
| Electronics | Used in electronic components and thermal management systems. |
| Cosmetics | A key ingredient in cosmetics due to its non-toxicity and shiny appearance. |
Let’s delve deeper into some of these applications.
Pharmaceuticals and Medical Use
Bismuth has been used in medicine for centuries, primarily due to its low toxicity and antibacterial properties. Spherical bismuth powder is commonly found in radiopaque agents for medical imaging, as well as in antacid formulations. Given its safety profile, it’s also used in cosmetics like lipsticks and face powders, where it adds a pearlescent sheen.
Metallurgy and Lead-Free Alloys
Bismuth is often used as a safer alternative to lead in various fusible alloys. These alloys are essential for applications like fire safety systems, where the alloy melts and triggers a response (like releasing water in a sprinkler system). The low melting point of bismuth allows for precise control in these systems, making it invaluable in industrial safety.
Electronics and Soldering
With the global push for lead-free electronics, spherical bismuth powder has emerged as a popular material in soldering. When alloyed with metals like tin or silver, bismuth forms a strong, conductive bond without the toxicity associated with lead. This makes it a perfect fit for the electronics industry, where environmental and health regulations are becoming stricter.
Specifications, Sizes, and Industry Standards for Spherical Bismuth Powder
When selecting spherical bismuth powder, it’s important to understand the specifications that impact its performance. These include particle size, purity, and compliance with industry standards. Let’s take a closer look at these factors.
Specifications and Sizes for Spherical Bismuth Powder
| Specification | Description |
|---|---|
| Particle Size Distribution | Available in ranges like 1-5 µm, 5-20 µm, and 20-100 µm, depending on the application. |
| Purity | Typically available in 99.5%, 99.9%, and 99.99% grades. |
| Bulk Density | Ranges from 4.5 to 6.0 g/cm³, depending on the particle size and shape. |
| Flowability | Excellent flowability due to the spherical shape, making it ideal for 3D printing and powder metallurgy. |
| Melting Point | 271°C (520°F), making it suitable for low-temperature applications. |
| Surface Area | Higher surface area for fine powders, enhancing reactivity in chemical processes. |
| Standards Compliance | Meets international standards like RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) for lead-free applications. |
Industry Standards for Spherical Bismuth Powder
Ensuring that your bismuth powder meets industry standards is crucial for its performance in specific applications. Here are some common standards:
- RoHS Compliance: Ensures the powder is free from hazardous substances like lead.
- ASTM B212: Standard for particle size analysis using sieving.
- ISO 3923-1: International standard for measuring the bulk density of metal powders.
- ASTM E1282: Standard for density testing of metal powders.
Suppliers and Pricing for Spherical Bismuth Powder
The cost of spherical bismuth powder can vary depending on factors like purity, particle size, and supplier reputation. Below, we compare several suppliers and provide pricing details to help you make an informed purchasing decision.
Suppliers and Pricing for Spherical Bismuth Powder
| Supplier | Country | Material | Price Range (per kg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| American Elements | USA | Spherical Bismuth Powder, 99.9% purity | $150 – $400 |
| Nanografi | Turkey | Fine Bismuth Powder for Pharmaceuticals | $250 – $600 |
| Goodfellow | UK | High-Purity Bismuth, 99.99% | $400 – $800 |
| SkySpring Nanomaterials | USA | Spherical Bismuth Nanoparticles | $500 – $1,200 |
| Stanford Materials | USA | Industrial Bismuth Powder | $100 – $300 |
Factors Influencing Pricing
Several factors can influence the price of spherical bismuth powder:
- Purity: Higher purity grades (99.99%) are more expensive due to the additional refining processes required.
- Particle Size: Finer powders, such as nanoparticles, generally cost more because of the specialized equipment needed to produce them.
- Supplier Reputation: Established suppliers with a strong track record, like American Elements and Goodfellow, may charge a premium for their high-quality products.
- Application-Specific Powders: Powders designed for niche uses, such as pharmaceuticals or 3D printing, often carry a higher price tag due to the additional testing involved.
Pros and Cons of Spherical Bismuth Powder
As with any material, spherical bismuth powder comes with its own set of advantages and limitations. Below, we outline both the pros and cons to help you assess whether this material fits your needs.
Advantages and Limitations of Spherical Bismuth Powder
| Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|
| Non-toxic and Environmentally Friendly | Higher Cost: Bismuth is generally more expensive than lead or other alternatives. |
| Excellent Flowability | Limited Use at High Temperatures: Bismuth’s low melting point can be a drawback in high-heat applications. |
| Good Electrical Conductivity | Relatively Soft Metal: Bismuth is brittle, which limits its use in structural applications. |
| Lead-Free Alternative | Oxidation: Bismuth can oxidize over time if not stored properly. |
| Recyclable and Abundant Supply | Supply Chain Volatility: Pricing can fluctuate based on global demand. |
Where the Advantages Outweigh the Limitations
In applications where toxicity is a concern, such as in pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and lead-free solders, the benefits of spherical bismuth powder far outweigh its limitations. Its environmental friendliness and non-toxic nature make it a superior choice, even if it comes at a slightly higher cost.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Spherical Bismuth Powder
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is spherical bismuth powder used for? | It’s used in pharmaceuticals, solders, 3D printing, cosmetics, and metal alloys. |
| Why is the spherical shape important? | The spherical shape improves flowability, packing density, and uniformity in applications like 3D printing and metallurgy. |
| Is spherical bismuth powder safe to use? | Yes, bismuth is non-toxic, making it safe for use in medical and cosmetic applications. |
| How much does spherical bismuth powder cost? | Prices typically range from $100 to $1,200 per kilogram, depending on factors like purity and particle size. |
| Can spherical bismuth powder replace lead? | Yes, it’s commonly used as a lead-free alternative in solders, alloys, and radiopaque agents. |
| Is bismuth powder flammable? | Bismuth powder is not highly flammable, but fine powders can pose a dust explosion risk under certain conditions. |
Conclusion
Spherical bismuth powder is a versatile and eco-friendly material that’s finding its way into more industries every year. From its role in pharmaceuticals and cosmetics to its use in lead-free solders and 3D printing, its unique properties make it a standout choice for a wide range of applications.
While it may come with a slightly higher price tag and some limitations in terms of heat resistance and structural strength, its non-toxic nature and environmental benefits make it a superior alternative to more harmful metals like lead.
As industries continue to push for sustainable materials and lead-free alternatives, spherical bismuth powder is likely to play an even larger role in the future of manufacturing, electronics, and medicine.
If you’re considering spherical bismuth powder for your next project, make sure to weigh the specifications, purity levels, and supplier options carefully to find the right material for your needs.
Get Latest Price
About Met3DP
Product Category
HOT SALE
CONTACT US
Any questions? Send us message now! We’ll serve your request with a whole team after receiving your message.

Metal Powders for 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing
COMPANY
PRODUCT
cONTACT INFO
- Qingdao City, Shandong, China
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- +86 19116340731








