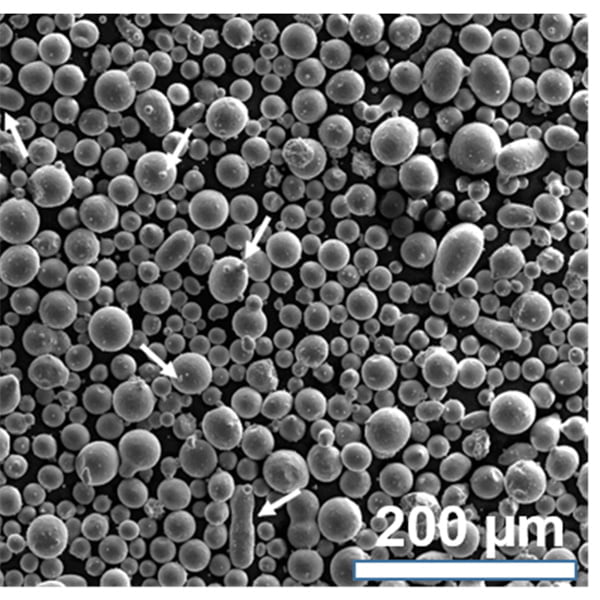
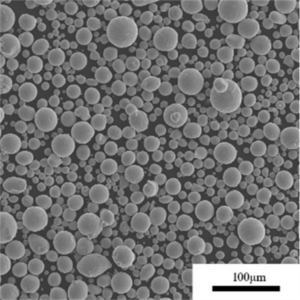
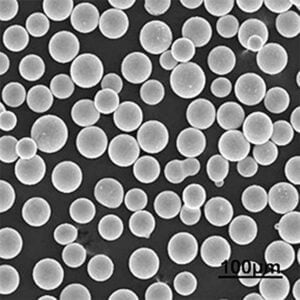
H13 Alloy Steel Powder For 3D Printing
Our nitrogen atomized H13 alloy steel powder has good hardenability, thermal strength, wear resistance and high impact toughness, thermal fatigue, widely used in the manufacture of hot work molds.Wear is one of the main failure modes of H13 steel hot-working die. Improving the surface wear resistance of H13 steel is an effective way to improve the life of die.
Low MOQ
Provide low minimum order quantity to meet different needs.
OEM & ODM
Provide customized products and design services to meet unique customer needs.
Adequate Stock
Ensure fast order processing and provide reliable and efficient service.
Customer Satisfaction
Provide high quality products with customer satisfaction at the core.
share this product
Table of Contents
H13 alloy steel powder is a highly versatile and widely used material in various industrial applications, particularly in the field of metal additive manufacturing (AM). This chromium-molybdenum hot-work tool steel is renowned for its exceptional properties, such as high hardness, excellent wear resistance, and good toughness, even at elevated temperatures.
| Composition | Content (%) |
|---|---|
| Carbon | 0.32 – 0.45 |
| Chromium | 4.75 – 5.50 |
| Molybdenum | 1.10 – 1.75 |
| Vanadium | 0.80 – 1.20 |
| Silicon | 0.80 – 1.20 |
| Manganese | 0.20 – 0.50 |
| Iron | Balance |
Typical chemical composition of H13 alloy steel powder
Properties and Characteristics
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Density | 7.8 g/cm³ |
| Hardness (Annealed) | 185 – 235 HB |
| Hardness (Heat Treated) | 48 – 52 HRC |
| Tensile Strength (Heat Treated) | 1800 – 2100 MPa |
| Yield Strength (Heat Treated) | 1500 – 1800 MPa |
| Elongation (Heat Treated) | 10 – 15% |
| Thermal Conductivity | 28.6 W/m·K at 20°C |
| Melting Point | 1427 – 1510°C |
Typical properties of H13 alloy steel
H13 alloy steel powder exhibits excellent dimensional stability, creep resistance, and thermal fatigue resistance, making it an ideal choice for various industrial applications. Its high hardness and wear resistance make it suitable for producing tools, dies, and components subjected to severe mechanical and thermal stresses.
Applications
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Extrusion Dies | Used for hot extrusion of metals, plastics, and other materials |
| Forging Dies | Utilized in hot forging processes for various metal components |
| Injection Molds | Employed in plastic injection molding for manufacturing plastic parts |
| Hot Shear Blades | Used in hot shearing operations for cutting metals at elevated temperatures |
| Casting Tooling | Utilized in the production of castings for various industries |
| Powder Metallurgy Tooling | Employed in the manufacturing of powder metallurgy components |
| Additive Manufacturing (AM) Components | Used for producing high-performance components via metal 3D printing techniques |
Common applications of H13 alloy steel powder
Specifications, Sizes, and Grades
| Specification | Description |
|---|---|
| ASTM A681 | Standard specification for tool steels alloy |
| DIN 1.2344 | German standard for hot-work tool steel |
| JIS SKD61 | Japanese Industrial Standard for hot-work die steel |
| BS BH13 | British Standard for hot-working die steel |
| AISI H13 | American Iron and Steel Institute specification for hot-work die steel |
Common specifications and standards for H13 alloy steel
H13 alloy steel powder is typically available in various particle size distributions, ranging from coarse to fine powders, to meet the requirements of different additive manufacturing processes, such as laser powder bed fusion (LPBF), electron beam powder bed fusion (EBPBF), and binder jetting.
Suppliers and Pricing
Met3DP manufactures a wide range of high-quality metal powders optimized for laser and electron beam powder bed fusion. Its portfolio includes innovative alloys such as TiNi, TiTa, TiAl, TiNbZr, CoCrMo, stainless steels, superalloys, and more.
The price of H13 alloy steel powder can vary based on several factors, including the supplier, quantity, particle size distribution, and quality specifications. Generally, the cost ranges from 50to150 per kilogram, with finer powders and specialized grades typically being more expensive.
FAQs
Q1: What makes H13 alloy steel powder suitable for additive manufacturing? A1: H13 alloy steel powder’s excellent mechanical properties, thermal resistance, and dimensional stability make it an ideal material for producing high-performance components via additive manufacturing processes like laser powder bed fusion and electron beam powder bed fusion.
Q2: Can H13 alloy steel powder be used for other manufacturing processes besides additive manufacturing? A2: Yes, H13 alloy steel powder can also be used in conventional manufacturing processes like powder metallurgy, hot isostatic pressing (HIP), and metal injection molding (MIM).
Q3: What are the typical post-processing steps for components made from H13 alloy steel powder? A3: Common post-processing steps for H13 alloy steel components include heat treatment, hot isostatic pressing (HIP), machining, and surface finishing operations like grinding, polishing, or coating.
Q4: How does the particle size distribution of H13 alloy steel powder affect its performance in additive manufacturing? A4: The particle size distribution plays a crucial role in the flowability, packing density, and processability of the powder during additive manufacturing. Finer powders generally provide better resolution and surface finish, while coarser powders may exhibit better mechanical properties.
Q5: Are there any specific safety precautions to consider when handling H13 alloy steel powder? A5: Yes, proper safety measures should be taken when handling H13 alloy steel powder, including the use of personal protective equipment (PPE), adequate ventilation, and proper disposal of waste materials. Additionally, precautions should be taken to prevent static discharge and dust explosions.
Get Latest Price
About Met3DP
Product Category
HOT SALE
CONTACT US
Any questions? Send us message now! We’ll serve your request with a whole team after receiving your message.

Metal Powders for 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing
COMPANY
PRODUCT
cONTACT INFO
- Qingdao City, Shandong, China
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- +86 19116340731