Ni60 Powder: The Alloy Built for Harsh and Abrasive Conditions
Low MOQ
Provide low minimum order quantity to meet different needs.
OEM & ODM
Provide customized products and design services to meet unique customer needs.
Adequate Stock
Ensure fast order processing and provide reliable and efficient service.
Customer Satisfaction
Provide high quality products with customer satisfaction at the core.
share this article
Table of Contents
Are you looking for a high-performance material that can withstand extreme conditions, offer exceptional wear resistance, and deliver reliable results in demanding applications? Look no further than Ni60 powder. This powerful nickel-based alloy is a game-changer in industries like aerospace, automotive, oil and gas, and additive manufacturing.
This guide will walk you through everything you need to know about Ni60 powder, including its composition, properties, applications, and pricing. Whether you’re a materials engineer looking for the perfect alloy or a manufacturer curious about its potential uses, we’ve got the answers. Let’s dive right in!
Overview of Ni60 Powder
Ni60 powder, also known as Nickel 60, is a nickel-based alloy with 60% nickel content. This material is renowned for its superior wear resistance, high hardness, and oxidation resistance at elevated temperatures. It is often used in thermal spraying, welding, and powder metallurgy to create components that need to endure abrasion, corrosion, and high-stress environments.
So, what makes Ni60 powder so special? It’s all about the combination of elements. With a mix of chromium, silicon, boron, and other elements, Ni60 powder has a self-fluxing ability that allows it to form a dense, strong layer when applied to surfaces. This makes it an ideal choice for hard-facing, repairing worn parts, and creating new components that need to last in harsh conditions.
Key Features :
- High Nickel Content: Provides excellent corrosion resistance and ensures oxidation stability.
- Wear Resistance: Perfect for applications that require abrasion resistance and durability.
- High Hardness: Offers outstanding hardness levels, especially after heat-treatment.
- Thermal Stability: Performs well in high-temperature environments.
- Self-Fluxing: Forms a strong, dense layer when applied, making it ideal for thermal spraying and hard-facing operations.
Composition and Properties of Ni60 Powder
The secret to Ni60 powder’s performance lies in its chemical composition. By combining nickel with other elements like chromium, silicon, and boron, this alloy offers a unique blend of mechanical strength, thermal stability, and wear resistance.
Chemical Composition
| Element | Weight Percentage (%) | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| Nickel (Ni) | 58.00 – 62.00 | Provides the base, ensuring oxidation resistance and thermal stability. |
| Chromium (Cr) | 14.00 – 17.00 | Enhances wear resistance, especially in high-stress and abrasive environments. |
| Silicon (Si) | 3.00 – 5.00 | Improves oxidation resistance and contributes to the alloy’s self-fluxing ability. |
| Boron (B) | 2.00 – 4.00 | Lowers the melting point, aiding in the formation of a dense, smooth coating. |
| Carbon (C) | 0.50 – 1.00 | Adds hardness and wear resistance to the alloy. |
| Iron (Fe) | 3.00 max | Provides additional mechanical strength while maintaining ductility. |
Mechanical and Thermal Properties
The unique blend of elements gives Ni60 powder its remarkable mechanical and thermal properties. These properties are critical for applications where high wear resistance, thermal stability, and mechanical strength are required.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Density | 8.4 g/cm³ |
| Melting Point | 980°C – 1050°C |
| Hardness (as sprayed) | 40-60 HRC |
| Ultimate Tensile Strength | 700-900 MPa |
| Thermal Conductivity | 14.0 W/m·K |
| Oxidation Resistance | Effective up to 800°C in oxidizing atmospheres. |
| Wear Resistance | Excellent in abrasive environments, especially at high temperatures. |
Why These Properties Matter
The combination of high hardness and thermal stability makes Ni60 powder ideal for applications that require materials to maintain their mechanical integrity under extreme conditions. Whether you’re using it for thermal spray coatings or welding consumables, Ni60 powder’s ability to resist wear, corrosion, and oxidation will give your components a longer service life.
Applications of Ni60 Powder
Given its exceptional wear resistance, oxidation resistance, and high hardness, Ni60 powder is used across a variety of industries. It’s particularly valuable in applications that require materials to withstand abrasive environments, high temperatures, and mechanical stress.
Common Applications
| Industry | Application |
|---|---|
| Aerospace | Used in thermal spraying for engine components and exhaust systems. |
| Automotive | Ideal for hard-facing parts like valve seats, camshafts, and bearings. |
| Oil & Gas | Applied to drill bits, valves, and tubing to resist corrosion and wear. |
| Power Generation | Used in boilers, turbines, and furnace parts to withstand high heat and abrasion. |
| Additive Manufacturing | Utilized for 3D printing functional components with high wear and heat resistance. |
| Thermal Spray Coatings | Applied to protect surfaces exposed to high wear, corrosion, and thermal stress. |
Ni60 Powder in Aerospace Applications
In the aerospace industry, components like engine parts and exhaust systems must withstand high temperatures and abrasion. Ni60 powder is frequently used in thermal spraying to coat these parts, ensuring they remain strong and resilient even in extreme environments.
Ni60 Powder in Automotive Applications
In the automotive industry, Ni60 powder is commonly used for hard-facing components like valve seats, camshafts, and bearings. These parts experience significant wear and tear, so the high hardness and wear resistance of Ni60 powder make it an ideal solution for extending the life of these critical components.
Specifications, Sizes, and Standards for Ni60 Powder
When selecting Ni60 powder for your application, it’s essential to understand the specifications, sizes, and standards that are available. These factors will help ensure that you choose the right form of Ni60 powder for your specific needs, whether you’re using it for thermal spraying, welding, or additive manufacturing.
Specifications and Standards
| Specification/Standard | Details |
|---|---|
| UNS Number | N06600 |
| ASTM Standards | ASTM B50 (Nickel-Chromium Alloy Wires), ASTM F3055 (Additive Manufacturing) |
| AMS Standards | AMS 4777 (Nickel Alloy Welding Rods) |
| ISO Standards | ISO 15156-3 (Materials for sour gas environments) |
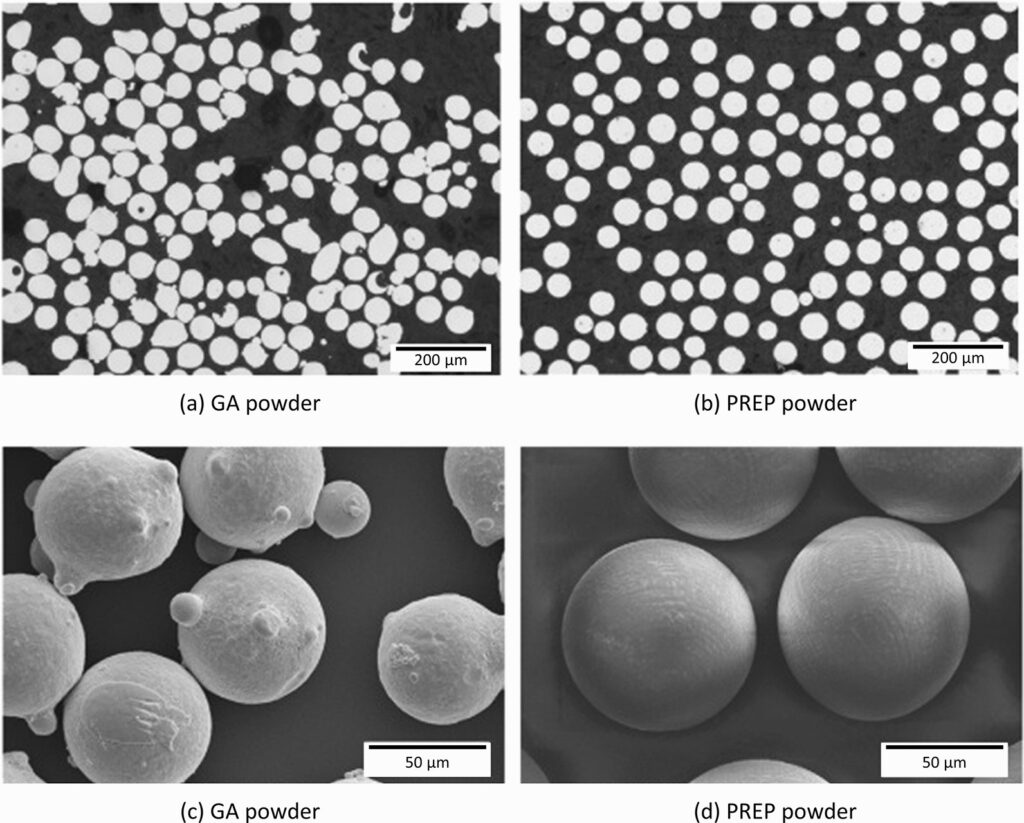
| Powder Particle Size | Typically ranges from 15 to 45 microns, depending on the application (e.g., thermal spraying or 3D printing). |
| Density | 8.4 g/cm³ |
| Melting Range | 980°C – 1050°C |
By adhering to these standards and choosing the correct specifications, you’ll ensure that Ni60 powder will perform optimally in your applications. For example, selecting the appropriate particle size is crucial for achieving the desired results in thermal spray coatings or additive manufacturing.
Available Sizes and Forms
| Form | Available Sizes |
|---|---|
| Powder | Particle sizes typically range from 15 to 45 microns, ideal for additive manufacturing and thermal spraying. |
| Welding Rods/Wires | Diameters from 1 mm to 3 mm, used for welding and hard-facing. |
Selecting the correct form and size of Ni60 powder is critical to achieving optimal performance. For instance, if you’re using Ni60 powder for 3D printing, you’ll want to ensure the particle size distribution matches the requirements of your printing system.
Suppliers and Pricing of Ni60 Powder
When sourcing Ni60 powder, you’ll want to consider factors such as quality, price, and availability. The cost of Ni60 powder can vary based on particle size, order volume, and supplier location.
Suppliers and Pricing
| Supplier | Price Range (per kg) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Höganäs AB | $180 – $300 | Specializes in metal powders for thermal spray and additive manufacturing. |
| Oerlikon Metco | $200 – $320 | Known for high-performance powders used in thermal spraying and laser cladding. |
| Kennametal Stellite | $190 – $310 | Offers premium powders for wear-resistant applications and hard-facing. |
| Carpenter Technology | $195 – $315 | Supplies nickel alloys for aerospace, automotive, and industrial applications. |
The price of Ni60 powder typically ranges from $180 to $320 per kilogram, depending on the supplier and particle size. Bulk orders often come with discounts, and it’s essential to balance cost with quality to ensure you get the best material for your needs.
Advantages and Limitations of Ni60 Powder
Like any material, Ni60 powder has its advantages and limitations. Understanding both will help you decide whether this alloy is the right choice for your specific application.
Advantages
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Wear Resistance: Exceptional wear resistance, even in abrasive environments. | Ideal for hard-facing and other high-wear applications. |
| Corrosion Resistance: Performs well in oxidizing and corrosive environments. | Suitable for chemical processing and oil & gas applications. |
| Thermal Stability: Can withstand high temperatures without losing strength or hardness. | Perfect for aerospace and power generation industries. |
| Self-Fluxing: The alloy’s ability to form a dense, hard layer when applied makes it ideal for thermal spraying. | Ensures long-lasting coatings in abrasive environments. |
Limitations
| Limitation | Description |
|---|---|
| Cost: More expensive than other nickel alloys and stainless steel. | Could be a limiting factor for cost-sensitive projects. |
| Brittleness: Can become brittle if not heat-treated properly. | Requires careful handling during processing and application. |
| Machinability: Difficult to machine due to its high hardness. | Specialized machining techniques and tools may be required, increasing overall production costs. |
Ni60 Powder vs. Other Nickel-Based Alloys
When selecting a nickel-based alloy, it’s essential to compare different options to see which one best fits your application. Below, we’ll compare Ni60 powder with other popular nickel-based alloys to highlight their strengths and weaknesses.
| Alloy | Strengths | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Ni60 Powder | Excellent wear resistance, high hardness, good oxidation resistance. | More expensive and harder to machine. |
| Inconel 625 | Outstanding corrosion resistance in aqueous and acidic environments. | Lower hardness and wear resistance. |
| Hastelloy C276 | Exceptional corrosion resistance in chloride and acidic environments. | Lower mechanical strength at high temperatures. |
| Stellite 6 | Great for wear resistance and corrosion protection, especially in welding. | Higher cost and limited availability. |
As you can see, Ni60 powder is an excellent choice for applications that require wear resistance and thermal stability, while alloys like Inconel 625 or Hastelloy C276 may be better suited for corrosion resistance in aqueous environments.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Are you still wondering if Ni60 powder is the right material for your project? Below, we’ve compiled answers to some of the most common questions about this versatile alloy.
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is Ni60 powder used for? | It is used in industries like aerospace, automotive, oil & gas, and power generation for applications that require high wear resistance and thermal stability. |
| How much does Ni60 powder cost? | Prices typically range from $180 to $320 per kilogram, depending on the supplier, particle size, and order volume. |
| Can Ni60 powder be used in 3D printing? | Yes, it is suitable for additive manufacturing and is often used to 3D print components requiring high wear resistance and heat stability. |
| What industries use Ni60 powder? | Industries such as aerospace, automotive, oil & gas, and power generation extensively use it for its thermal and wear resistance in critical applications. |
| Is Ni60 powder weldable? | Yes, it is commonly used in welding applications, particularly for hard-facing operations that require wear resistance and durability. |
| How does Ni60 powder compare to Inconel 625? | While both are nickel-based alloys, Ni60 offers superior hardness and wear resistance, making it ideal for abrasive environments, whereas Inconel 625 excels in corrosive, aqueous environments. |
Conclusion: Why Ni60 Powder is the Ideal Choice for Wear-Resistant Applications
If you’re looking for a high-performance material that can withstand extreme wear, high temperatures, and abrasive environments, it is your go-to solution. With its high hardness, thermal stability, and self-fluxing properties,it is perfect for applications in industries like aerospace, automotive, oil & gas, and power generation.
While the cost may be higher than other nickel alloys, the longevity and durability of components made with Ni60 powder often justify the investment. Whether you’re looking to extend the life of wear-prone parts or create new components with superior resistance to corrosion and abrasion, it offers the performance you need.
In short, Ni60 powder is a material that delivers exceptional results in the most demanding environments.
Get Latest Price
About Met3DP
Product Category
HOT SALE
CONTACT US
Any questions? Send us message now! We’ll serve your request with a whole team after receiving your message.

Metal Powders for 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing
COMPANY
PRODUCT
cONTACT INFO
- Qingdao City, Shandong, China
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- +86 19116340731








