Spherical Vanadium Powder: Elevating Advanced Manufacturing
Low MOQ
Provide low minimum order quantity to meet different needs.
OEM & ODM
Provide customized products and design services to meet unique customer needs.
Adequate Stock
Ensure fast order processing and provide reliable and efficient service.
Customer Satisfaction
Provide high quality products with customer satisfaction at the core.
share this article
Table of Contents
Vanadium—often referred to as a “miracle metal”—is one of the most versatile elements in the periodic table. Its unique properties make it indispensable in high-performance alloys, energy storage systems, and even in medical applications. But when vanadium takes the form of spherical vanadium powder, it unlocks a whole new level of potential in advanced manufacturing processes, including 3D printing, powder metallurgy, aerospace components, and battery technologies.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll break down everything you need to know about spherical vanadium powder. Whether you’re a materials scientist, an engineer, or someone looking to understand the role of this powder in high-tech applications, we’ve got you covered. From its composition and properties to its applications and pricing, we’ll dive deep into why vanadium powder is becoming essential in modern industries.
Overview: What is Spherical Vanadium Powder?
Spherical vanadium powder is a specialized form of vanadium that has been processed into fine, uniformly shaped spherical particles. The spherical shape offers a wide range of benefits over traditional irregular powders, particularly when it comes to flowability, packing density, and uniformity—all critical factors in additive manufacturing and powder metallurgy.
Vanadium (chemical symbol V, atomic number 23) is a transition metal with impressive characteristics, including high strength, corrosion resistance, and stability under extreme temperatures. When processed into powder form, vanadium can be used in a variety of high-performance applications, from improving alloy strength to enhancing battery efficiency.
Key Properties of Spherical Vanadium Powder:
- High Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Vanadium is lightweight yet incredibly strong, making it ideal for aerospace and automotive industries.
- Corrosion Resistance: Excellent resistance to oxidation and corrosion, even at high temperatures.
- Thermal Stability: Vanadium maintains its structural integrity under extreme heat.
- Improved Flowability: The spherical form allows for better flow in 3D printing and powder metallurgy applications.
- High Packing Density: Spheres pack more efficiently than irregular particles, ensuring uniformity and consistency in final products.
Types, Composition, and Properties of Spherical Vanadium Powder
When selecting spherical vanadium powder for specific applications, it’s important to understand the various types and compositions available. These powders can vary based on purity levels, particle size, and alloying elements, each of which influences the powder’s performance in different scenarios.
Types and Composition of Spherical Vanadium Powder
| Type | Composition | Purity Level | Key Properties |
|---|---|---|---|
| High-Purity Vanadium Powder | 99.9% Vanadium | Ultra-high purity | Perfect for high-tech applications like electronics and aerospace |
| Vanadium-Aluminum Alloy | Vanadium + Aluminum (80-20%) | 80% Vanadium | Increased strength, ideal for aerospace applications |
| Vanadium-Nitrogen Alloy | Vanadium + Nitrogen | 85-90% Vanadium | Enhanced hardness and wear resistance, used in tool steels |
| Vanadium-Titanium Alloy | Vanadium + Titanium | 90% Vanadium | Lightweight and strong, suitable for aerospace and medical applications |
Physical and Mechanical Properties of Spherical Vanadium Powder
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Density | 6.11 g/cm³ |
| Melting Point | 1,910°C (3,470°F) |
| Thermal Conductivity | 30.7 W/m·K |
| Electrical Resistivity | 197 nΩ·m |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent, especially at high temperatures |
| Tensile Strength | 800 MPa (in alloy forms) |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion | 8.4 µm/m·K (at 20°C) |
The combination of high melting point, corrosion resistance, and thermal stability makes spherical vanadium powder a preferred choice for industries requiring materials that perform well under stress and extreme conditions.
Applications of Spherical Vanadium Powder
Spherical vanadium powder is used in a variety of industries, but its most significant contributions are seen in aerospace, energy storage, medical implants, and manufacturing. Thanks to its excellent mechanical properties, this powder is a crucial component in enhancing the performance of high-strength alloys, batteries, and 3D-printed components.
Key Applications of Spherical Vanadium Powder
| Industry | Application | Why Vanadium? |
|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Jet engine components, lightweight alloys | High strength-to-weight ratio, thermal stability |
| Energy Storage | Vanadium redox flow batteries (VRFBs) | Vanadium’s ability to store and release energy makes it ideal for large-scale energy storage |
| Additive Manufacturing | 3D-printed aerospace and automotive parts | Excellent flowability and packing density for precise component manufacturing |
| Medical | Implants, prosthetics | Lightweight, biocompatible, and corrosion-resistant |
| Tool Steels | Hardening agent in high-performance steels | Increases wear resistance and hardness |
Example: Vanadium in Energy Storage
One of the most promising applications of spherical vanadium powder right now is in vanadium redox flow batteries (VRFBs). These batteries use vanadium ions in different oxidation states to store and release energy, making them ideal for renewable energy storage. Unlike lithium-ion batteries, VRFBs can store large amounts of energy for extended periods, making them perfect for grid-scale energy storage.
But how does the spherical shape of vanadium powder improve this technology? Simple. Spherical particles allow for more efficient packing in the electrodes, improving the battery’s overall energy density and lifespan. This makes spherical vanadium powder a key player in the future of sustainable energy.
Specifications, Sizes, Grades, and Standards for Spherical Vanadium Powder
When purchasing spherical vanadium powder, it’s essential to ensure that it meets the required specifications for your specific application. Different industries have varying demands when it comes to purity, particle size, and standards.
Common Specifications and Grades of Spherical Vanadium Powder
| Specification | Value |
|---|---|
| Purity | 99.0% – 99.9% |
| Particle Size | 10 µm – 100 µm |
| Flowability | Excellent for powder metallurgy and additive manufacturing |
| Packing Density | High, thanks to the spherical shape, ensuring uniformity in applications |
| Standards | ASTM B348 (Vanadium in aerospace applications), ISO 9001 (Quality Management) |
| Grade | Vanadium Grade V-1, V-2 (High-purity vanadium for aerospace and medical use) |
Available Sizes and Forms
The particle size of spherical vanadium powder can vary depending on the intended use. For example, finer powders (<10 µm) are often used in coatings and electronics, while larger particles (up to 100 µm) are used in powder metallurgy and additive manufacturing.
| Size Range | Application |
|---|---|
| Submicron (<1 µm) | Thin films, coatings, electronics |
| 1-10 µm | Additive manufacturing, fine powder metallurgy |
| 10–50 µm | Aerospace components, 3D printing |
| 50–100 µm | Powder metallurgy, large-scale additive manufacturing |
Standards for Spherical Vanadium Powder
Various industry standards ensure that spherical vanadium powder is consistent in quality and performance. These standards guide everything from manufacturing to testing and ensure that the powder meets the rigorous demands of industries like aerospace and medical technology.
- ASTM B348: Standard specification for vanadium used in aerospace applications.
- ISO 9001: A widely recognized standard for quality management systems, ensuring consistency in manufacturing processes.
- AMS 6515: Aerospace Material Specification for vanadium used in high-performance alloys and jet engines.
These standards ensure that the spherical vanadium powder you purchase is suitable for critical applications where failure is not an option.
Suppliers and Pricing of Spherical Vanadium Powder
The cost of spherical vanadium powder can vary significantly depending on factors like purity, particle size, and production method. Prices typically range from affordable for lower-purity powders to expensive for high-purity or specialty powders used in industries like aerospace and medical.
Suppliers of Spherical Vanadium Powder
| Supplier | Location | Available Grades | Price per Kg (Approx.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| American Elements | USA | High-purity vanadium powders, alloys | $600 – $2,000 |
| Stanford Advanced Materials | USA | Submicron vanadium powders, high-purity grades | $700 – $2,500 |
| Advanced Refractory Metals | USA | Vanadium alloys, high-purity powders | $650 – $2,200 |
| H.C. Starck | Germany | Specialty vanadium powders for aerospace and medical | $750 – $2,500 |
| Goodfellow | UK | Vanadium and vanadium alloys | $700 – $2,300 |
Factors Affecting the Price of Spherical Vanadium Powder
Several factors influence the price of spherical vanadium powder, including:
- Purity Levels: Higher-purity powders (99.9% and above) typically cost more due to the refinement processes involved.
- Particle Size: Submicron powders are more expensive to produce and are often used in specialized applications like coatings and electronics.
- Production Method: Techniques like gas atomization and plasma atomization add to the cost but result in superior powder quality.
- Volume: Like most materials, purchasing in bulk reduces the per-unit cost, making it more economical for large-scale manufacturers.
For example, high-purity spherical vanadium powder used in aerospace or medical applications will generally be more expensive than lower-purity powders used in tool steels.
Pros and Cons of Spherical Vanadium Powder
As with any material, spherical vanadium powder offers both advantages and limitations. Understanding these pros and cons will help you determine if it’s the right material for your application.
Advantages and Limitations of Spherical Vanadium Powder
| Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|
| High Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Ideal for aerospace | Cost: Vanadium can be expensive, especially at high purity levels |
| Corrosion Resistance: Great for harsh environments | Availability: Vanadium is less abundant compared to other metals |
| Thermal Stability: Performs well at high temperatures | Processing Difficulty: Requires specialized equipment to handle powder |
| Excellent Flowability: Perfect for additive manufacturing | Price Volatility: The price of vanadium can fluctuate based on market demand and availability |
For instance, while spherical vanadium powder is a top choice for aerospace and energy storage applications due to its strength and thermal stability, its high cost and limited availability may make it less suitable for mass-market products.
Spherical Vanadium Powder vs. Other Materials
When deciding whether to use spherical vanadium powder, it’s essential to compare it against other materials that might provide similar benefits. Metals like titanium, tantalum, and niobium share some overlapping characteristics but differ in price, availability, and overall performance in specific conditions.
Comparison of Spherical Vanadium Powder with Other Materials
| Material | Key Properties | Cost Comparison | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vanadium (V) | High strength, corrosion resistance | Moderate to high | Aerospace, energy storage, tool steels |
| Titanium (Ti) | Lightweight, excellent corrosion resistance | Slightly cheaper than vanadium | Aerospace, medical implants, automotive |
| Tantalum (Ta) | Superior corrosion resistance, high density | More expensive than vanadium | Medical devices, chemical processing, electronics |
| Niobium (Nb) | High melting point, superconductivity | Similar to or cheaper than vanadium | Superalloys, electronics, energy storage |
Compared to titanium, vanadium offers better performance in high-temperature environments, making it ideal for aerospace and energy storage. However, titanium is more affordable and may be a better option for applications that don’t require the extreme properties of vanadium.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Spherical Vanadium Powder
Common Questions About Spherical Vanadium Powder
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is spherical vanadium powder used for? | Spherical vanadium powder is used in aerospace, energy storage, additive manufacturing, and tool steels due to its strength, corrosion resistance, and thermal stability. |
| Why is vanadium expensive? | Vanadium is less abundant than other metals, and its extraction and refinement process is complex, which drives up its price. |
| Can vanadium be recycled? | Yes, vanadium can be recycled, particularly in industries like aerospace and energy storage, where its value and performance are critical. |
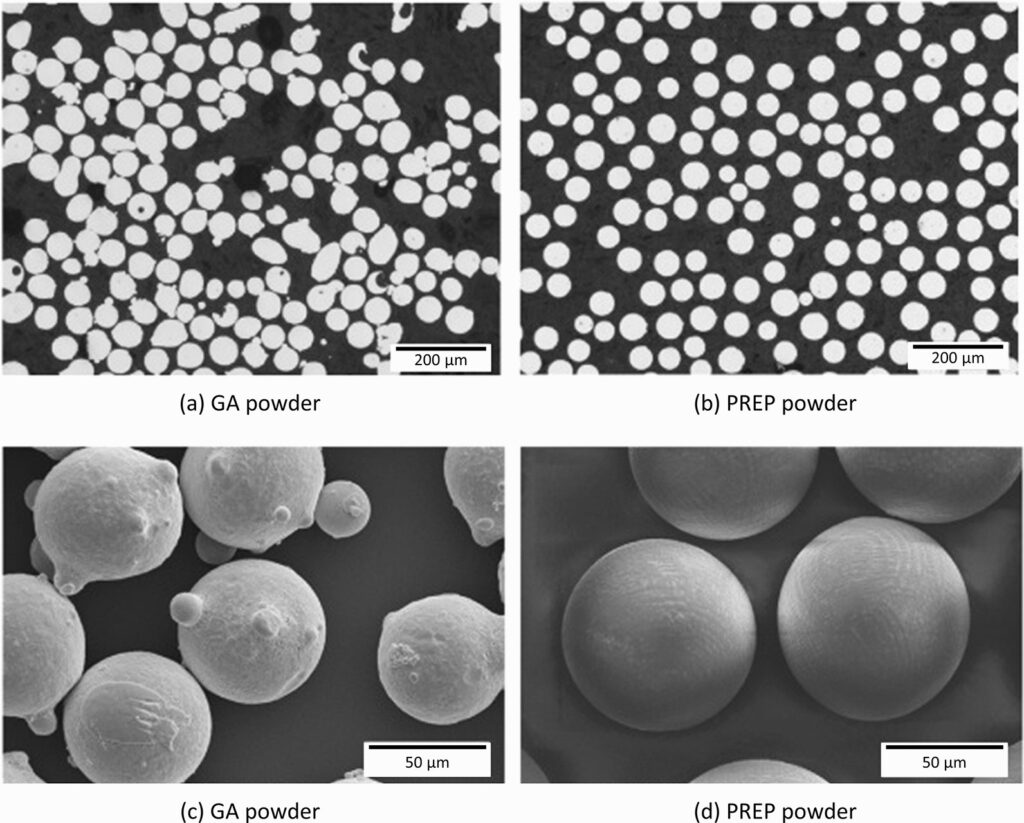
| How is spherical vanadium powder made? | Spherical vanadium powder is typically produced through methods like gas atomization or plasma spheroidization, which create uniform spherical particles. |
| What industries use vanadium the most? | The aerospace, energy, and automotive industries are the largest consumers of vanadium, especially in high-strength alloys and energy storage applications. |
| How does vanadium compare to titanium? | While both are used in aerospace, vanadium offers better high-temperature performance, whereas titanium is more affordable and widely available. |
| What is the typical particle size for spherical vanadium powder? | Particle sizes typically range from submicron to 100 µm, depending on the application. |
Conclusion: Is Spherical Vanadium Powder Right for Your Project?
In summary, spherical vanadium powder is a high-performance material that is transforming industries like aerospace, energy storage, and additive manufacturing. Its strength, corrosion resistance, and thermal stability make it ideal for applications that demand durability and precision.
However, the cost of vanadium can be a limiting factor, especially for mass-production applications. If your project requires materials that can withstand extreme conditions—such as high temperatures or corrosive environments—then spherical vanadium powder might be the perfect solution. But for more cost-sensitive applications, you may want to consider alternatives like titanium or niobium.
Ultimately, if you’re looking for a material that offers superior performance in high-tech and high-stress environments, spherical vanadium powder is a top contender.
Get Latest Price
About Met3DP
Product Category
HOT SALE
CONTACT US
Any questions? Send us message now! We’ll serve your request with a whole team after receiving your message.

Metal Powders for 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing
COMPANY
PRODUCT
cONTACT INFO
- Qingdao City, Shandong, China
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- +86 19116340731








